9. Examine Table 1 regarding recommended childhood vaccinations. Based upon the definitions and information in the table, which of these vaccine-preventable diseases is NOT considered communicable or contagious? Table 1. Childhood Diseases and Available Preventative Vaccines. Disease Disease complications Infected blisters, bleeding disorders, encephalitis (brain swelling), pneumonia (infection in the lungs) Vaccine Disease spread by Air, direct contact Disease symptoms Rash, tiredness, headache, fever Chickenpox Varicella vaccine protects against chickenpox. Diphtheria Sore throat, mild fever, weakness, swollen glands in neck May be no symptoms unless bacteria enter the blood Air, direct contact Swelling of the heart muscle, heart failure, coma, paralysis, death DTAP vaccine protects against diphtheria. Meningitis (infection of the covering around the brain and spinal cord), intellectual disability, epiglottitis (life- threatening infection that can block the windpipe and lead to serious breathing problems), pneumonia (infection in the lungs), death Chronic liver infection, liver failure, liver Hib Hib vaccine protects against Haemophilus infuenzae type b. Air, direct contact May be no symptoms, fever, headache, weakness, vomit- ing, jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), joint pain Fever, muscle pain, sore throat, cough, extreme fatigue Rash, fever, cough, runny nose, pinkeye Swollen salivary glands (un- der the jaw), fever, headache, tiredness, muscle pain Severe cough, runny nose, apnea (a pause in breathing in infants) May be no symptoms, sore throat, fever, nausea, Contact with blood or body fluids Hepatitis B HepB vaccine protects against hepatitis B. cancer Flu Air, direct contact Pneumonia (infection in the lungs) Flu vaccine protects against influenza. Encephalitis (brain swelling), pneumonia (infection in the lungs), death Meningitis (infection of the covering around the brain and spinal cord), encephalitis (brain swelling), inflamma- tion of testicles or ovaries, deafness Pneumonia (infection in the lungs), death Measles MMR vaccine protects Air, direct contact against measles. MMR vaccine protects against mumps. Mumps Air, direct contact DTAP vaccine protects against pertussis (whooping cough). IPV vaccine protects against polio. Pertussis Air, direct contact Polio Paralysis, death Air, direct contact, through the mouth headache Bacteremia (blood infection), meningitis (infection of the covering around the brain and spinal cord), death Severe diarrhea, dehydration Air, direct contact May be no symptoms, pneumonia (infection in the lungs) Diarrhea, fever, vomiting Pneumococcal PCV vaccine protects against pneumococcus. Disease Rotavirus RV vaccine protects against rotavirUS. MMR vaccine protects against rubella. Through the mouth Children infected with rubella Very serious in pregnant women- can virus sometimes have a rash, fever, swollen lymph nodes Stiffness in neck and abdominal muscles, difficulty swallowing, muscle spasms, fever Rubella Air, direct contact lead to miscarriage, stillbirth, premature delivery, birth defects Broken bones, breathing difficulty, death DTAP vaccine protects against tetanus. Exposure through cuts in skin Tetanus
9. Examine Table 1 regarding recommended childhood vaccinations. Based upon the definitions and information in the table, which of these vaccine-preventable diseases is NOT considered communicable or contagious? Table 1. Childhood Diseases and Available Preventative Vaccines. Disease Disease complications Infected blisters, bleeding disorders, encephalitis (brain swelling), pneumonia (infection in the lungs) Vaccine Disease spread by Air, direct contact Disease symptoms Rash, tiredness, headache, fever Chickenpox Varicella vaccine protects against chickenpox. Diphtheria Sore throat, mild fever, weakness, swollen glands in neck May be no symptoms unless bacteria enter the blood Air, direct contact Swelling of the heart muscle, heart failure, coma, paralysis, death DTAP vaccine protects against diphtheria. Meningitis (infection of the covering around the brain and spinal cord), intellectual disability, epiglottitis (life- threatening infection that can block the windpipe and lead to serious breathing problems), pneumonia (infection in the lungs), death Chronic liver infection, liver failure, liver Hib Hib vaccine protects against Haemophilus infuenzae type b. Air, direct contact May be no symptoms, fever, headache, weakness, vomit- ing, jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), joint pain Fever, muscle pain, sore throat, cough, extreme fatigue Rash, fever, cough, runny nose, pinkeye Swollen salivary glands (un- der the jaw), fever, headache, tiredness, muscle pain Severe cough, runny nose, apnea (a pause in breathing in infants) May be no symptoms, sore throat, fever, nausea, Contact with blood or body fluids Hepatitis B HepB vaccine protects against hepatitis B. cancer Flu Air, direct contact Pneumonia (infection in the lungs) Flu vaccine protects against influenza. Encephalitis (brain swelling), pneumonia (infection in the lungs), death Meningitis (infection of the covering around the brain and spinal cord), encephalitis (brain swelling), inflamma- tion of testicles or ovaries, deafness Pneumonia (infection in the lungs), death Measles MMR vaccine protects Air, direct contact against measles. MMR vaccine protects against mumps. Mumps Air, direct contact DTAP vaccine protects against pertussis (whooping cough). IPV vaccine protects against polio. Pertussis Air, direct contact Polio Paralysis, death Air, direct contact, through the mouth headache Bacteremia (blood infection), meningitis (infection of the covering around the brain and spinal cord), death Severe diarrhea, dehydration Air, direct contact May be no symptoms, pneumonia (infection in the lungs) Diarrhea, fever, vomiting Pneumococcal PCV vaccine protects against pneumococcus. Disease Rotavirus RV vaccine protects against rotavirUS. MMR vaccine protects against rubella. Through the mouth Children infected with rubella Very serious in pregnant women- can virus sometimes have a rash, fever, swollen lymph nodes Stiffness in neck and abdominal muscles, difficulty swallowing, muscle spasms, fever Rubella Air, direct contact lead to miscarriage, stillbirth, premature delivery, birth defects Broken bones, breathing difficulty, death DTAP vaccine protects against tetanus. Exposure through cuts in skin Tetanus
Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap Course List)
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781111306663
Author:Margaret Rodriguez, Paul Price
Publisher:Margaret Rodriguez, Paul Price
Chapter1: Introduction To Microbiology
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3UTM
Related questions
Question
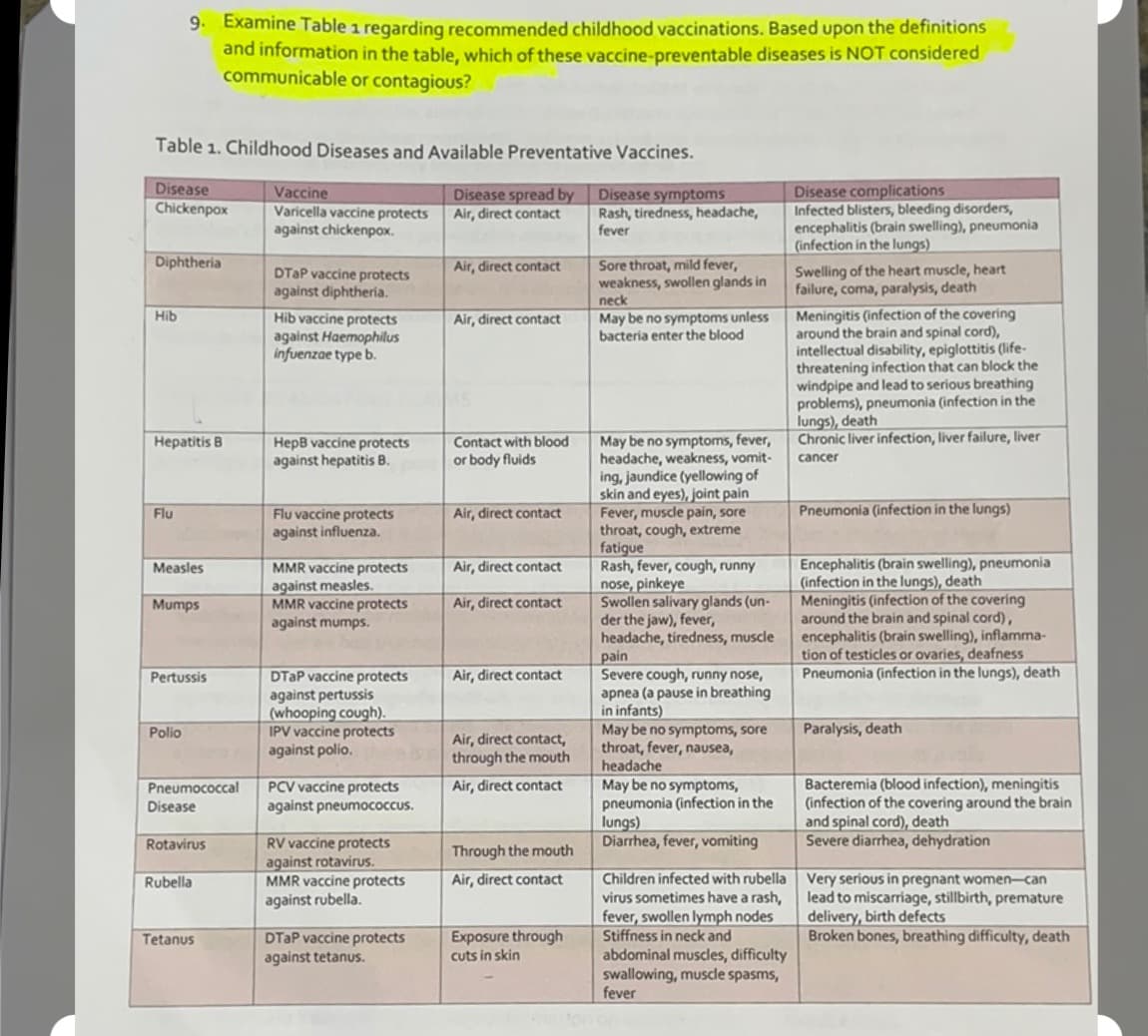
Transcribed Image Text:9. Examine Table 1 regarding recommended childhood vaccinations. Based upon the definitions
and information in the table, which of these vaccine-preventable diseases is NOT considered
communicable or contagious?
Table 1. Childhood Diseases and Available Preventative Vaccines.
Disease
Chickenpox
Disease complications
Infected blisters, bleeding disorders,
encephalitis (brain swelling), pneumonia
(infection in the lungs)
Vaccine
Disease spread by
Varicella vaccine protects
against chickenpox.
Disease symptoms
Rash, tiredness, headache,
fever
Air, direct contact
Diphtheria
Sore throat, mild fever,
weakness, swollen glands in
neck
Air, direct contact
DTAP vaccine protects
against diphtheria.
Swelling of the heart muscle, heart
failure, coma, paralysis, death
Meningitis (infection of the covering
around the brain and spinal cord),
intellectual disability, epiglottitis (life-
threatening infection that can block the
windpipe and lead to serious breathing
problems), pneumonia (infection in the
lungs), death
Chronic liver infection, liver failure, liver
May be no symptoms unless
bacteria enter the blood
Hib
Hib vaccine protects
against Haemophilus
infuenzae type b.
Air, direct contact
May be no symptoms, fever,
headache, weakness, vomit-
ing, jaundice (yellowing of
skin and eyes), joint pain
Fever, muscle pain, sore
throat, cough, extreme
fatigue
Rash, fever, cough, runny
nose, pinkeye
Swollen salivary glands (un-
der the jaw), fever,
headache, tiredness, muscle
pain
Severe cough, runny nose,
apnea (a pause in breathing
in infants)
May be no symptoms, sore
throat, fever, nausea,
headache
Hepatitis B
Contact with blood
HepB vaccine protects
against hepatitis B.
or body fluids
cancer
Flu
Air, direct contact
Pneumonia (infection in the lungs)
Flu vaccine protects
against influenza.
Encephalitis (brain swelling), pneumonia
(infection in the lungs), death
Meningitis (infection of the covering
around the brain and spinal cord),
encephalitis (brain swelling), inflamma-
tion of testicles or ovaries, deafness
Pneumonia (infection in the lungs), death
Air, direct contact
MMR vaccine protects
against measles.
MMR vaccine protects
against mumps.
Measles
Mumps
Air, direct contact
DTAP vaccine protects
against pertussis
(whooping cough).
IPV vaccine protects
against polio.
Pertussis
Air, direct contact
Polio
Paralysis, death
Air, direct contact,
through the mouth
May be no symptoms,
pneumonia (infection in the
lungs)
Diarrhea, fever, vomiting
Bacteremia (blood infection), meningitis
(infection of the covering around the brain
and spinal cord), death
Severe diarrhea, dehydration
Air, direct contact
Pneumococcal
Disease
PCV vaccine protects
against pneumococcus.
RV vaccine protects
against rotavirUs.
MMR vaccine protects
against rubella.
Rotavirus
Through the mouth
Children infected with rubella Very serious in pregnant womencan
virus sometimes have a rash,
fever, swollen lymph nodes
Stiffness in neck and
abdominal muscles, difficulty
swallowing, muscdle spasms,
fever
Rubella
Air, direct contact
lead to miscarriage, stillbirth, premature
delivery, birth defects
Broken bones, breathing difficulty, death
DTAP vaccine protects
against tetanus.
Exposure through
cuts in skin
Tetanus
Expert Solution
Step 1
Communicable diseases spread from one person associateother|to a different} or from an animal to someone. It spread via air viruses or bacterium, however additionally through blood or different liquid body substance. The terms infectious and contagious also are wont to describe disease. during this section, find out about coordinated efforts to combat some of the foremost serious communicable diseases on a world level.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781111306663
Author:
Margaret Rodriguez, Paul Price
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a…
Nursing
ISBN:
9781305964792
Author:
Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy Correa
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781111306663
Author:
Margaret Rodriguez, Paul Price
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a…
Nursing
ISBN:
9781305964792
Author:
Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy Correa
Publisher:
Cengage Learning