A block of mass m1 = 2.15 kg and a block of mass m2 = 6.10 kg are connected by a massless string over a pulley in the shape of a solid disk having radius R 0.250 m and mass M = 10.0 kg. The fixed, wedge-shaped ramp makes an angle of 0 = 30.0° as shown in the figure. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.360 for both blocks. Use g=9.8 m/s2. М, R (b) Determine the acceleration of the two blocks. (Enter the magnitude of the acceleration.) m/s2 (c) Determine the tensions in the string on both sides of the pulley. left of the pulley right of the pulley
A block of mass m1 = 2.15 kg and a block of mass m2 = 6.10 kg are connected by a massless string over a pulley in the shape of a solid disk having radius R 0.250 m and mass M = 10.0 kg. The fixed, wedge-shaped ramp makes an angle of 0 = 30.0° as shown in the figure. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.360 for both blocks. Use g=9.8 m/s2. М, R (b) Determine the acceleration of the two blocks. (Enter the magnitude of the acceleration.) m/s2 (c) Determine the tensions in the string on both sides of the pulley. left of the pulley right of the pulley
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter12: Rotation I: Kinematics And Dynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 53PQ: A square plate with sides 2.0 m in length can rotatearound an axle passingthrough its center of...
Related questions
Question
100%
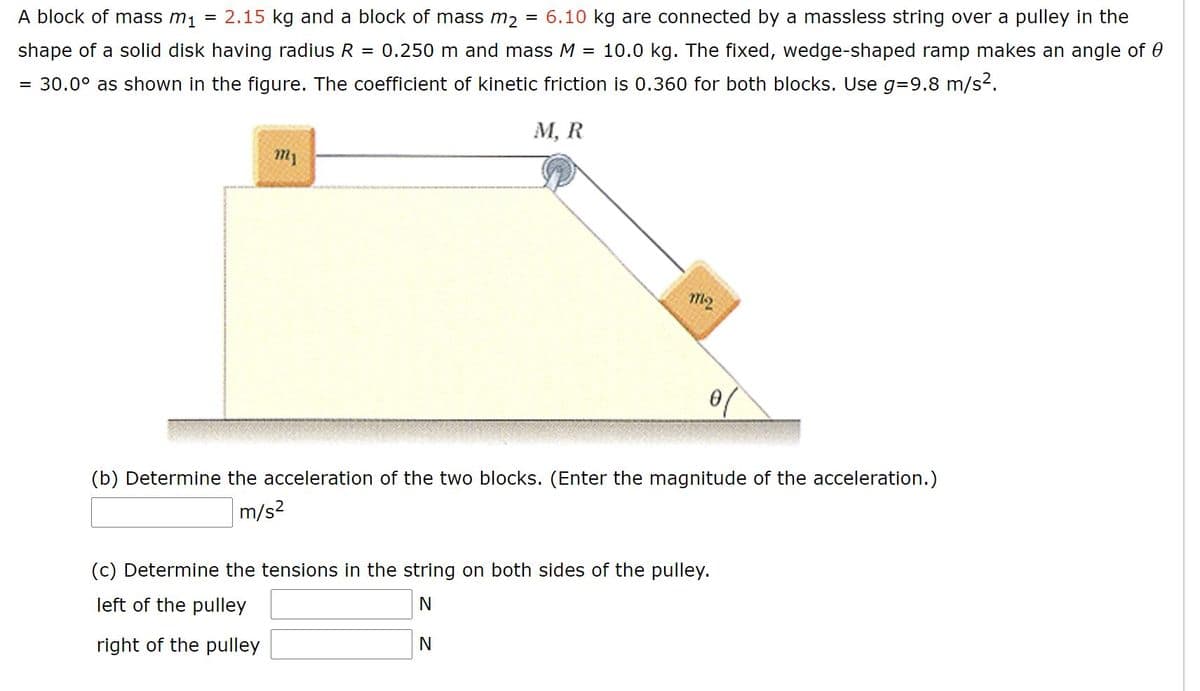
Transcribed Image Text:A block of mass m1
= 2.15 kg and a block of mass m, = 6.10 kg are connected by a massless string over a pulley in the
shape of a solid disk having radius R
= 0.250 m and mass M
= 10.0 kg. The fixed, wedge-shaped ramp makes an angle of 0
= 30.0° as shown in the figure. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.360 for both blocks. Use g=D9.8 m/s2.
М, R
m2
(b) Determine the acceleration of the two blocks. (Enter the magnitude of the acceleration.)
m/s2
(c) Determine the tensions in the string on both sides of the pulley.
left of the pulley
right of the pulley

Transcribed Image Text:A spool of thread consists of a cylinder of radius R1
7.2 cm with end caps of radius R2
= 9.0 cm as depicted in the end
view shown in the figure below. The mass of the spool, including the thread, is m = 180 g. The spool is placed on a rough,
horizontal surface so that it rolls without slipping when a force T = 0.450 N acting to the right is applied to the free end of
the thread. For the moment of inertia treat the spool as being a solid cylinder of radius R1, as the extended edges are thin
and therefore light.
\R2
R1
(a) What is the acceleration of the spool? Take positive to be to the right.
m/s2
(b) Determine the direction of the force of friction.
to the left
to the right
straight up
straight down
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning