5.4-23. Let X be N(0,1). Use the mgf technique to show that Y = X² is x2(1). HINT: Evaluate the integral repre- senting E(e¹x²) by writing w=x√//1-2t.
5.4-23. Let X be N(0,1). Use the mgf technique to show that Y = X² is x2(1). HINT: Evaluate the integral repre- senting E(e¹x²) by writing w=x√//1-2t.
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter6: Vector Spaces
Section6.6: The Matrix Of A Linear Transformation
Problem 29EQ
Related questions
Question
Note:-
• Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism.
• Answer completely.
• You will get up vote for sure.
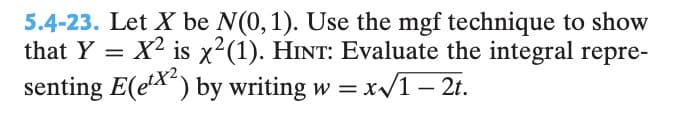
Transcribed Image Text:5.4-23. Let X be N(0,1). Use the mgf technique to show
that Y = X² is x2(1). HINT: Evaluate the integral repre-
senting E(e¹x²) by writing w=x√//1-2t.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra for College Students
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195780
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra for College Students
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195780
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning