A continues fractionation column, operation at atmospheric pressure, is to be designed to separate a mixture containing 27% CS₂ and 73% CCl4 into an overhead product containing 95% CS2 and a waste of 95% CCl4 (all mole percent). If the reflux ratio is taken as 3.16, using the data below. Determine the number of plates required in the following cases: - a-Feed inlet at T = 290 k b- Feed inlet at T = 336 k Given the following data:- cpr = 225.42 kJ/kmol.k, TB.p=336k, λ = 25900 kJ/kmol. y% 8.23 15.55 26.6 33.2 49.5 63.4 74.7 82.9 87.8 93.1 x% 2.96 6.15 11.06 14.35 25.85 53.18 66.3 75.75 86.2 39
A continues fractionation column, operation at atmospheric pressure, is to be designed to separate a mixture containing 27% CS₂ and 73% CCl4 into an overhead product containing 95% CS2 and a waste of 95% CCl4 (all mole percent). If the reflux ratio is taken as 3.16, using the data below. Determine the number of plates required in the following cases: - a-Feed inlet at T = 290 k b- Feed inlet at T = 336 k Given the following data:- cpr = 225.42 kJ/kmol.k, TB.p=336k, λ = 25900 kJ/kmol. y% 8.23 15.55 26.6 33.2 49.5 63.4 74.7 82.9 87.8 93.1 x% 2.96 6.15 11.06 14.35 25.85 53.18 66.3 75.75 86.2 39
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
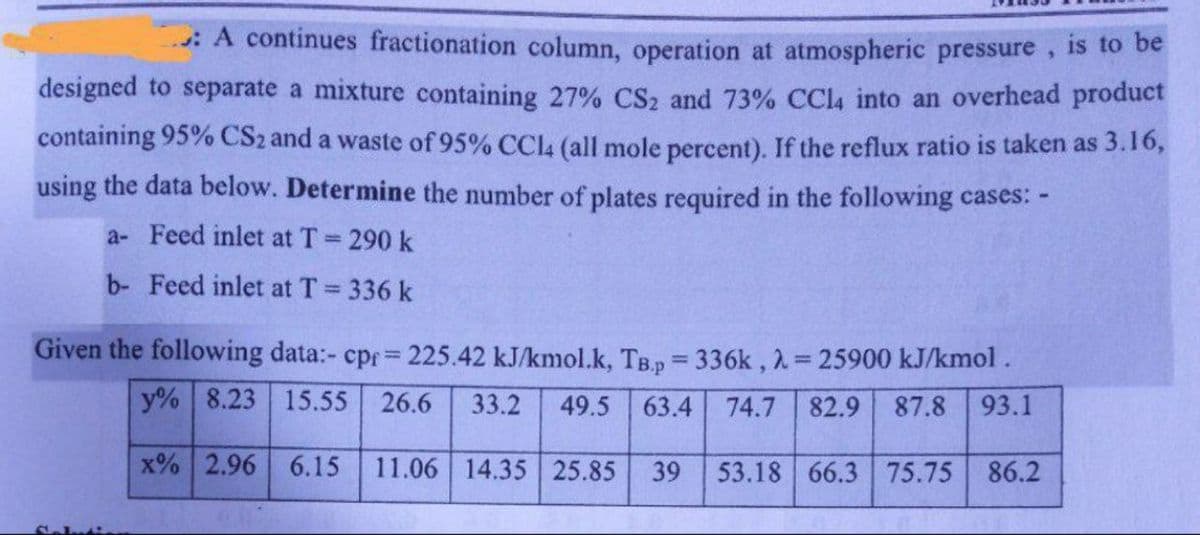
Transcribed Image Text:A continues fractionation column, operation at atmospheric pressure, is to be
designed to separate a mixture containing 27% CS₂ and 73% CCl4 into an overhead product
containing 95% CS2 and a waste of 95% CCl4 (all mole percent). If the reflux ratio is taken as 3.16,
using the data below. Determine the number of plates required in the following cases: -
a-Feed inlet at T = 290 k
b- Feed inlet at T = 336 k
Given the following data:- cpr = 225.42 kJ/kmol.k, TB.p=336k, λ = 25900 kJ/kmol.
63.4 74.7 82.9 87.8 93.1
y% 8.23 15.55 26.6 33.2 49.5
x% 2.96 6.15 11.06 14.35 25.85
39 53.18 66.3 75.75 86.2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The