35 mm 10 kN-m 2.36 x10° mm G, 50 GPa (1) C2 40 mm (2) 4.02 x10° mm A G2 = 25 GPa 2400 mm 3100 mm A composite torsion member consists of two solid shafts joined at flange B. Shafts (1) and (2) are attached to rigid supports at A and C, respectively. kN-m kN-m T2 A concentrated torque T is applied to flange B in the direction shown. Determine the internal torques and shear stresses in each shaft. Also, determine the rotation angle of flange B. MPa MPa (Use the sign convention detailed in the fourth scene of this movie for internal torques and rotation rad PB Shaft properties I| ||||
35 mm 10 kN-m 2.36 x10° mm G, 50 GPa (1) C2 40 mm (2) 4.02 x10° mm A G2 = 25 GPa 2400 mm 3100 mm A composite torsion member consists of two solid shafts joined at flange B. Shafts (1) and (2) are attached to rigid supports at A and C, respectively. kN-m kN-m T2 A concentrated torque T is applied to flange B in the direction shown. Determine the internal torques and shear stresses in each shaft. Also, determine the rotation angle of flange B. MPa MPa (Use the sign convention detailed in the fourth scene of this movie for internal torques and rotation rad PB Shaft properties I| ||||
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter1: Tension, Compression, And Shear
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.8.10P: A steel punch consists of two shafts: upper shaft and lower shaft. Assume that the upper shaft has a...
Related questions
Question
engineering of materials review
how to solve this
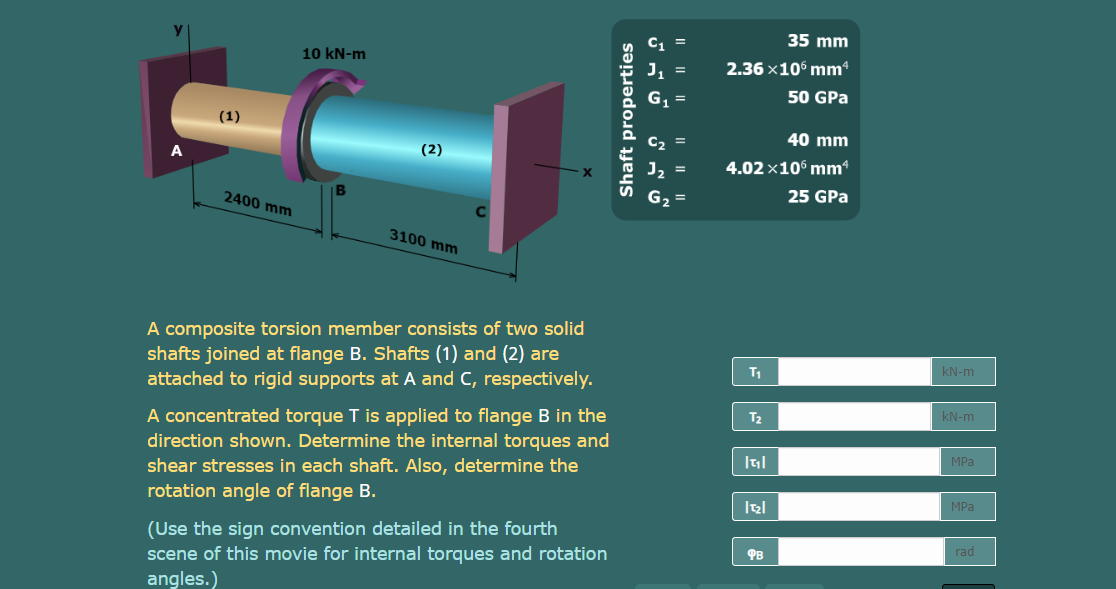
Transcribed Image Text:35 mm
10 kN-m
2.36 ×106 mmª
50 GPa
(1)
40 mm
(2)
4.02 ×10° mm“
B
25 GPa
2400 mm
3100 mm
A composite torsion member consists of two solid
shafts joined at flange B. Shafts (1) and (2) are
attached to rigid supports at A and C, respectively.
kN-m
T1
KN-m
A concentrated torque T is applied to flange B in the
direction shown. Determine the internal torques and
shear stresses in each shaft. Also, determine the
rotation angle of flange B.
T2
MPa
MPa
(Use the sign convention detailed in the fourth
scene of this movie for internal torques and rotation
rad
PB
angles.)
Shaft properties
I| || |
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning