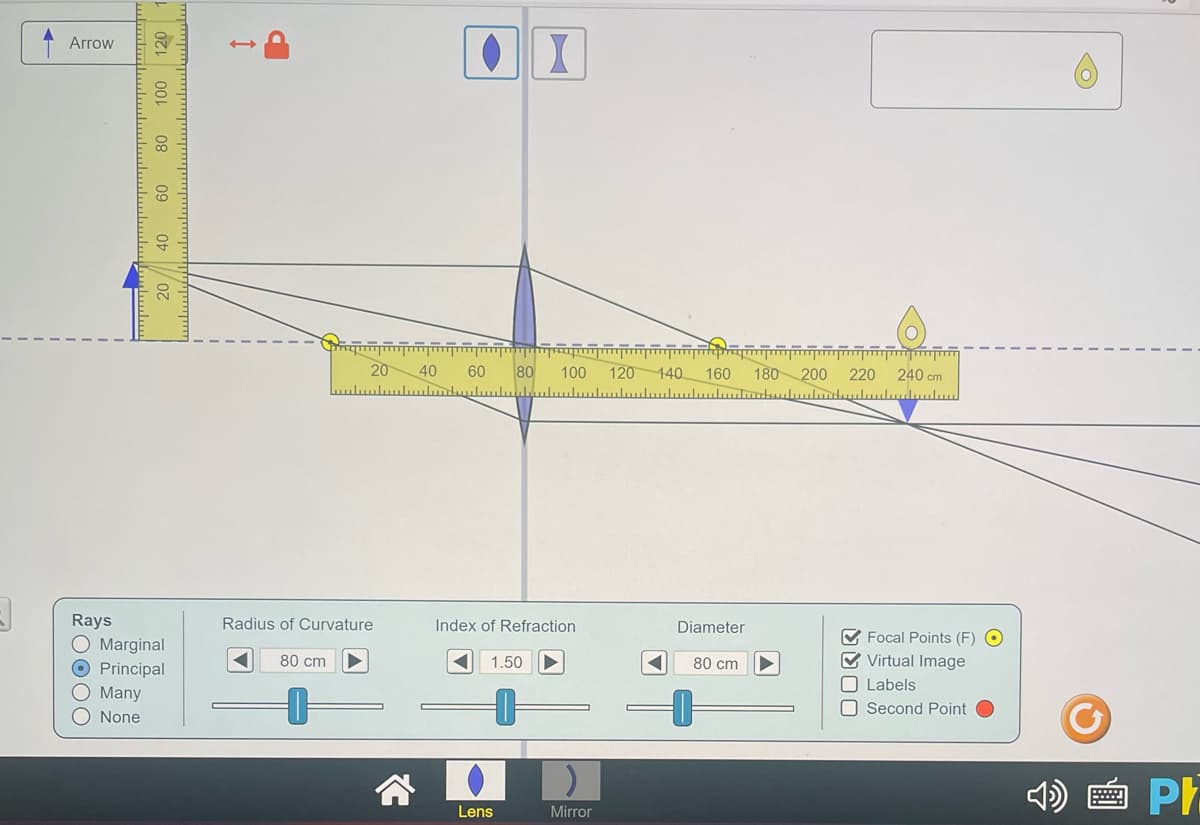
a) Based on your principal ray diagram, is the image virtual or real? Explain how you can tell. b) Based on your principal ray diagram, is the image upright or inverted? c) Based on your principal ray diagram, is the image larger or smaller than the object?
a) Based on your principal ray diagram, is the image virtual or real? Explain how you can tell. b) Based on your principal ray diagram, is the image upright or inverted? c) Based on your principal ray diagram, is the image larger or smaller than the object?
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter25: Reflection And Refraction Of Light
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4OQ
Related questions
Concept explainers
Applications Of Reflection Of Light
When a light ray (termed as the incident ray) hits a surface and bounces back (forms a reflected ray), the process of reflection of light has taken place.
Sign Convention for Mirrors
A mirror is made of glass that is coated with a metal amalgam on one side due to which the light ray incident on the surface undergoes reflection and not refraction.
Question
Please I need help with this lab
Transcribed Image Text:Arrow
120
O None
100
80
60
40
Rays
O Marginal
Principal
Many
20 40
Radius of Curvature
80 cm
ווןווווןווון
60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200
X
Index of Refraction
1.50
Lens
Mirror
Diameter
80 cm
וווןוווןווווןווון
220 240 cm
لسلسيلسسلسلين
Focal Points (F) O
Virtual Image
Labels
Second Point
Ph.

Transcribed Image Text:a) Based on your principal ray diagram, is the image virtual or real? Explain how
tell.
b) Based on your principal ray diagram, is the image upright or inverted?
you can
c) Based on your principal ray diagram, is the image larger or smaller than the object?
3) Your object distance is 240 cm, and your focal length is 80 cm. Use the thin-lens equation to
predict the theoretical location of the image di,theo. Show
your
work below.
di,theo =
4) Use the magnification equation to predict the theoretical magnification of the image. Show your
work below.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:
9781305079137
Author:
James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:
9781305079137
Author:
James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning