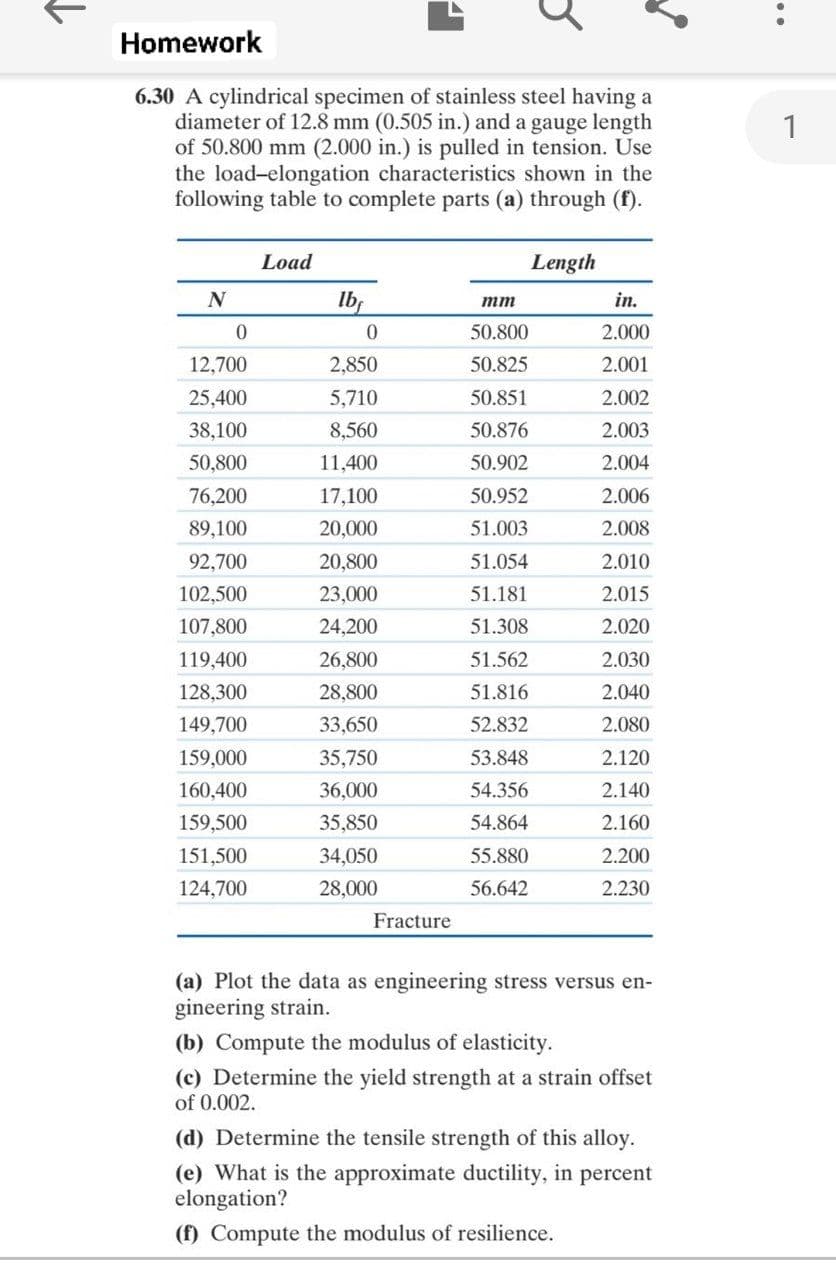
6.30 A cylindrical specimen of stainless steel having a diameter of 12.8 mm (0.505 in.) and a gauge length of 50.800 mm (2.000 in.) is pulled in tension. Use the load-elongation characteristics shown in the following table to complete parts (a) through (f). Load Length N Ib, in. mm 50.800 2.000 12,700 2,850 50.825 2.001 25,400 5,710 50.851 2.002 38,100 8,560 50.876 2.003 50,800 11,400 50.902 2.004 76,200 17,100 50.952 2.006 89,100 20,000 51.003 2.008 92,700 20,800 51.054 2.010 102,500 23,000 51.181 2.015 107,800 24,200 51.308 2.020 119,400 26,800 51.562 2.030 128,300 28,800 51.816 2.040 149,700 33,650 52.832 2.080 159,000 35,750 53.848 2.120 160,400 36,000 54.356 2.140 159,500 35,850 54.864 2.160 151,500 34,050 55.880 2.200 124,700 28,000 56.642 2.230 Fracture (a) Plot the data as engineering stress versus en- gineering strain. (b) Compute the modulus of elasticity. (c) Determine the yield strength at a strain offset of 0.002.
6.30 A cylindrical specimen of stainless steel having a diameter of 12.8 mm (0.505 in.) and a gauge length of 50.800 mm (2.000 in.) is pulled in tension. Use the load-elongation characteristics shown in the following table to complete parts (a) through (f). Load Length N Ib, in. mm 50.800 2.000 12,700 2,850 50.825 2.001 25,400 5,710 50.851 2.002 38,100 8,560 50.876 2.003 50,800 11,400 50.902 2.004 76,200 17,100 50.952 2.006 89,100 20,000 51.003 2.008 92,700 20,800 51.054 2.010 102,500 23,000 51.181 2.015 107,800 24,200 51.308 2.020 119,400 26,800 51.562 2.030 128,300 28,800 51.816 2.040 149,700 33,650 52.832 2.080 159,000 35,750 53.848 2.120 160,400 36,000 54.356 2.140 159,500 35,850 54.864 2.160 151,500 34,050 55.880 2.200 124,700 28,000 56.642 2.230 Fracture (a) Plot the data as engineering stress versus en- gineering strain. (b) Compute the modulus of elasticity. (c) Determine the yield strength at a strain offset of 0.002.
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Homework
6.30 A cylindrical specimen of stainless steel having a
diameter of 12.8 mm (0.505 in.) and a gauge length
of 50.800 mm (2.000 in.) is pulled in tension. Use
the load-elongation characteristics shown in the
following table to complete parts (a) through (f).
1
Load
Length
N
Ib
in.
mm
50.800
2.000
12,700
2,850
50.825
2.001
25,400
5,710
50.851
2.002
38,100
8,560
50.876
2.003
50,800
11,400
50.902
2.004
76,200
17,100
50.952
2.006
89,100
20,000
51.003
2.008
92,700
20,800
51.054
2.010
102,500
23,000
51.181
2.015
107,800
24,200
51.308
2.020
119,400
26,800
51.562
2.030
128,300
28,800
51.816
2.040
149,700
33,650
52.832
2.080
159,000
35,750
53.848
2.120
160,400
36,000
54.356
2.140
159,500
35,850
54.864
2.160
151,500
34,050
55.880
2.200
124,700
28,000
56.642
2.230
Fracture
(a) Plot the data as engineering stress versus en-
gineering strain.
(b) Compute the modulus of elasticity.
(c) Determine the yield strength at a strain offset
of 0.002.
(d) Determine the tensile strength of this alloy.
(e) What is the approximate ductility, in percent
elongation?
(f) Compute the modulus of resilience.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY