4. Data for the progression of college students at a particular college are summarized in the following matrix of transition probabilities: Graduate Drop Out Freshman Sophomore Junior Senior 0.00 0.00 Graduate 1.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.65 0.10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Drop Out 1.00 0.00 0.20 0.15 Freshman 0.00 0.15 0.00 0.00 Sophomore Junior 0.00 0.00 0.75 0.05 0.85 0.00 0.90 0.10 0.00 Senior 0.05 0.00 0.00 0.05 a. What states are absorbing states? b. Interpret the transition probabilities for a sophomore. c. Compute the probabilities that a sophomore will graduate and that a sophomore will drop out. d. In an address to the incoming class of 600 freshmen, the dean asks the students to look around the auditorium and realize that about 50% of the freshmen present today will not make it to graduation day. Does your Markov process analysis support the dean's statement? Explain. e. Currently, the college has 600 freshmen, 520 sophomores, 460 juniors, and 420 seniors. What percentage of the 2000 students attending the college will eventually graduate?
4. Data for the progression of college students at a particular college are summarized in the following matrix of transition probabilities: Graduate Drop Out Freshman Sophomore Junior Senior 0.00 0.00 Graduate 1.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.65 0.10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Drop Out 1.00 0.00 0.20 0.15 Freshman 0.00 0.15 0.00 0.00 Sophomore Junior 0.00 0.00 0.75 0.05 0.85 0.00 0.90 0.10 0.00 Senior 0.05 0.00 0.00 0.05 a. What states are absorbing states? b. Interpret the transition probabilities for a sophomore. c. Compute the probabilities that a sophomore will graduate and that a sophomore will drop out. d. In an address to the incoming class of 600 freshmen, the dean asks the students to look around the auditorium and realize that about 50% of the freshmen present today will not make it to graduation day. Does your Markov process analysis support the dean's statement? Explain. e. Currently, the college has 600 freshmen, 520 sophomores, 460 juniors, and 420 seniors. What percentage of the 2000 students attending the college will eventually graduate?
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305658004
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Ron Larson
Chapter2: Matrices
Section2.5: Markov Chain
Problem 47E: Explain how you can determine the steady state matrix X of an absorbing Markov chain by inspection.
Related questions
Concept explainers
Equations and Inequations
Equations and inequalities describe the relationship between two mathematical expressions.
Linear Functions
A linear function can just be a constant, or it can be the constant multiplied with the variable like x or y. If the variables are of the form, x2, x1/2 or y2 it is not linear. The exponent over the variables should always be 1.
Question
Show your complete solution especially for B to E.
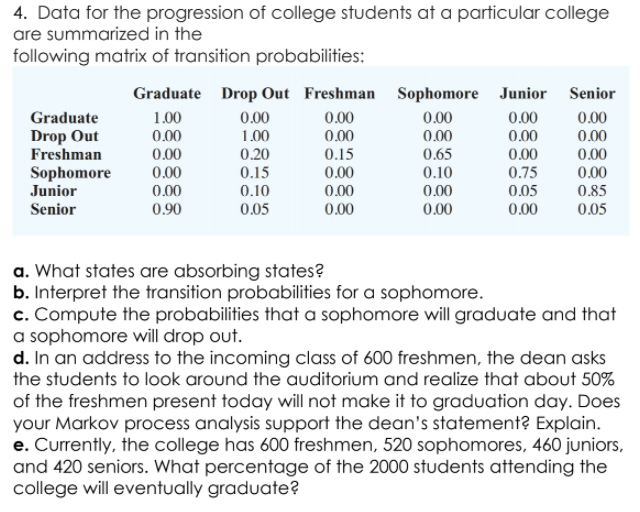
Transcribed Image Text:4. Data for the progression of college students at a particular college
are summarized in the
following matrix of transition probabilities:
Graduate Drop Out Freshman Sophomore Junior Senior
0.00
0.00
Graduate
1.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
1.00
Drop Out
Freshman
Sophomore
Junior
Senior
0.00
0.65
0.10
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.20
0.15
0.15
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.75
0.00
0.10
0.00
0.05
0.85
0.90
0.05
0.00
0.00
0.05
a. What states are absorbing states?
b. Interpret the transition probabilities for a sophomore.
c. Compute the probabilities that a sophomore will graduate and that
a sophomore will drop out.
d. In an address to the incoming class of 600 freshmen, the dean asks
the students to look around the auditorium and realize that about 50%
of the freshmen present today will not make it to graduation day. Does
your Markov process analysis support the dean's statement? Explain.
e. Currently, the college has 600 freshmen, 520 sophomores, 460 juniors,
and 420 seniors. What percentage of the 2000 students attending the
college will eventually graduate?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, probability and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning