4. Consider a wedge of mass m2 = 2M on a frictionless sur- face. Assume the incline angle 0 > 30°. A block of mass m3 = 2M lies on the incline plane. It is attached to a string that runs over a light frictionless pulley. The other end of the string is attached to a hanging block of mass mị = M. There is no space between the hanging mass and the wedge. Find the acceleration of all three masses. Explain why 0 > 30° makes this problem doable whereas smaller angles would be much more difficult to handle. m3 m2
4. Consider a wedge of mass m2 = 2M on a frictionless sur- face. Assume the incline angle 0 > 30°. A block of mass m3 = 2M lies on the incline plane. It is attached to a string that runs over a light frictionless pulley. The other end of the string is attached to a hanging block of mass mị = M. There is no space between the hanging mass and the wedge. Find the acceleration of all three masses. Explain why 0 > 30° makes this problem doable whereas smaller angles would be much more difficult to handle. m3 m2
Related questions
Question
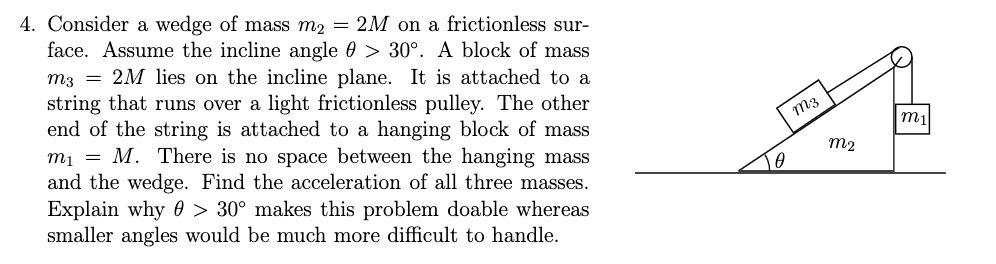
Transcribed Image Text:4. Consider a wedge of mass m2 = 2M on a frictionless sur-
face. Assume the incline angle 0 > 30°. A block of mass
m3 = 2M lies on the incline plane. It is attached to a
string that runs over a light frictionless pulley. The other
end of the string is attached to a hanging block of mass
mị = M. There is no space between the hanging mass
and the wedge. Find the acceleration of all three masses.
Explain why 0 > 30° makes this problem doable whereas
smaller angles would be much more difficult to handle.
m3
m2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images
