A 5cm by 5cm rectangular coil of wire with 500 turns carrying a current of 0.1 amos comprising the armature of an electric motor lies in the xy plane. The coil is subjected to a uniform magnetic field B with strength 0.05 Tesla in the z direction as shown in the figure. The armature is free to rotate without friction about the x axis with an assoxiated moment of inertia of 1 x 10^-2 kgm^2. Initially the armature is in
A 5cm by 5cm rectangular coil of wire with 500 turns carrying a current of 0.1 amos comprising the armature of an electric motor lies in the xy plane. The coil is subjected to a uniform magnetic field B with strength 0.05 Tesla in the z direction as shown in the figure. The armature is free to rotate without friction about the x axis with an assoxiated moment of inertia of 1 x 10^-2 kgm^2. Initially the armature is in
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Chapter3: Two-dimensional Kinematics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 64PE: (a) Use the distance and velocity data in Figure 3.64 to find the rate of expansion as a function of...
Related questions
Question
100%
A 5cm by 5cm rectangular coil of wire with 500 turns carrying a current of 0.1 amos comprising the armature of an electric motor lies in the xy plane. The coil is subjected to a uniform magnetic field B with strength 0.05 Tesla in the z direction as shown in the figure. The armature is free to rotate without friction about the x axis with an assoxiated moment of inertia of 1 x 10^-2 kgm^2. Initially the armature is in the (unstable) equilibriu, with magnetic moment m. antiparallel to B, but it begins to rotate after a slight nudge. What is the change in potential energy, and what is its rotation rate, when m is parallel to B?
Transcribed Image Text:Bb My Blackboard Content – Black X
Bb Homework11 (Spring 2021)(1). X
个)→ C
https://learn.unm.edu/bbcswebdav/pid-6786431-dt-content-rid-59937715_1/courses/51181.202110/Homework11 (Spring 2021)(1).pdf
...
Most Visited
Getting Started
Other Bookmarks
个↓
3 of 5
Automatic Zoom
3. What is the magnetic moment M of the wire loop in the previous problem
(magnitude and direction)? How much energy is required to flip the loop over?
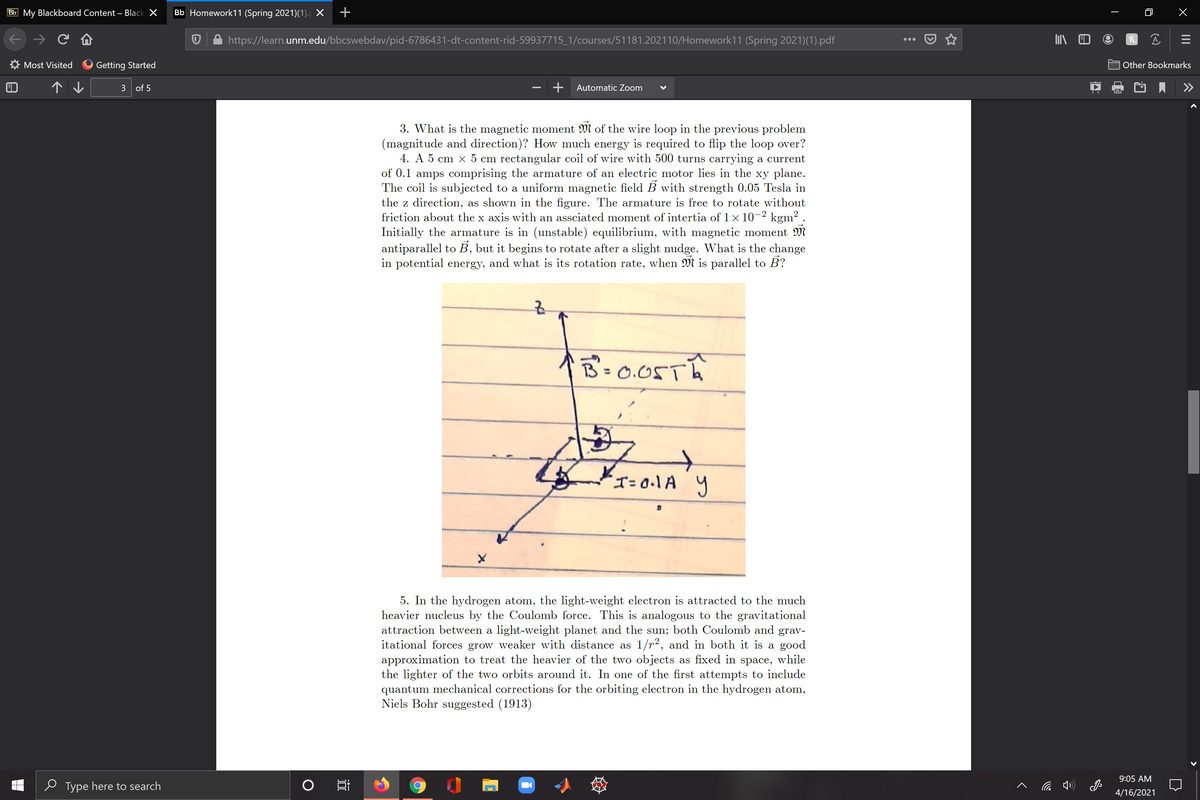
4. A 5 cm x 5 cm rectangular coil of wire with 500 turns carrying a current
of 0.1 amps comprising the armature of an electric motor lies in the xy plane.
The coil is subjected to a uniform magnetic field B with strength 0.05 Tesla in
the z direction, as shown in the figure. The armature is free to rotate without
friction about the x axis with an assciated moment of intertia of 1 x 10-2 kgm? .
Initially the armature is in (unstable) equilibrium, with magnetic moment M
antiparallel to B, but it begins to rotate after a slight nudge. What is the change
in potential energy, and what is its rotation rate, when M is parallel to B?
B'= 0.05TA
'T=0.1A y
5. In the hydrogen atom, the light-weight electron is attracted to the much
heavier nucleus by the Coulomb force. This is analogous to the gravitational
attraction between a light-weight planet and the sun; both Coulomb and grav-
itational forces grow weaker with distance as 1/r2, and in both it is a good
approximation to treat the heavier of the two objects as fixed in space, while
the lighter of the two orbits around it. In one of the first attempts to include
quantum mechanical corrections for the orbiting electron in the hydrogen atom,
Niels Bohr suggested (1913)
9:05 AM
e Type here to search
底 )
4/16/2021
II
近
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305960961
Author:
Michael A. Seeds, Dana Backman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305960961
Author:
Michael A. Seeds, Dana Backman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University