380- 370- 360- 350+ 340+ 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 ++ 2010 Video Example EXAMPLE 3 The linear equation C = 1.65429t2938.07 models the average CO₂, carbon dioxide, level (measured in parts per million) in the atmosphere at an observatory from 1980 to 2008. Use the linear model to estimate the average CO₂ level for 1995 and to predict the level for the year 2019. According to this model, when will the CO₂ level exceed 430 parts per million? SOLUTION Using C = 1.65429t2938.07 with t= 1995, we estimate that the average CO₂ level in 1995 was C(1995) = 1.65429 5429( (rounded to two decimal places). This is an example of interpolation because we have estimated a value between observed values. With t=2019, we get C(2019) = 1.65429 (rounded to two decimal places). So we predict the average CO₂ level in the year 2019 will be ppm (rounded to two decimal places). This is an example of extrapolation because we have predicted a value outside the region of observations. Consequently, we are far less certain about the accuracy of our prediction. 2938.07 - 2938.07% Using C = 1.65429t2938.07, we see that the CO₂ level exceeds 430 ppm when 1.65429t2938.07 > 430. Solving this inequality, we get t> (rounded to two decimal places). 1.65429 We therefore predict that the CO₂ level will exceed 430 ppm in the year . This prediction is risky because it involves a time quite remote from our observations. In fact, we see from the figure that the trend has been for CO₂ levels to increase rather more rapidly in recent years, so the level might exceed 430 ppm well before
380- 370- 360- 350+ 340+ 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 ++ 2010 Video Example EXAMPLE 3 The linear equation C = 1.65429t2938.07 models the average CO₂, carbon dioxide, level (measured in parts per million) in the atmosphere at an observatory from 1980 to 2008. Use the linear model to estimate the average CO₂ level for 1995 and to predict the level for the year 2019. According to this model, when will the CO₂ level exceed 430 parts per million? SOLUTION Using C = 1.65429t2938.07 with t= 1995, we estimate that the average CO₂ level in 1995 was C(1995) = 1.65429 5429( (rounded to two decimal places). This is an example of interpolation because we have estimated a value between observed values. With t=2019, we get C(2019) = 1.65429 (rounded to two decimal places). So we predict the average CO₂ level in the year 2019 will be ppm (rounded to two decimal places). This is an example of extrapolation because we have predicted a value outside the region of observations. Consequently, we are far less certain about the accuracy of our prediction. 2938.07 - 2938.07% Using C = 1.65429t2938.07, we see that the CO₂ level exceeds 430 ppm when 1.65429t2938.07 > 430. Solving this inequality, we get t> (rounded to two decimal places). 1.65429 We therefore predict that the CO₂ level will exceed 430 ppm in the year . This prediction is risky because it involves a time quite remote from our observations. In fact, we see from the figure that the trend has been for CO₂ levels to increase rather more rapidly in recent years, so the level might exceed 430 ppm well before
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305071742
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter1: Equations And Graphs
Section1.FOM: Focus On Modeling: Fitting Lines To Data
Problem 4P
Related questions
Question
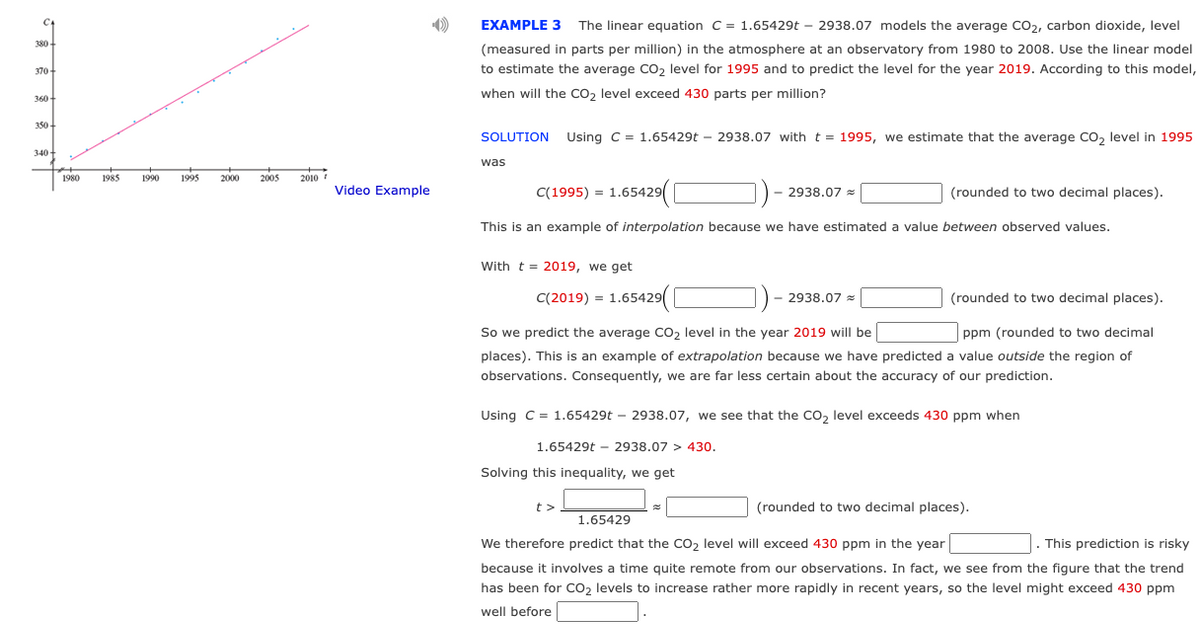
Transcribed Image Text:C
380
370
360+
350+
340+
1980
1985
1990
1995 2000
2005
2010/
Video Example
EXAMPLE 3 The linear equation C = 1.65429t2938.07 models the average CO2, carbon dioxide, level
(measured in parts per million) in the atmosphere at an observatory from 1980 to 2008. Use the linear model
to estimate the average CO₂ level for 1995 and to predict the level for the year 2019. According to this model,
when will the CO₂ level exceed 430 parts per million?
SOLUTION Using C
was
Using C = 1.65429t2938.07 with t = 1995, we estimate that the average CO₂ level in 1995
= 1.65429t
C(1995) = 1.65429
(rounded to two decimal places).
This is an example of interpolation because we have estimated a value between observed values.
With t = 2019, we get
C(2019) = 1.65429[
- 2938.07
(rounded to two decimal places).
So we predict the average CO₂ level in the year 2019 will be
ppm (rounded to two decimal
places). This is an example of extrapolation because we have predicted a value outside the region of
observations. Consequently, we are far less certain about the accuracy of our prediction.
Solving this inequality, we get
- 2938.07
Using C = 1.65429t2938.07, we see that the CO₂ level exceeds 430 ppm when
1.65429t2938.07 > 430.
t>
(rounded to two decimal places).
1.65429
This prediction is risky
We therefore predict that the CO₂ level will exceed 430 ppm in the year
because it involves a time quite remote from our observations. In fact, we see from the figure that the trend
has been for CO₂ levels to increase rather more rapidly in recent years, so the level might exceed 430 ppm
well before
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning