A circle C has center at the origin and radius 9. Another circle K has a diameter with one end at the origin and the other end at the point (0, 15). The circles C and K intersect in two points. Let P be the point of intersection of C and K which lies in the first quadrant. Let (r, 0) be the polar coordinates of P, chosen so that r is positive and 0 < e < 2. Find r and 0.
A circle C has center at the origin and radius 9. Another circle K has a diameter with one end at the origin and the other end at the point (0, 15). The circles C and K intersect in two points. Let P be the point of intersection of C and K which lies in the first quadrant. Let (r, 0) be the polar coordinates of P, chosen so that r is positive and 0 < e < 2. Find r and 0.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter11: Topics From Analytic Geometry
Section11.5: Polar Coordinates
Problem 101E
Related questions
Question
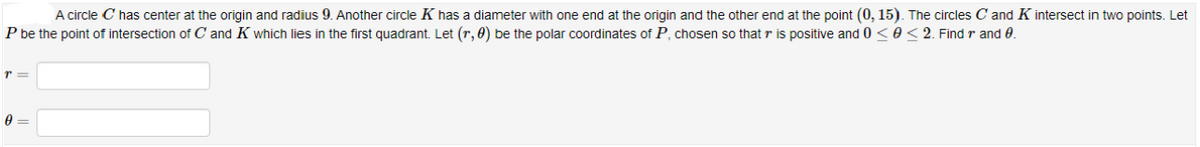
Transcribed Image Text:A circle C has center at the origin and radius 9. Another circle K has a diameter with one end at the origin and the other end at the point (0, 15). The circles C and K intersect in two points. Let
P be the point of intersection of C and K which lies in the first quadrant. Let (r, 0) be the polar coordinates of P, chosen so that r is positive and 0 < e < 2. Find r and 0.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,