A 0.250 kg toy car moving with a speed of 0.820 m/s collides with a wall. The figure shows the force exerted on the car by the wall over the course of the collision. What is the magnitude of the velocity, or final speed, of the car after the collision? .540 final speed = m/s Incorrect 5 0.1 0.2 Time (s) Force (N)
A 0.250 kg toy car moving with a speed of 0.820 m/s collides with a wall. The figure shows the force exerted on the car by the wall over the course of the collision. What is the magnitude of the velocity, or final speed, of the car after the collision? .540 final speed = m/s Incorrect 5 0.1 0.2 Time (s) Force (N)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter11: Collisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 40PQ: Initially, ball 1 rests on an incline of height h, and ball 2 rests on an incline of height h/2 as...
Related questions
Question
A 0.250 kg toy car moving with a speed of 0.820 m/s collides with a wall. The figure shows the force exerted on the car by the wall over the course of the collision.
What is the magnitude of the velocity, or final speed, of the car after the collision?
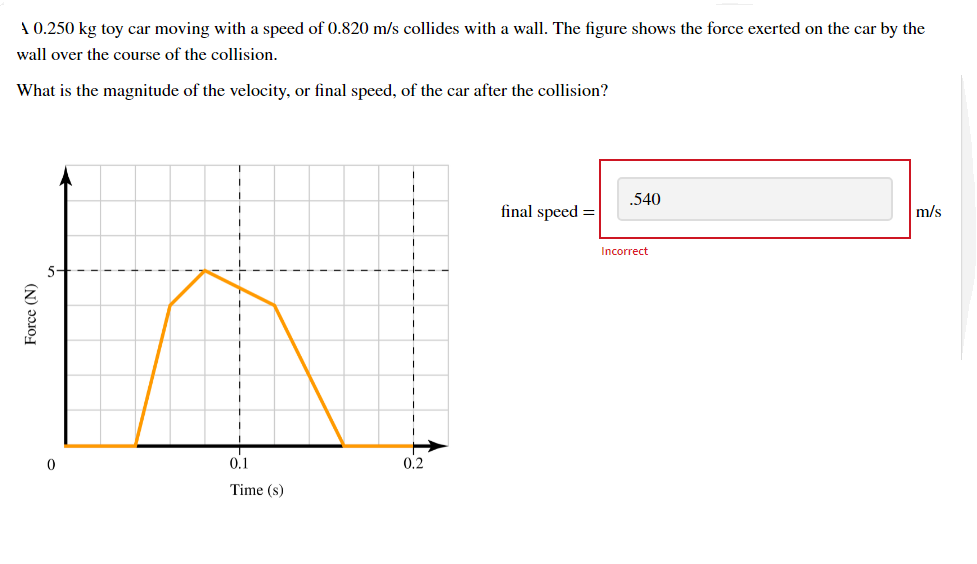
Transcribed Image Text:A 0.250 kg toy car moving with a speed of 0.820 m/s collides with a wall. The figure shows the force exerted on the car by the
wall over the course of the collision.
What is the magnitude of the velocity, or final speed, of the car after the collision?
.540
final speed =
m/s
Incorrect
0.1
0.2
Time (s)
Force (N)

Transcribed Image Text:When the car collides with the wall, the
wall exerts a backwards force on the
car. The effect of this force is to change
the momentum of the car. You are given
a graph which shows the magnitude of
the force exerted by the wall on the car,
so you can determine the magnitude of
the change in the car's momentum.
The change in the car's momentum over
the course of the impact is equal to the
impulse imparted to the car by the wall.
The impulse can be found by measuring
the area under the force-time curve for
the interaction between the car and
wall. In this case, the area can be
determined by examining the graph, but
pay careful attention to the scales of
the axes.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning