A calorimeter contains 30.0 mL of water at 14.0 °C When 1.70 g of X (a substance with a molar mass of 76.0 g/mol ) is added, it dissolves via the reaction X(s) + H2O(1)-X(aq) and the temperature of the solution increases to 30.0 "C. Calculate the enthalpy change, AH for this reaction per mole of X. Assume that the specific heat of the resulting solution is equal to that of water [4 18 J/(g- "C) that density of water is 1.00 g/mL, and that no heat is lost to the calorimeter itself, nor to the surroundings. Express the change in enthalpy in kilojoules per mole to three significant figures. > View Available Hint(s)
A calorimeter contains 30.0 mL of water at 14.0 °C When 1.70 g of X (a substance with a molar mass of 76.0 g/mol ) is added, it dissolves via the reaction X(s) + H2O(1)-X(aq) and the temperature of the solution increases to 30.0 "C. Calculate the enthalpy change, AH for this reaction per mole of X. Assume that the specific heat of the resulting solution is equal to that of water [4 18 J/(g- "C) that density of water is 1.00 g/mL, and that no heat is lost to the calorimeter itself, nor to the surroundings. Express the change in enthalpy in kilojoules per mole to three significant figures. > View Available Hint(s)
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter9: Energy And Chemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9.101PAE
Related questions
Question
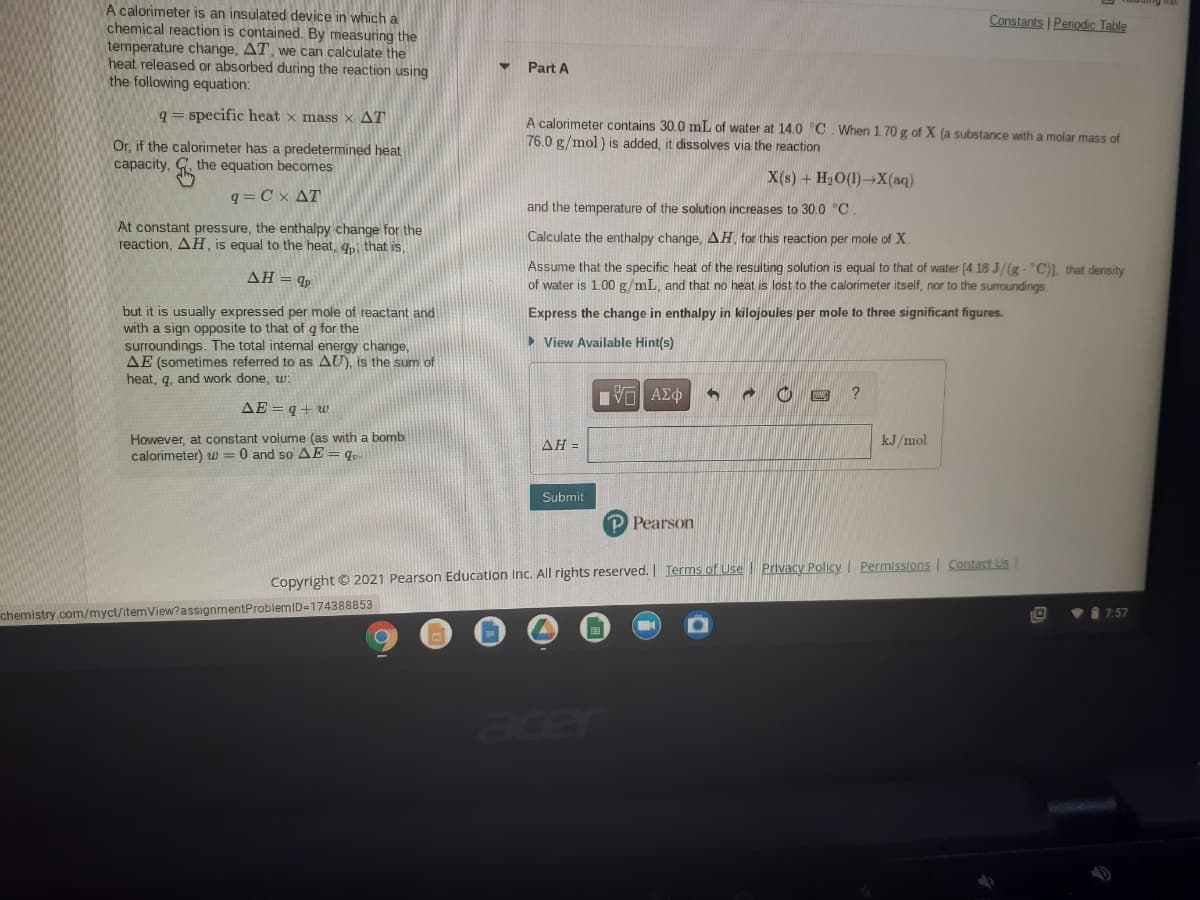
Transcribed Image Text:A calorimeter is an insulated device in which a
chemical reaction is contained. By measuring the
temperature change, AT, we can calculate the
heat released or absorbed during the reaction using
the following equation:
Constants | Periodic Table
Part A
q= specific heat x mass x AT
A calorimeter contains 30.0 mL of water at 14.0 °C. When 1.70 g of X (a substance with a molar mass of
76.0 g/mol) is added, it dissolves via the reaction
Or, if the calorimeter has a predetermined heat
capacity, G. the equation becomes
X(s) + H2O(1)→X(aq)
q= Cx AT
and the temperature of the solution increases to 30.0 °C.
At constant pressure, the enthalpy change for the
reaction, AH, is equal to the heat, qi that is,
Calculate the enthalpy change, AH for this reaction per mole of X.
Assume that the specific heat of the resulting solution is equal to that of water [4.18 J/(g- "C)), that density
of water is 1.00 g/mL, and that no heat is lost to the calorimeter itself, nor to the surroundings
ΔΗp
but it is usually expressed per mole of reactant and
with a sign opposite to that of q for the
surroundings. The total internal energy change,
AE (sometimes referred to as AU), is the sum of
heat, q, and work done, w:
Express the change in enthalpy in kilojoules per mole to three significant figures.
> View Available Hint(s)
AE =q+uw
However, at constant volume (as with a bomb
calorimeter) w = 0 and so AE= q«
ΔΗ-
kJ/mol
Submit
P Pearson
Copyright © 2021 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Pollcy | Permissions I Contact Us
chemistry.com/myct/itemView?assignmentProblemID=174388853
7:57
acer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618562763
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin College Div