A chem ngineer is studying the following reaction: 4 HCl(g) + O₂(g) → 2 H₂O(g) +2C1₂(g) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant Kp for this reaction is 0.17. The engineer charges ("fills") four reaction vessels with hydrogen chloride and oxygen, and lets the reaction begin. She then measures the composition of the mixture inside each vessel from time to time. Her first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time she measures the compositions. reaction vessel A B U с compound H CI 0₂ H₂O C1₂ H CI 0₂ H₂O C1₂ H CI 0₂ H₂O C1₂ pressure 6.10 atm 5.69 atm 9.07 atm 4.08 atm. 6.65 atm. 5.36 atm 7.21 atm 2.91 atm 4.19 atm. 4.74 atm 8.43 atm. 4.13 atm expected change in pressure Ot increase Ot increase ↑ Ot increase Ot increase Ot increase Ot increase Ot increase Ot increase ↑ increase Ot increase Ot increase Ot increase decrease O decrease O decrease Odecrease decrease Odecrease Odecrease Odecrease Odecrease Odecrease decrease Odecrease O(no change) O(no change) O(no change) O(no change) (no change) O(no change) O (no change) (no change) O (no change) O(no change) O(no change) (no change)
A chem ngineer is studying the following reaction: 4 HCl(g) + O₂(g) → 2 H₂O(g) +2C1₂(g) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant Kp for this reaction is 0.17. The engineer charges ("fills") four reaction vessels with hydrogen chloride and oxygen, and lets the reaction begin. She then measures the composition of the mixture inside each vessel from time to time. Her first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time she measures the compositions. reaction vessel A B U с compound H CI 0₂ H₂O C1₂ H CI 0₂ H₂O C1₂ H CI 0₂ H₂O C1₂ pressure 6.10 atm 5.69 atm 9.07 atm 4.08 atm. 6.65 atm. 5.36 atm 7.21 atm 2.91 atm 4.19 atm. 4.74 atm 8.43 atm. 4.13 atm expected change in pressure Ot increase Ot increase ↑ Ot increase Ot increase Ot increase Ot increase Ot increase Ot increase ↑ increase Ot increase Ot increase Ot increase decrease O decrease O decrease Odecrease decrease Odecrease Odecrease Odecrease Odecrease Odecrease decrease Odecrease O(no change) O(no change) O(no change) O(no change) (no change) O(no change) O (no change) (no change) O (no change) O(no change) O(no change) (no change)
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Chapter14: Chemical Equilibirum
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14.109QP: Gaseous acetic acid molecules have a certain tendency to form dimers. (A dimer is a molecule formed...
Related questions
Question
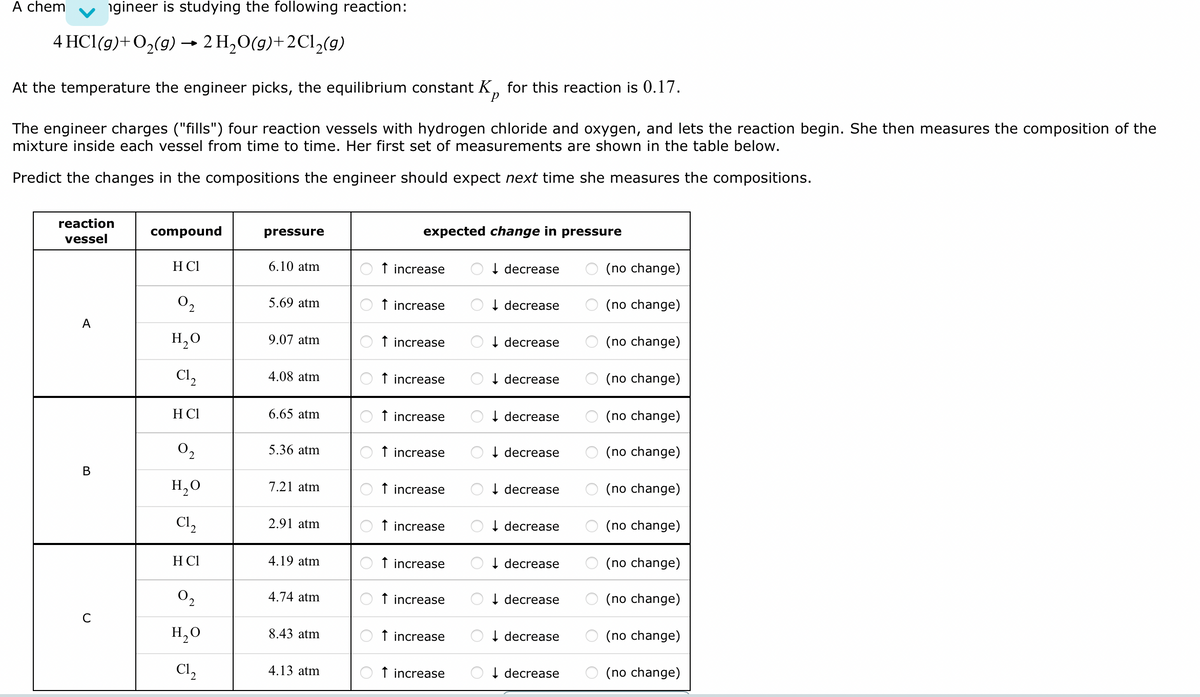
Transcribed Image Text:A chem ngineer is studying the following reaction:
4 HCl(g) + O₂(g) → 2H₂O(g) + 2Cl₂(g)
At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.17.
P
The engineer charges ("fills") four reaction vessels with hydrogen chloride and oxygen, and lets the reaction begin. She then measures the composition of the
mixture inside each vessel from time to time. Her first set of measurements are shown in the table below.
Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time she measures the compositions.
reaction
vessel
A
B
C
compound
HCl
02
H₂O
C1₂
H CI
H₂O
C1₂
H Cl
0₂
H₂O
C12
pressure
6.10 atm
5.69 atm
9.07 atm
4.08 atm
6.65 atm
5.36 atm
7.21 atm
2.91 atm
4.19 atm
4.74 atm
8.43 atm
4.13 atm
expected change in pressure
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↓ decrease
decrease
decrease
decrease
↓ decrease
↓ decrease
↓ decrease
↓ decrease
↓ decrease
↓ decrease
↓ decrease
↓ decrease
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 13 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
