4. In the high jump, the kinetic energy of an athlete is transformed into gravitational potential energy without the aid of a pole. With what minimum speed must the athlete leave the ground in order to lift his center of mass 2.10 m and cross the bar with a speed of 0.50 m/s? Draw a diagram each choose origin and axes
4. In the high jump, the kinetic energy of an athlete is transformed into gravitational potential energy without the aid of a pole. With what minimum speed must the athlete leave the ground in order to lift his center of mass 2.10 m and cross the bar with a speed of 0.50 m/s? Draw a diagram each choose origin and axes
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter13: Universal Gravitation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13.1CQ: Each Voyager spacecraft was accelerated toward escape speed from the Sun by the gravitational force...
Related questions
Question
Please follow required steps to better understand. Thank you!!!! 4
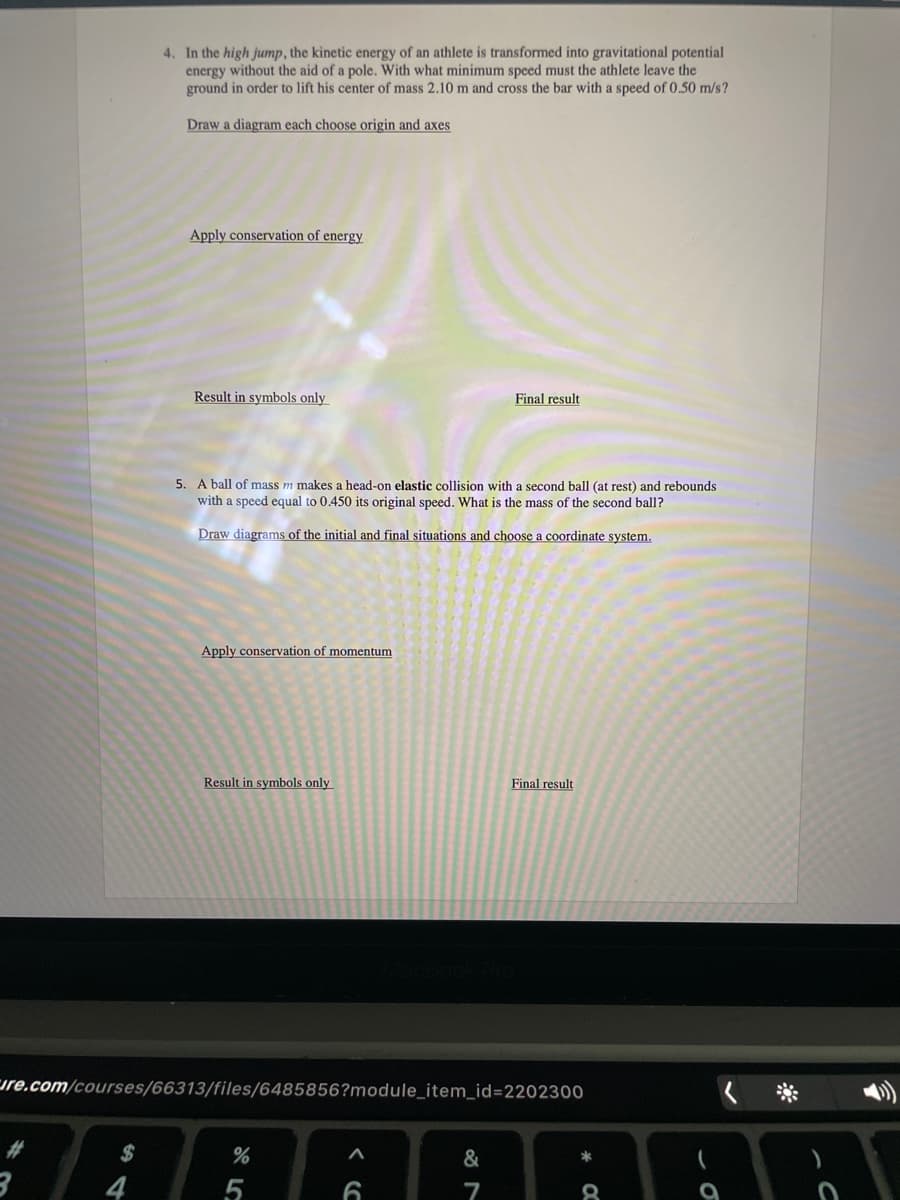
Transcribed Image Text:4. In the high jump, the kinetic energy of an athlete is transformed into gravitational potential
energy without the aid of a pole. With what minimum speed must the athlete leave the
ground in order to lift his center of mass 2.10 m and cross the bar with a speed of 0.50 m/s?
Draw a diagram each choose origin and axes
Apply conservation of energy
Result in symbols only
Final result
5. A ball of mass m makes a head-on elastic collision with a second ball (at rest) and rebounds
with a speed equal to 0.450 its original speed. What is the mass of the second ball?
Draw diagrams of the initial and final situations and choose a coordinate system.
Apply conservation of momentum
Result in symbols only
Final result
ure.com/courses/66313/files/6485856?module_item_id=2202300
く *
%23
$
&
4
5
6
7
8
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning