4. The diagram represents the path of a ball that has been thrown upward. Discuss how the kinetic energy (KE), gravitational potential energy (GPE), and total mechanical energy (ME) change between points A (where the ball is thrown from), B (the highest point reached by the ball), and C (where the ball hits the ground). Ignore friction between the ball and the air. (3 points)
4. The diagram represents the path of a ball that has been thrown upward. Discuss how the kinetic energy (KE), gravitational potential energy (GPE), and total mechanical energy (ME) change between points A (where the ball is thrown from), B (the highest point reached by the ball), and C (where the ball hits the ground). Ignore friction between the ball and the air. (3 points)
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter7: Conservation Of Energy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 38P
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
Transcribed Image Text:TUR
Copy of VLA Phy.Science 2.1.5 Practice:Conservation of Energy
ale Edit View Insert Format Tools Add-ons Help
Last edit was yesterday at 10:33 PM
E A, P
в I
E - E -E E
100%
Normal text
Roboto
11
1 2
. .. 3 I 4 ..
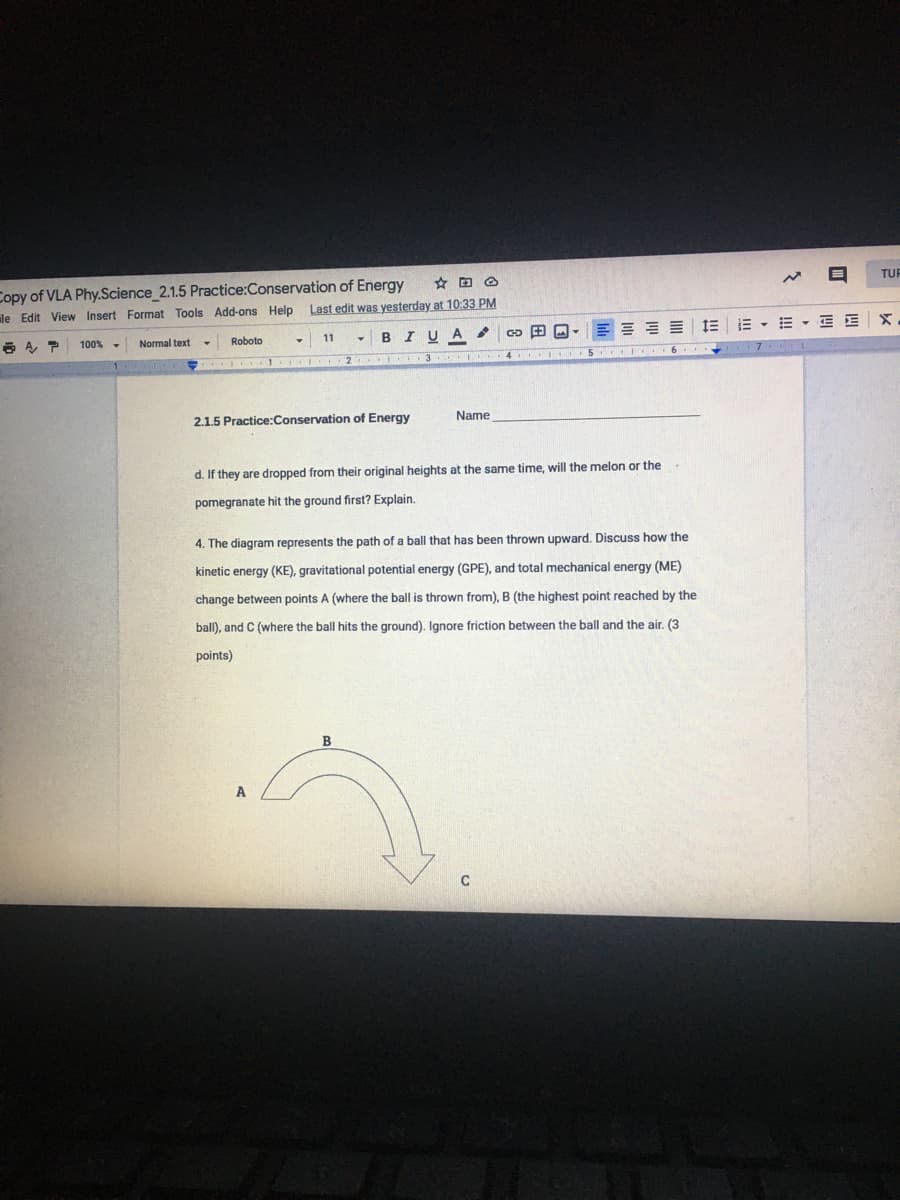
2.1.5 Practice:Conservation of Energy
Name
d. If they are dropped from their original heights at the same time, will the melon or the.
pomegranate hit the ground first? Explain.
4. The diagram represents the path of a ball that has been thrown upward. Discuss how the
kinetic energy (KE), gravitational potential energy (GPE), and total mechanical energy (ME)
change between points A (where the ball is thrown from), B (the highest point reached by the
ball), and C (where the ball hits the ground). Ignore friction between the ball and the air. (3
points)
B
A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning