9. The freezing point depression can be calculated using the equation AT/ Ky mi where AT is the change in freezing point, I is the number of ions in the solution per mole of dissolved NaCl (1=2), m is the molality of the solution, and Ky is the molal freezing point constant for water which is 1.86°C/m. Using this equation and the data recorded above, calculate the molar mass for NaCl. g/mol
9. The freezing point depression can be calculated using the equation AT/ Ky mi where AT is the change in freezing point, I is the number of ions in the solution per mole of dissolved NaCl (1=2), m is the molality of the solution, and Ky is the molal freezing point constant for water which is 1.86°C/m. Using this equation and the data recorded above, calculate the molar mass for NaCl. g/mol
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
11th Edition
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Chapter1: Matter, Energy, And Measurement
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.86P: 1-86 The specific heats of some elements at 25oC are as follows: aluminum = 0.215 cal/g · oC; carbon...
Related questions
Question
Asking for Q 9
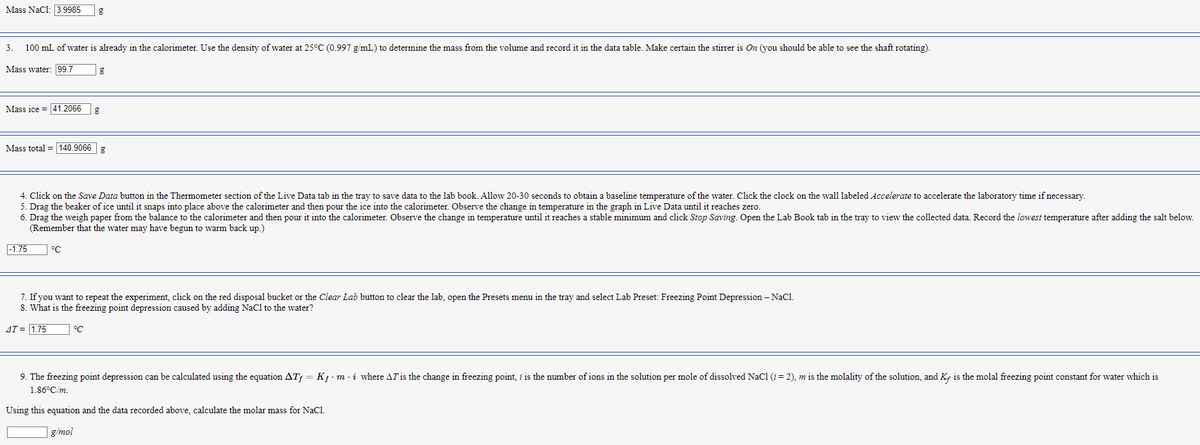
Transcribed Image Text:Mass NaC1: 3.9985
3. 100 mL of water is already in the calorimeter. Use the density of water at 25°C (0.997 g/mL) to determine the mass from the volume and record it in the data table. Make certain the stirrer is On (you should be able to see the shaft rotating).
Mass water: 99.7
Mass ice 41.2066
Mass total = 140.9066 g
-1.75
g
4. Click on the Save Data button in the Thermometer section of the Live Data tab in the tray to save data to the lab book. Allow 20-30 seconds to obtain a baseline temperature of the water. Click the clock on the wall labeled Accelerate to accelerate the laboratory time if necessary.
5. Drag the beaker of ice until it snaps into place above the calorimeter and then pour the ice into the calorimeter. Observe the change in temperature in the graph in Live Data until it reaches zero.
6. Drag the weigh paper from the balance to the calorimeter and then pour it into the calorimeter. Observe the change in temperature until it reaches a stable minimum and click Stop Saving. Open the Lab Book tab in the tray to view the collected data. Record the lowest temperature after adding the salt below.
(Remember that the water may have begun to warm back up.)
°C
g
°C
7. If you want to repeat the experiment, click on the red disposal bucket or the Clear Lab button to clear the lab, open the Presets menu in the tray and select Lab Preset: Freezing Point Depression - NaCl.
8. What is the freezing point depression caused by adding NaCl to the water?
AT = 1.75
9. The freezing point depression can be calculated using the equation ATƒ = Kƒ · m · i where AT is the change in freezing point, i is the number of ions in the solution per mole of dissolved NaC1 (i = 2), m is the molality of the solution, and Ky is the molal freezing point constant for water which is
1.86°C/m.
Using this equation and the data recorded above, calculate the molar mass for NaCl.
g/mol
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax