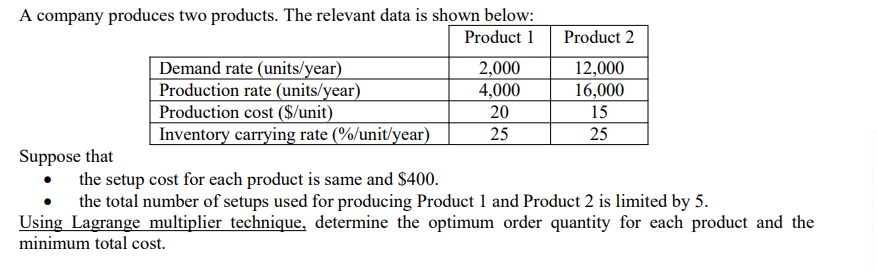
A company produces two products. The relevant data is shown below: Product 1 Suppose that Demand rate (units/year) Production rate (units/year) Production cost ($/unit) Inventory carrying rate (%/unit/year) 2,000 4,000 20 25 Product 2 12,000 16,000 15 25 the setup cost for each product is same and $400. the total number of setups used for producing Product 1 and Product 2 is limited by 5. Using Lagrange multiplier technique, determine the optimum order quantity for each product and the minimum total cost.
Q: Johnson Industries received a contract to develop and produce four high-Intensity long-distance…
A: Given, First unit took T1 = 2000 hours Purchased $39000 worth Second unit took T2 = 1500 hours…
Q: How are the five product-flow processes different and similar?
A: The five product-flow processes are the following: 1. Continues flow 2. Assembly line 3. Batch flow…
Q: explain these please Strengths High-quality and pure spring water source from a natural spring…
A: Strengths of a company or product that provides bottled spring water in Grenada, a Caribbean…
Q: Use Prim's algorithm to find the minimum weighted spanning tree for the graph in figure K. Fill in…
A: Minimum spanning tree: Graph/route containing all the vertices (nodes) with minimum number of edges…
Q: 4. Discuss Porter's five generic strategies.
A: Organizations work to develop a competitive edge in operations management so they may distinguish…
Q: George Kyparisis makes bowling balls in his Miami plant. With recent increases in his costs, he has…
A: Given that: Last year Now Cost per Input Unit Units Produced 1000 1000 Labor 300 275 12…
Q: CASE STUDY P & B Energy Systems Limited (P & B), a wholly owned Zambian company proposes to…
A: In order to alleviate the power constraints brought on by reduced water levels at Kariba Dam and…
Q: Learn the differences between functional, matrix, and project structures. Specify the effects of…
A: Functional, matrix, and project structures are three common organizational structures used in…
Q: Professional integrity in project management is crucial.
A: Integrity can be defined as a framework or an item that is the quality or condition total; solid…
Q: Coordination is a continuous activity in Management’. Explain.
A: Coordination is the process of synchronizing and harmonizing the activities of different…
Q: Using the five (5) key elements of leadership that are: Leaders-Followers, Influence, Organizational…
A: In a competitive business environment, compelling leadership is a fundamental necessity in order to…
Q: What are common operational metrics utilized by healthcare organizations? Where do they come from…
A: Common operational metrics utilized by healthcare organizations include: Length of stay (LOS):…
Q: You may need to use the appropriate technology to answer this question. Blue Lagoon is a contractor…
A: First we will calculate some details. Those are given in below tables along with formulas: Formula:…
Q: A time standard was set as 0.20 hour per unit based on the 50th, unit produced. Assume the task has…
A: Learning Rate = 90% Time Standard set as 0.20 hours based on 50th unit
Q: Trucks using a single-server loading dock have a mean arrival rate of 14 per day. The…
A: The M/M/1 queuing model, where arrivals follow a Poisson process at a rate of 14 per day and service…
Q: 1. Develop a WBS with at least two levels for a project (e.g., moving away to college, registering…
A: As the name says work breakdown structure can be defined as the representation that divides the work…
Q: How can CRM, ERP, and EAI help businesses?
A: Customers continued patronage is crucial to any company's ability to keep its profit margins stable…
Q: 4. A project has the following activities, durations, costs, and precedence relationships: Immediate…
A: Given-
Q: Outline if adaptive or predictive projects have been more fruitful in the long run, and provide…
A: The project management strategy adopted is one of several variables that affect a project's success.…
Q: There are 11 project selection methods which are: Benefit measurement methods Benefit/cost ratio…
A: The selection of a project selection method depends on the project's specific characteristics and…
Q: Table below provides the demand forecast and production day information for an aggregate plan.…
A: Find the Given details below: Month January February March April May June Demand Forecast 3,000…
Q: Do you think that the organisation is solely responsible for the career management of its employees?…
A: Organizational career management refers to the procedures and methods used by businesses to assist…
Q: Explain what you mean by the terms "functional," "matrix," and "project." Describe the effects of…
A: The terms "functional," "matrix," and "project" are different types of organizational structures…
Q: What are the four helpful principles for effective negotiation? Explain and expand.
A: Effective negotiation is the process of two or more parties coming to a mutually acceptable…
Q: Solve this LP max z = 2x12x2 + 3x3 s.t. 2x1 + x2 + x3 x1 - x2 + x3 1, 2, 3 urs ≤1 ≤0 Set up the…
A: To set up the initial simplex tableau, we first convert the maximization problem into a minimization…
Q: Explain the steps that John can take to become more socially responsible?
A: John has an obligation to his community and environment as a business owner.
Q: As the production planner for Xiangling Hu Products, Inc., you have been given a bill of material…
A: Given Product structure-
Q: Provide an explanation for the operation of predictive analytics and a scenario in which it might be…
A: Predictive analytics is the utilization of data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning…
Q: Consider a production line with five stations in serial. The stations have the following process…
A: Find the Calculation methods below: Capacity = Process timeNumber of machines Bottleneck = Slowest…
Q: What InfoSec duties should a smaller organisation with three full-time and two or three part-time…
A: Each organization's total security posture must include information security (InfoSec) as a critical…
Q: Bjorn and Thor are plumbers who have been scheduled to work on the construction of a new school…
A: Given Gantt Chart-
Q: Talk about basic supply chain measures.
A: Any firm that relies on suppliers to provide products and services to its consumers must perform the…
Q: The '% of total sales from products introduced in the last 12 months' is a metric used to…
A: Option a. = It is incorrect option because demand flexibility is relative with production of the…
Q: (b) Suppose now that all is as in the previous question but that only 320L of Important Chemical A…
A: Linear Programming is a mathematical and statistical tool that is used in operations management to…
Q: ) Calculate the three point moving averages (quarters) and seasonal variation for the above data b)…
A: “Since you have posted multiple questions, we will provide the solution only to the specified sub…
Q: The following time series represents the number of automobiles sold by a car dealership each of the…
A: Given-
Q: time it took to complete several recent jobs. Some of his workers are very optimistic completion…
A: Formula used-Expected time =a+4m+b6Variance =b-a236
Q: The New England Cheese Company produces two cheese spreads by blending mild cheddar cheese with…
A: 1 pound = 16 ounces Regular container has 80% mild cheddar and 20% extra sharp Cost for regular…
Q: Can we identify a specific area of difficulty being tackled by the workflow management tool?
A: The design, planning, execution, and control of company operations are all part of operations…
Q: As part of a major plant renovation project, the industrial engineering department has been asked to…
A: Given-
Q: Explain the SAP ERP system's approach to distinguishing between tasks, jobs, and employees.
A: SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system is a software platform developed by SAP SE, a German…
Q: The production process shown below consists of five stages. The numbers in parentheses are the times…
A: CONCEPT- A bottleneck is a place of blockage in a production framework that eases back or stops…
Q: 1. Draw the Activity on Node network. 2. Perform the CPM calculations using the forward and backward…
A: As per Bartleby guidelines, we can only solve the first three subparts of one question at a…
Q: Now that you have learned how to conduct a Root Cause Analysis (RCA), please perform one for the…
A: Disclaimer: A generalized answer format is provided. As it is not possible to submit a template or…
Q: Which of the following allows researchers to collect primary data via online infrastructures? OA…
A: The data collection infrastructure gathers execution profiling data for appropriate applications and…
Q: Lack of Intellectual Property (IP) protection hurts International Firms in form of lost sales, less…
A: Intellectual property rights (IPR) is a significant aspect to businesses and specially for those who…
Q: Base: enter your response here units (enter your response as a whole number). Spring: enter your…
A: Given Product Structure:
Q: You are the owner of Orion Project Services Ltd (OPS). Your company has won the bid to execute a…
A: Customer relationship management (CRM) systems have developed into a crucial tool for managing…
Q: How would you recommend establishing a structure to accommodate workers who often travel from one…
A: In today's globalized and interconnected business environment, many employees frequently travel from…
Q: On page 32, Alex and his team learn some things about robot efficiencies. Rogo notes, "To give the…
A: Given data: Capacity per hour=25 parts Cost per hour=$20
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

- Assume the demand for a companys drug Wozac during the current year is 50,000, and assume demand will grow at 5% a year. If the company builds a plant that can produce x units of Wozac per year, it will cost 16x. Each unit of Wozac is sold for 3. Each unit of Wozac produced incurs a variable production cost of 0.20. It costs 0.40 per year to operate a unit of capacity. Determine how large a Wozac plant the company should build to maximize its expected profit over the next 10 years.The Pigskin Company produces footballs. Pigskin must decide how many footballs to produce each month. The company has decided to use a six-month planning horizon. The forecasted monthly demands for the next six months are 10,000, 15,000, 30,000, 35,000, 25,000, and 10,000. Pigskin wants to meet these demands on time, knowing that it currently has 5000 footballs in inventory and that it can use a given months production to help meet the demand for that month. (For simplicity, we assume that production occurs during the month, and demand occurs at the end of the month.) During each month there is enough production capacity to produce up to 30,000 footballs, and there is enough storage capacity to store up to 10,000 footballs at the end of the month, after demand has occurred. The forecasted production costs per football for the next six months are 12.50, 12.55, 12.70, 12.80, 12.85, and 12.95, respectively. The holding cost incurred per football held in inventory at the end of any month is 5% of the production cost for that month. (This cost includes the cost of storage and also the cost of money tied up in inventory.) The selling price for footballs is not considered relevant to the production decision because Pigskin will satisfy all customer demand exactly when it occursat whatever the selling price is. Therefore. Pigskin wants to determine the production schedule that minimizes the total production and holding costs. Can you guess the results of a sensitivity analysis on the initial inventory in the Pigskin model? See if your guess is correct by using SolverTable and allowing the initial inventory to vary from 0 to 10,000 in increments of 1000. Keep track of the values in the decision variable cells and the objective cell.The Pigskin Company produces footballs. Pigskin must decide how many footballs to produce each month. The company has decided to use a six-month planning horizon. The forecasted monthly demands for the next six months are 10,000, 15,000, 30,000, 35,000, 25,000, and 10,000. Pigskin wants to meet these demands on time, knowing that it currently has 5000 footballs in inventory and that it can use a given months production to help meet the demand for that month. (For simplicity, we assume that production occurs during the month, and demand occurs at the end of the month.) During each month there is enough production capacity to produce up to 30,000 footballs, and there is enough storage capacity to store up to 10,000 footballs at the end of the month, after demand has occurred. The forecasted production costs per football for the next six months are 12.50, 12.55, 12.70, 12.80, 12.85, and 12.95, respectively. The holding cost incurred per football held in inventory at the end of any month is 5% of the production cost for that month. (This cost includes the cost of storage and also the cost of money tied up in inventory.) The selling price for footballs is not considered relevant to the production decision because Pigskin will satisfy all customer demand exactly when it occursat whatever the selling price is. Therefore. Pigskin wants to determine the production schedule that minimizes the total production and holding costs. As indicated by the algebraic formulation of the Pigskin model, there is no real need to calculate inventory on hand after production and constrain it to be greater than or equal to demand. An alternative is to calculate ending inventory directly and constrain it to be nonnegative. Modify the current spreadsheet model to do this. (Delete rows 16 and 17, and calculate ending inventory appropriately. Then add an explicit non-negativity constraint on ending inventory.)
- The Pigskin Company produces footballs. Pigskin must decide how many footballs to produce each month. The company has decided to use a six-month planning horizon. The forecasted monthly demands for the next six months are 10,000, 15,000, 30,000, 35,000, 25,000, and 10,000. Pigskin wants to meet these demands on time, knowing that it currently has 5000 footballs in inventory and that it can use a given months production to help meet the demand for that month. (For simplicity, we assume that production occurs during the month, and demand occurs at the end of the month.) During each month there is enough production capacity to produce up to 30,000 footballs, and there is enough storage capacity to store up to 10,000 footballs at the end of the month, after demand has occurred. The forecasted production costs per football for the next six months are 12.50, 12.55, 12.70, 12.80, 12.85, and 12.95, respectively. The holding cost incurred per football held in inventory at the end of any month is 5% of the production cost for that month. (This cost includes the cost of storage and also the cost of money tied up in inventory.) The selling price for footballs is not considered relevant to the production decision because Pigskin will satisfy all customer demand exactly when it occursat whatever the selling price is. Therefore. Pigskin wants to determine the production schedule that minimizes the total production and holding costs. Modify the Pigskin model so that there are eight months in the planning horizon. You can make up reasonable values for any extra required data. Dont forget to modify range names. Then modify the model again so that there are only four months in the planning horizon. Do either of these modifications change the optima] production quantity in month 1?Lemingtons is trying to determine how many Jean Hudson dresses to order for the spring season. Demand for the dresses is assumed to follow a normal distribution with mean 400 and standard deviation 100. The contract between Jean Hudson and Lemingtons works as follows. At the beginning of the season, Lemingtons reserves x units of capacity. Lemingtons must take delivery for at least 0.8x dresses and can, if desired, take delivery on up to x dresses. Each dress sells for 160 and Hudson charges 50 per dress. If Lemingtons does not take delivery on all x dresses, it owes Hudson a 5 penalty for each unit of reserved capacity that is unused. For example, if Lemingtons orders 450 dresses and demand is for 400 dresses, Lemingtons will receive 400 dresses and owe Jean 400(50) + 50(5). How many units of capacity should Lemingtons reserve to maximize its expected profit?Based on Zangwill (1992). Murray Manufacturingruns a day shift and a night shift. Regardless of thenumber of units produced, the only production costduring a shift is a setup cost. It costs $8000 to run theday shift and $4500 to run the night shift. Demand forthe next two days is as follows: day 1, 2000; night 1,3000; day 2, 2000; night 2, 3000. It costs $1 per unitto hold a unit in inventory for a shift.a. Determine a production schedule that minimizesthe sum of setup and inventory costs. All demandmust be met on time. (Note: Not all shifts have tobe run.)b. After listening to a seminar on the virtues of theJapanese theory of production, Murray has cut thesetup cost of its day shift to $1000 per shift and thesetup cost of its night shift to $3500 per shift. Nowdetermine a production schedule that minimizes thesum of setup and inventory costs. All demand mustbe met on time. Show that the decrease in setupcosts has actually raised the average inventorylevel. Is this reasonable?
- (Need both parts a and b) During the next four months, a customer requires, respectively, 500, 650, 1000, and 700 units of a commodity, and no backlogging is allowed (that is, the customer’s requirements must be met on time). Production costs are $50, $80, $40, and $70 per unit during these months. The storage cost from one month to the next is $20 per unit (assessed on ending inventory). It is estimated that each unit on hand at the end of month 4 can be sold for $60. Assume there is no beginning inventory. A. What is the objective function in this problem? B. What are the constraints in this problem? Write algebraic expressions for eachA company produces three different products; x,y, and z. For the production of 1 unit of product x, 1 unit of A and 1 unit of B are used as input. 1 unit of A and 2 units of B are used to produce 1 unit of product y. To produce 1 unit of product z, only 1 unit of A is used. The company holds 40 units of A and 20 units of B periodically in total. By the way, the company can not produce product y more than the twice of product z. On the other hand, the sale price of 1 unit of product x is 10 TL, product y is 15 TL and product z is 12 TL. Furthermore, the cost of 1 unit of product x is 8 TL, product y is 9 TL and product z is 7 TL. According to above information, what should be the company’s optimal product mix to maximize its profit? Construct the problem as a Linear programming model. Solve the above problem by using Simplex Method.A company produces three types of items. A singlemachine is used to produce the three items on a cyclicalbasis. The company has the policy that every item isproduced once during each cycle, and it wants to determinethe number of production cycles per year that will minimizethe sum of holding and setup costs (no shortages areallowed). The following data are given:Pi number of units of product i that could be producedper year if the machine were entirely devoted toproducing product iDi annual demand for product iKi cost of setting up production for product ihi cost of holding one unit of product i in inventoryfor one yeara Suppose there are N cycles per year. Assuming thatduring each cycle, a fraction N1of all demand for eachproduct is met, determine the annual holding cost andthe annual setup cost.b Let qi* be the number of units of product i producedduring each cycle. Determine the optimal value of N(call it N*) and qi*. c Let EROQi be the optimal production run size forproduct i if…

