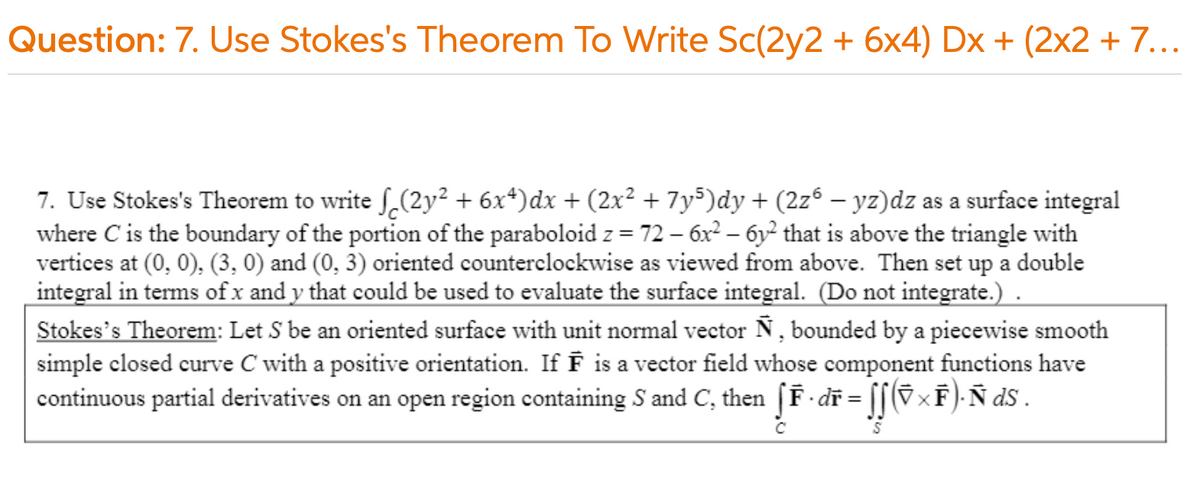
7. Use Stokes's Theorem to write S.(2y² + 6x*)dx + (2x² + 7y³)dy+ (2z° – yz)dz as a surface integral where C is the boundary of the portion of the paraboloid z = 72 – 6x2 – 6y² that is above the triangle with vertices at (0, 0), (3, 0) and (0, 3) oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above. Then set up a double integral in tems of x and y that could be used to evaluate the surface integral. (Do not integrate.). Stokes's Theorem: Let S be an oriented surface with unit normal vector Ñ, bounded by a piecewise smooth simple closed curve C with a positive orientation. If F is a vector field whose component functions have continuous partial derivatives on an open region containing S and C, then [F dĩ = (ExF)-Ñ ds .
7. Use Stokes's Theorem to write S.(2y² + 6x*)dx + (2x² + 7y³)dy+ (2z° – yz)dz as a surface integral where C is the boundary of the portion of the paraboloid z = 72 – 6x2 – 6y² that is above the triangle with vertices at (0, 0), (3, 0) and (0, 3) oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above. Then set up a double integral in tems of x and y that could be used to evaluate the surface integral. (Do not integrate.). Stokes's Theorem: Let S be an oriented surface with unit normal vector Ñ, bounded by a piecewise smooth simple closed curve C with a positive orientation. If F is a vector field whose component functions have continuous partial derivatives on an open region containing S and C, then [F dĩ = (ExF)-Ñ ds .
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Chapter10: Analytic Geometry
Section10.6: The Three-dimensional Coordinate System
Problem 41E: Does the sphere x2+y2+z2=100 have symmetry with respect to the a x-axis? b xy-plane?
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Question: 7. Use Stokes's Theorem To Write Sc(2y2 + 6x4) Dx + (2x2 + 7...
7. Use Stokes's Theorem to write ſ,(2y² + 6x*)dx + (2x² + 7y5)dy + (2zº – yz)dz as a surface integral
where C is the boundary of the portion of the paraboloid z = 72 – 6x² – 6y² that is above the triangle with
vertices at (0, 0), (3, 0) and (0, 3) oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above. Then set up a double
integral in terms of x and y that could be used to evaluate the surface integral. (Do not integrate.).
Stokes's Theorem: Let S be an oriented surface with unit normal vector N, bounded by a piecewise smooth
simple closed curve C with a positive orientation. If F is a vector field whose component functions have
continuous partial derivatives on an open region containing S and C, then [F dĩ = [[(§×F)- Ñ dS .
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,