3.15P) The excess electron concentration and Electic field is plotted in a bar of an n-type semiconductor. a) Show the directions of the electron drift and diffusion current flow and explain clearly. b) What would happen to these currents, if we increase the donor doping in semiconductor. c) What would happen to these currents, if we increase the excess electron doping in semiconductor.

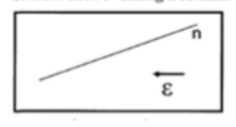
The given plot is shown below:
(a)
DRIFT:
Whenever an electric field is applied to a n type semiconductor, the free electrons are affected by the electric field. Additionally, these electrons move against the field direction. This is known as drift, and the current resulting from the drift will flow as in direction of drift field. The holes travel in the electric field's direction. Positive charges are driven in the direction of the electric field in general. As a result, the field is left behind by the negatively charged electrons.
The ratio of electric force to charge it is acting on is known as the electric field.
Therefore, for positive charges, the field points in same direction as that of the force, whereas for negative charges, it points in the opposite way.
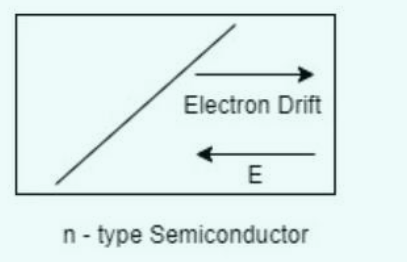
DIFFUSION:
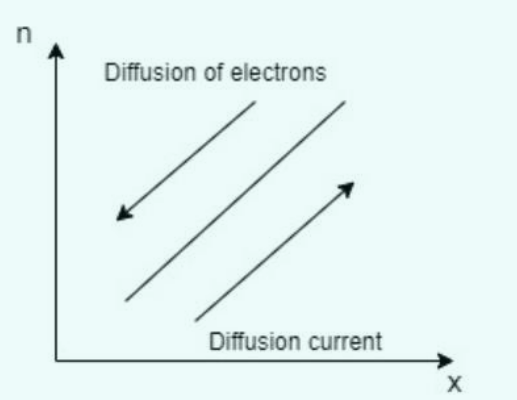
It involves the transfer of carrier charges from a state of high concentration to one of low concentration. Where there are more electrons present, a region is said to have a high concentration, and where there are fewer, a region has a low concentration. Diffusion current is the name given to the current produced by the motion of the charge carriers. The right side of the conductor has a higher electron concentration in the given n type semiconductor than the left. The movement of the electron will be against the specified concentration gradient because diffusion happens from high concentration to low concentration.
For electrons, the diffusion current density is given by:
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images









