A certain catalyzed reaction is known to have an activation energy E=58.0 kJ/mol. Furthermore, the rate of this reaction is measured at 284. K and found to be 2.2 × 10 M/s. Use this information to answer the questions in the table below. (You may need to use the scrollbar to see all the choices.) Suppose the concentrations of all reactants is kept the same, but the temperature is raised by 5% from 284. K to 298. K. How will the rate of the reaction change? Suppose the concentrations of all reactants is kept the same, but the catalyst is removed, which has the effect of raising the activation energy by 5%, from 58.0 kJ/mol to 60.9 kJ/mol. How will the rate of the reaction change? The rate will The rate will ✓ choose one stay the same rise about 5% rise more than 5% rise less than 5% fall about 5% fall more than 5% fall less than 5% choose one
A certain catalyzed reaction is known to have an activation energy E=58.0 kJ/mol. Furthermore, the rate of this reaction is measured at 284. K and found to be 2.2 × 10 M/s. Use this information to answer the questions in the table below. (You may need to use the scrollbar to see all the choices.) Suppose the concentrations of all reactants is kept the same, but the temperature is raised by 5% from 284. K to 298. K. How will the rate of the reaction change? Suppose the concentrations of all reactants is kept the same, but the catalyst is removed, which has the effect of raising the activation energy by 5%, from 58.0 kJ/mol to 60.9 kJ/mol. How will the rate of the reaction change? The rate will The rate will ✓ choose one stay the same rise about 5% rise more than 5% rise less than 5% fall about 5% fall more than 5% fall less than 5% choose one
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter11: Chemical Kinetics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11.30PAE: The rate of the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, depends on the concentration of iodide ion...
Related questions
Question
Options are same for both.
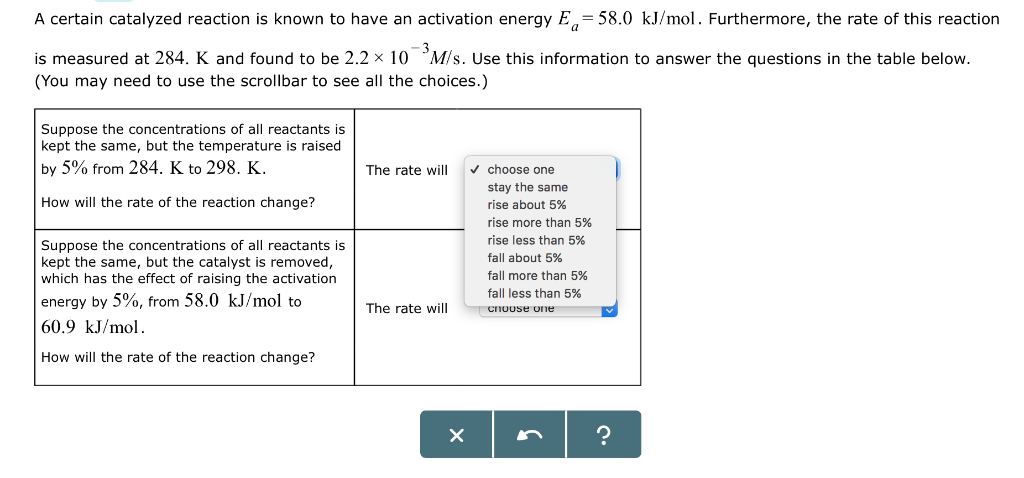
Transcribed Image Text:A certain catalyzed reaction is known to have an activation energy E=58.0 kJ/mol. Furthermore, the rate of this reaction
is measured at 284. K and found to be 2.2 × 10 M/s. Use this information to answer the questions in the table below.
(You may need to use the scrollbar to see all the choices.)
Suppose the concentrations of all reactants is
kept the same, but the temperature is raised
by 5% from 284. K to 298. K.
How will the rate of the reaction change?
Suppose the concentrations of all reactants is
kept the same, but the catalyst is removed,
which has the effect of raising the activation
energy by 5%, from 58.0 kJ/mol to
60.9 kJ/mol.
How will the rate of the reaction change?
The rate will
The rate will
X
✓ choose one
stay the same
rise about 5%
rise more than 5%
rise less than 5%
fall about 5%
fall more than 5%
fall less than 5%
choose one
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
