8*. Suppose that a vector in R° has a head at (2,-3,6) and a tail at (5,3,4). Write this vector in standard notation. Then draw the vector in standard notation in R 7 and c = 9. Let a 4 (a) Compute a, 3a, and -2a, and draw each vector in the same xy-plane. |(b) Compute a plane (but a different one from the one you drew for (a). How are the vectors a -b and b - a -b, -b, and b - a, and draw the vectors a, b, a b, a - b, and b - a in the same xy- a related? (c) Compute -2c and 3a - 2c, and draw the vectors a, c, 3a, -2c, and 3a - 2c in the same xy-plane (but a different one from the one you drew for (a) and (b))
8*. Suppose that a vector in R° has a head at (2,-3,6) and a tail at (5,3,4). Write this vector in standard notation. Then draw the vector in standard notation in R 7 and c = 9. Let a 4 (a) Compute a, 3a, and -2a, and draw each vector in the same xy-plane. |(b) Compute a plane (but a different one from the one you drew for (a). How are the vectors a -b and b - a -b, -b, and b - a, and draw the vectors a, b, a b, a - b, and b - a in the same xy- a related? (c) Compute -2c and 3a - 2c, and draw the vectors a, c, 3a, -2c, and 3a - 2c in the same xy-plane (but a different one from the one you drew for (a) and (b))
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter8: Applications Of Trigonometry
Section8.4: The Dot Product
Problem 46E
Related questions
Question
Question 9 please

Transcribed Image Text:8*. Suppose that a vector in R° has a head at (2,-3,6) and a tail at (5,3,4). Write this vector in
standard notation. Then draw the vector in standard notation in R
7
and c =
9. Let a
4
(a) Compute a, 3a, and -2a, and draw each vector in the same xy-plane.
|(b) Compute a
plane (but a different one from the one you drew for (a). How are the vectors a -b and b - a
-b,
-b, and b - a, and draw the vectors a, b, a b, a - b, and b - a in the same xy-
a
related?
(c) Compute -2c and 3a - 2c, and draw the vectors a, c, 3a, -2c, and 3a - 2c in the same xy-plane
(but a different one from the one you drew for (a) and (b))
Expert Solution
Step 1
a)
Compute a, 3a and -2a as follows.
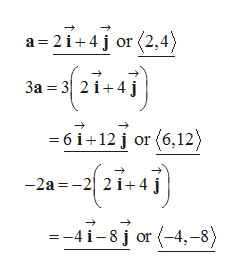
Step 2
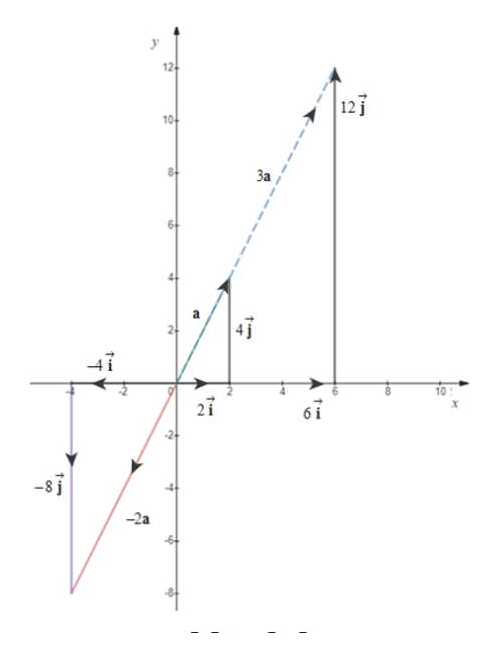
Draw a, 3a and -2a in xy coordinates as shown in below figure.
Step 3
b) Compute a + b, a - b and b - a as follows.
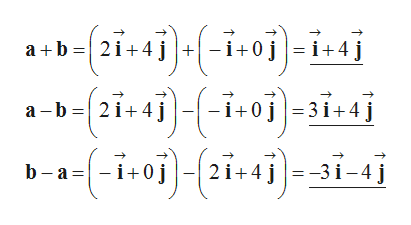
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning