a) A box of mass, m, slides down an inclined plane that makes an angle 0 with the horizontal as shown in Figure 1. Find a differential equation for the velocity v(t) of the box at time t in each of the following three cases: i. No sliding friction and no air resistance. ii. With sliding friction and no air resistance. jii. With sliding friction and air resistance.
a) A box of mass, m, slides down an inclined plane that makes an angle 0 with the horizontal as shown in Figure 1. Find a differential equation for the velocity v(t) of the box at time t in each of the following three cases: i. No sliding friction and no air resistance. ii. With sliding friction and no air resistance. jii. With sliding friction and air resistance.
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter4: The Laws Of Motion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 25P: In Example 4.6, we investigated the apparent weight of a fish in an elevator. Now consider a 72.0-kg...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
100%
4 a)
i
ii
iii
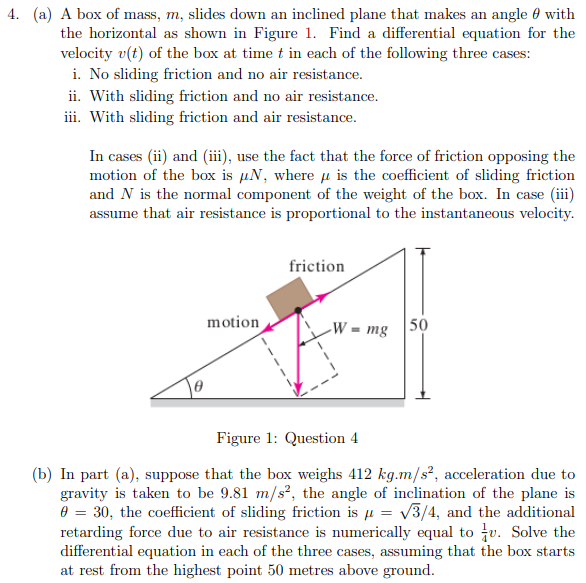
Transcribed Image Text:4. (a) A box of mass, m, slides down an inclined plane that makes an angle 0 with
the horizontal as shown in Figure 1. Find a differential equation for the
velocity v(t) of the box at time t in each of the following three cases:
i. No sliding friction and no air resistance.
ii. With sliding friction and no air resistance.
iii. With sliding friction and air resistance.
In cases (ii) and (iii), use the fact that the force of friction opposing the
motion of the box is µN, where u is the coefficient of sliding friction
and N is the normal component of the weight of the box. In case (iii)
assume that air resistance is proportional to the instantaneous velocity.
friction
motion
-W = mg |50
Figure 1: Question 4
(b) In part (a), suppose that the box weighs 412 kg.m/s², acceleration due to
gravity is taken to be 9.81 m/s², the angle of inclination of the plane is
0 = 30, the coefficient of sliding friction is µ = v3/4, and the additional
retarding force due to air resistance is numerically equal to u. Solve the
differential equation in each of the three cases, assuming that the box starts
at rest from the highest point 50 metres above ground.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning