A box with an open top has vertical sides, a square bottom, and a volume of 108 cubic meters. If the box has the least possible surface area, find its dimensions. Part 1: Find the surface area of the open box as a function of x and h, where x represents the length of the sides of the square base and h the height of the open box.. A(x, h) = Part 2: Find the volume of the open box as a function of x and h. Part 3: Find the value of h as a function of x, using the given value of the volume. Part 4: Rewrite the surface area of the open box as a function of x only. Part 5: Find the derivative of the surface area of the open box with respect to x. Part 6: Find the height and length values that minimize the surface area of the open box.
A box with an open top has vertical sides, a square bottom, and a volume of 108 cubic meters. If the box has the least possible surface area, find its dimensions. Part 1: Find the surface area of the open box as a function of x and h, where x represents the length of the sides of the square base and h the height of the open box.. A(x, h) = Part 2: Find the volume of the open box as a function of x and h. Part 3: Find the value of h as a function of x, using the given value of the volume. Part 4: Rewrite the surface area of the open box as a function of x only. Part 5: Find the derivative of the surface area of the open box with respect to x. Part 6: Find the height and length values that minimize the surface area of the open box.
Chapter4: Rational Functions And Conics
Section4.2: Graphs Of Rational Functions
Problem 81E: A page that is x inches wide and y inches high contains 30 square inches of print. The top and...
Related questions
Question
100%
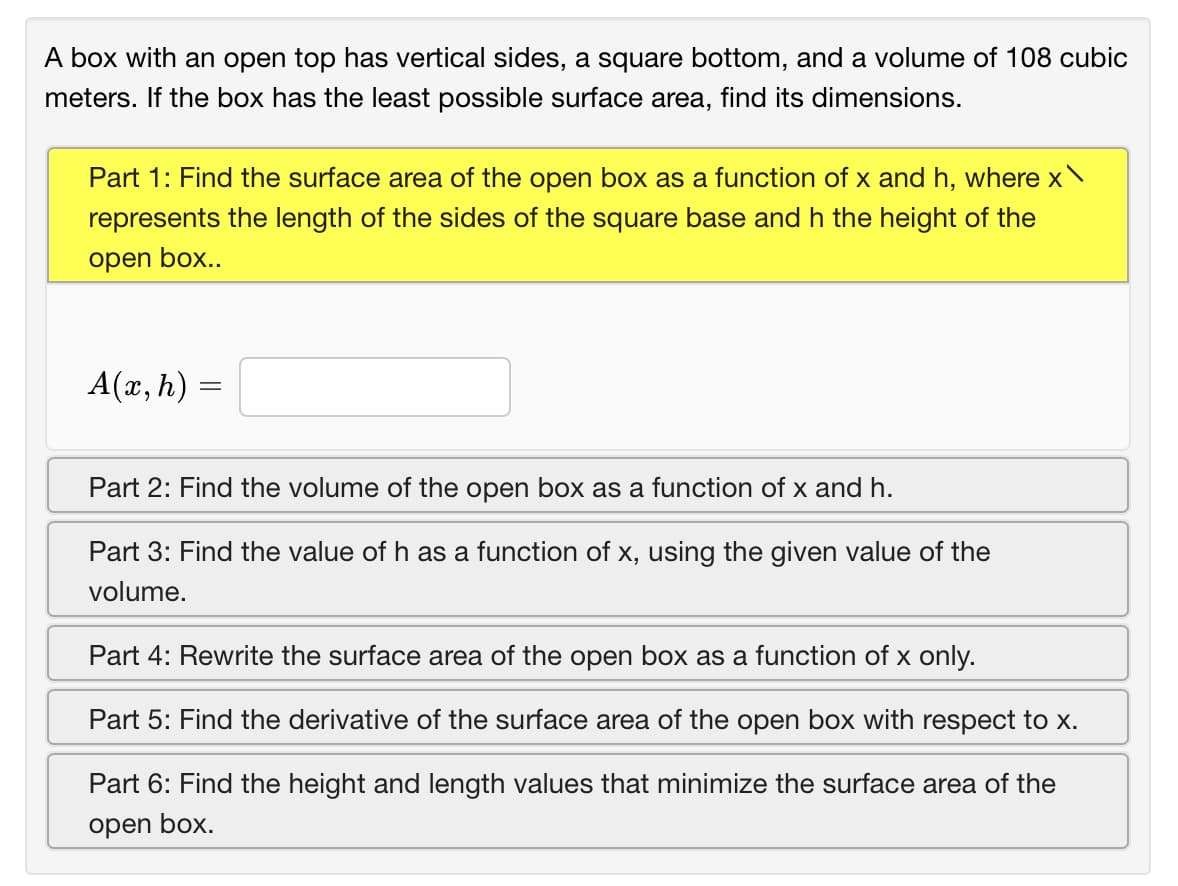
Transcribed Image Text:A box with an open top has vertical sides, a square bottom, and a volume of 108 cubic
meters. If the box has the least possible surface area, find its dimensions.
Part 1: Find the surface area of the open box as a function of x and h, where x
represents the length of the sides of the square base and h the height of the
open box..
A(x, h) =
Part 2: Find the volume of the open box as a function of x and h.
Part 3: Find the value of h as a function of x, using the given value of the
volume.
Part 4: Rewrite the surface area of the open box as a function of x only.
Part 5: Find the derivative of the surface area of the open box with respect to x.
Part 6: Find the height and length values that minimize the surface area of the
open box.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell