A 0.747 mol sample of O₂ gas is confined in a 18.3 liter container at 25.9 °C. If the volume of the gas sample is increased to 36.6 L, holding the temperature constant, the pressure will decrease. Which of the following kinetic theory ideas apply? (Select all that apply.) At higher volumes molecules have lower average speeds. ✔With a larger volume to move in, the molecules hit the walls of the container less often. O With lower average speeds, on average the molecules hit the walls of the container with less force. O For a given gas at constant temperature, the force per collision is constant. Some other factor must cause the pressure decrease. None of the above.
Ideal and Real Gases
Ideal gases obey conditions of the general gas laws under all states of pressure and temperature. Ideal gases are also named perfect gases. The attributes of ideal gases are as follows,
Gas Laws
Gas laws describe the ways in which volume, temperature, pressure, and other conditions correlate when matter is in a gaseous state. The very first observations about the physical properties of gases was made by Robert Boyle in 1662. Later discoveries were made by Charles, Gay-Lussac, Avogadro, and others. Eventually, these observations were combined to produce the ideal gas law.
Gaseous State
It is well known that matter exists in different forms in our surroundings. There are five known states of matter, such as solids, gases, liquids, plasma and Bose-Einstein condensate. The last two are known newly in the recent days. Thus, the detailed forms of matter studied are solids, gases and liquids. The best example of a substance that is present in different states is water. It is solid ice, gaseous vapor or steam and liquid water depending on the temperature and pressure conditions. This is due to the difference in the intermolecular forces and distances. The occurrence of three different phases is due to the difference in the two major forces, the force which tends to tightly hold molecules i.e., forces of attraction and the disruptive forces obtained from the thermal energy of molecules.

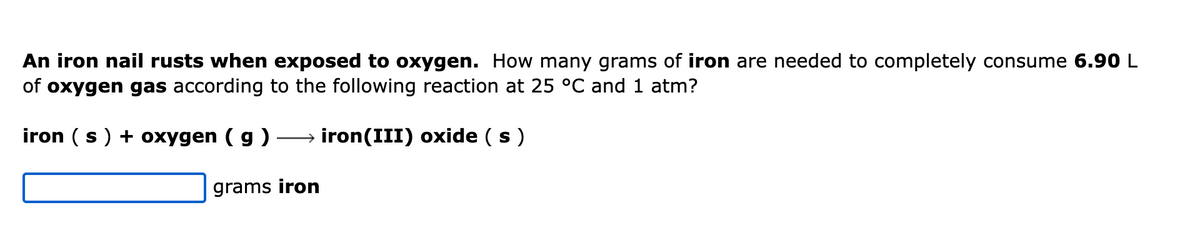
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps









