4) The composite shaft consists of a solid brass segment (1) and a solid aluminum segment (2) that are connected at flange B and securely attached to rigid walls at A and C. Brass segment (1) has a diameter of 18 mm, a length of L, = 235 mm, and a shear modulus of 39 GPa. Aluminum segment (2) has a diameter of 24 mm, a length of L₂ = 165 mm, and a shear modulus of 28 GPa. If a concentrated torque of 270 Nm is applied to flange B, determine (a) the maximum shear stress magnitudes in segments (1) and (2). (b) the rotation angle of flange B relative to support A. N y 235 mm (1) B 165 mm 270 N-m C X
4) The composite shaft consists of a solid brass segment (1) and a solid aluminum segment (2) that are connected at flange B and securely attached to rigid walls at A and C. Brass segment (1) has a diameter of 18 mm, a length of L, = 235 mm, and a shear modulus of 39 GPa. Aluminum segment (2) has a diameter of 24 mm, a length of L₂ = 165 mm, and a shear modulus of 28 GPa. If a concentrated torque of 270 Nm is applied to flange B, determine (a) the maximum shear stress magnitudes in segments (1) and (2). (b) the rotation angle of flange B relative to support A. N y 235 mm (1) B 165 mm 270 N-m C X
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter3: Torsion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3.3.12P: A propeller shaft for a small yacht is made of a solid steel bar 104 mm in diameter. The allowable...
Related questions
Question
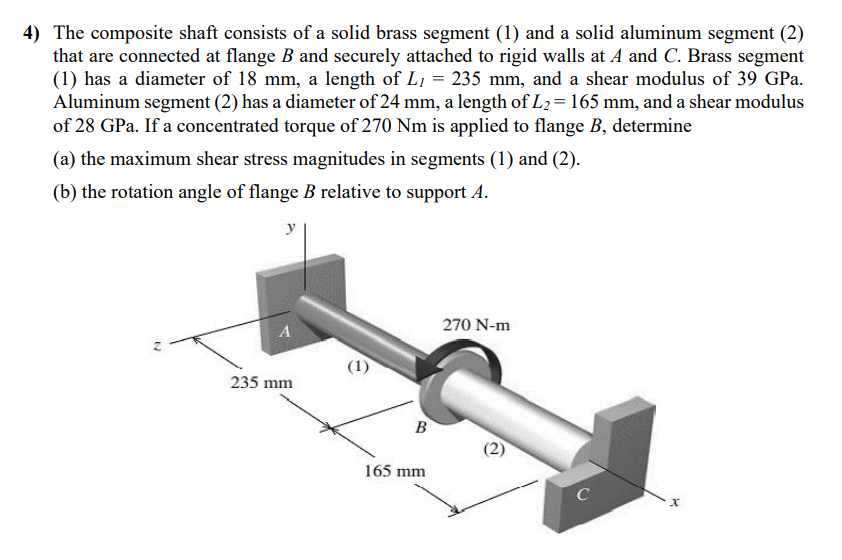
Transcribed Image Text:4) The composite shaft consists of a solid brass segment (1) and a solid aluminum segment (2)
that are connected at flange B and securely attached to rigid walls at A and C. Brass segment
(1) has a diameter of 18 mm, a length of L₁ = 235 mm, and a shear modulus of 39 GPa.
Aluminum segment (2) has a diameter of 24 mm, a length of L₂ = 165 mm, and a shear modulus
of 28 GPa. If a concentrated torque of 270 Nm is applied to flange B, determine
(a) the maximum shear stress magnitudes in segments (1) and (2).
(b) the rotation angle of flange B relative to support A.
N
y
A
235 mm
(1)
B
165 mm
270 N-m
(2)
C
x
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning