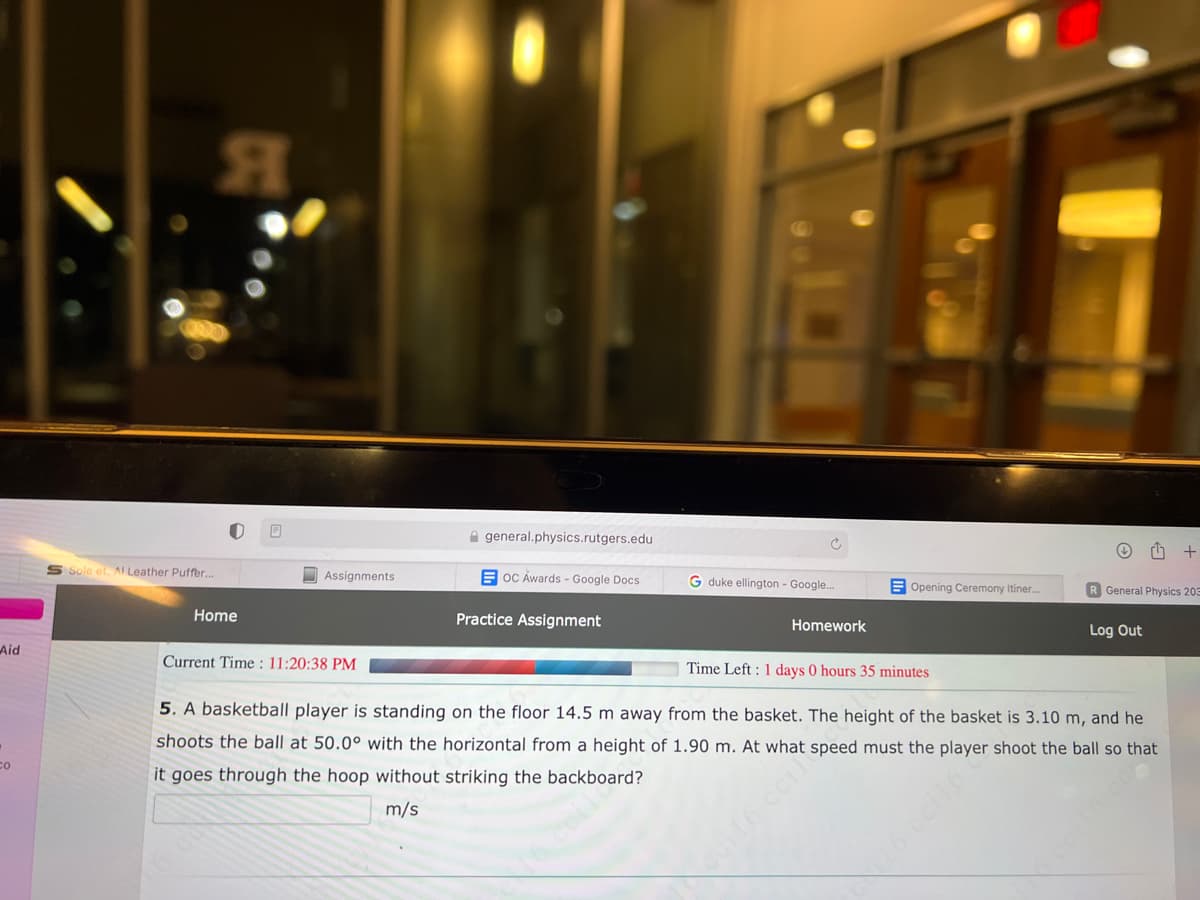
5. A basketball player is standing on the floor 14.5 m away from the basket. The height of the basket is 3.10 m, and he shoots the ball at 50.0° with the horizontal from a height of 1.90 m. At what speed must the player shoot the ball so that it goes through the hoop without striking the backboard? m/s
5. A basketball player is standing on the floor 14.5 m away from the basket. The height of the basket is 3.10 m, and he shoots the ball at 50.0° with the horizontal from a height of 1.90 m. At what speed must the player shoot the ball so that it goes through the hoop without striking the backboard? m/s
Chapter12: Relativity, Particle Physics, And Cosmology
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4Q
Related questions
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Aid
.
co
Sole et. Al Leather Puffer...
Я
Home
0
Assignments
Current Time: 11:20:38 PM
general.physics.rutgers.edu
Oc Awards - Google Docs
Practice Assignment
G duke ellington - Google...
Homework
Opening Ceremony Itiner...
cil6 ccil
Ⓒ
G
Log Out
Time Left: 1 days 0 hours 35 minutes
5. A basketball player is standing on the floor 14.5 m away from the basket. The height of the basket is 3.10 m, and he
shoots the ball at 50.0° with the horizontal from a height of 1.90 m. At what speed must the player shoot the ball so that
it goes through the hoop without striking the backboard?
m/s
R General Physics 203
+
Expert Solution
Introduction:
Projectile motion and equation of motion:
When an object is thrown at angle from the horizontal surface, object follows a curved path before reaching to ground.
The total time of flight (t in s) is the time during which it remains in the projectile motion.
Object has two components of initial velocities: First component is horizontal velocity (vx)and second component is vertical velocity (vy).
- vx will remain constant through out it's flight time (t)= v cos
- vy is the initial velocity and final velocity can be calculated based on constant acceleration due to gravity in vertical direction and for that equation of motion is used.
Equation of motion:
It is used to establish relationship between distance travelled, initial & final velocities during the time (t) travelled under constant acceleration.
Mathematically,
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305960961
Author:
Michael A. Seeds, Dana Backman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning