8. At what distance a should the bearing supports at A and B be placed so that the deflection at the enter of the shaft is equal to the deflection at its ends? Use MAM.
8. At what distance a should the bearing supports at A and B be placed so that the deflection at the enter of the shaft is equal to the deflection at its ends? Use MAM.
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter9: Deflections Of Beams
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9.3.9P: Obtain a formula for the ratio c/maxof the deflection at the midpoint to the maximum deflection for...
Related questions
Question
8. At what distance a should the bearing supports at A and B be placed so that the deflection at the enter of the shaft is equal to the deflection at its ends? Use MAM. The bearings exert only on the hafts. The flexural rigidity is constant.
9. For this beam example, let's say we are interested in finding the deflections at every key point of the beam (A, C, and E) using the conjugate beam method.
10. Determine the equations of the elastic curve using the coordinates x1 and x3 and specify the slope and deflection at point B. El is constant.
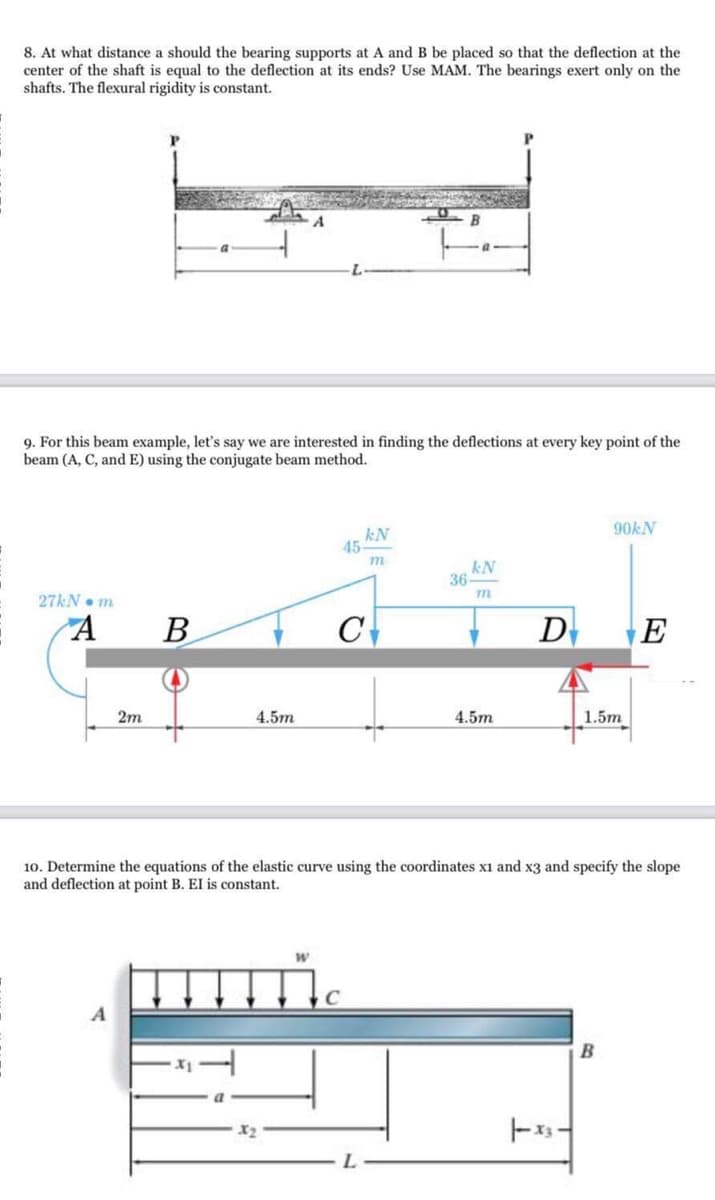
Transcribed Image Text:8. At what distance a should the bearing supports at A and B be placed so that the deflection at the
center of the shaft is equal to the deflection at its ends? Use MAM. The bearings exert only on the
shafts. The flexural rigidity is constant.
9. For this beam example, let's say we are interested in finding the deflections at every key point of the
beam (A, C, and E) using the conjugate beam method.
90KN
kN
45
m
kN
36
27KN• m
B
C
D
E
2m
4.5m
4.5m
1.5m
10. Determine the equations of the elastic curve using the coordinates x1 and x3 and specify the slope
and deflection at point B. EI is constant.
C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning