5. Consider the following diagram from one of the lecture slides: 111 Hot fluid Ta Cold fuid T F I Heat tanster trough a plane wall (4) Temperate distribution. () Equivalent themal circut Focus on temperature distribution from T,1 to Ts,1- which represents convective heat transfer from hot fluid to solid surface at x=0. Clearly, this distribution is nonlinear in nature (and it corresponds to boundary layer of the fluid). (a) Even though this is a nonlinear function, why we could use electrical circuit analogy for this situation i.e. heat convection from hot fluid to solid surface at x=0? (b) Heat conduction on the other hand, explicitly requires linear temperature distribution (see distribution from x-0 to x=L in solid) for electrical analogy to be used in the problem, why is that?
5. Consider the following diagram from one of the lecture slides: 111 Hot fluid Ta Cold fuid T F I Heat tanster trough a plane wall (4) Temperate distribution. () Equivalent themal circut Focus on temperature distribution from T,1 to Ts,1- which represents convective heat transfer from hot fluid to solid surface at x=0. Clearly, this distribution is nonlinear in nature (and it corresponds to boundary layer of the fluid). (a) Even though this is a nonlinear function, why we could use electrical circuit analogy for this situation i.e. heat convection from hot fluid to solid surface at x=0? (b) Heat conduction on the other hand, explicitly requires linear temperature distribution (see distribution from x-0 to x=L in solid) for electrical analogy to be used in the problem, why is that?
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
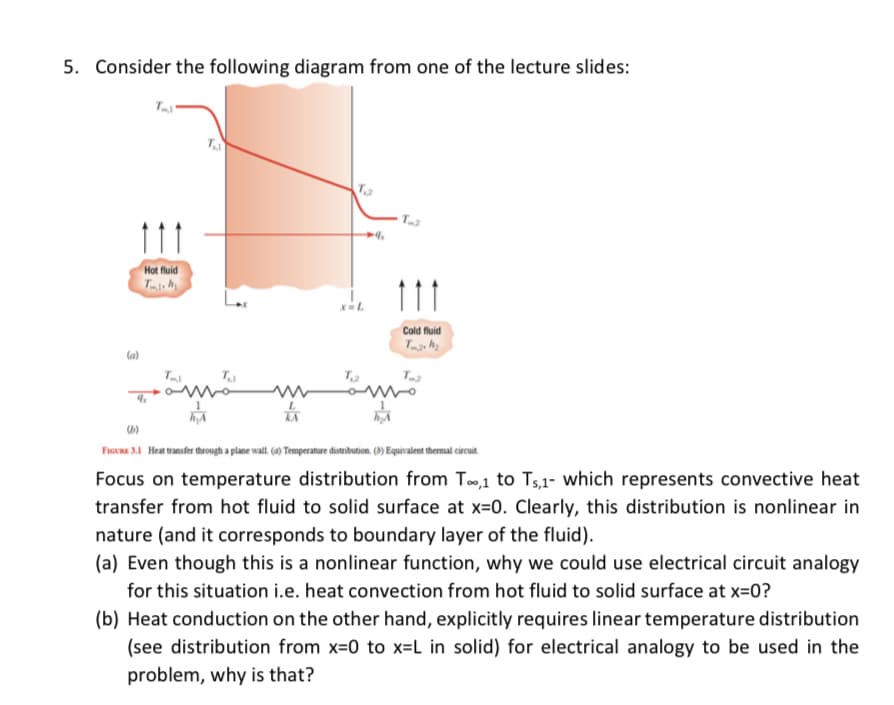
Transcribed Image Text:5. Consider the following diagram from one of the lecture slides:
T2
11
Hot fluid
Cold fluid
la)
KA
FIGURE 31 Heat transfer thưough a plane wall. (a) Temperature distribution. (8) Equivalent thermal circuit.
Focus on temperature distribution from T,1 to Ts,1- which represents convective heat
transfer from hot fluid to solid surface at x=0. Clearly, this distribution is nonlinear in
nature (and it corresponds to boundary layer of the fluid).
(a) Even though this is a nonlinear function, why we could use electrical circuit analogy
for this situation i.e. heat convection from hot fluid to solid surface at x=0?
(b) Heat conduction on the other hand, explicitly requires linear temperature distribution
(see distribution from x=0 to x=L in solid) for electrical analogy to be used in the
problem, why is that?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The