A copper specimen of Young's modulus 130 GPa is subjected to a tensile test in a laboratory. The following data are obtained. The initial length of the specimen = 80 mm Yield stress = 130 N/mm² Fracture stress = 145 N/mm² The initial diameter of the specimen = 6 mm Ultimate stress = 210 N/mm² The percentage of elongation = 40 % The percentage of reduction in area = 45% Determine the following. i) The elongation of the specimen at load 2.75 kN (2 Marks) ii) Load at yielding (1 Mark) iv) Final length (1 Mark) iii) Maximum load (1 Mark) v) Final diameter (2 Marks)
A copper specimen of Young's modulus 130 GPa is subjected to a tensile test in a laboratory. The following data are obtained. The initial length of the specimen = 80 mm Yield stress = 130 N/mm² Fracture stress = 145 N/mm² The initial diameter of the specimen = 6 mm Ultimate stress = 210 N/mm² The percentage of elongation = 40 % The percentage of reduction in area = 45% Determine the following. i) The elongation of the specimen at load 2.75 kN (2 Marks) ii) Load at yielding (1 Mark) iv) Final length (1 Mark) iii) Maximum load (1 Mark) v) Final diameter (2 Marks)
Oh no! Our experts couldn't answer your question.
Don't worry! We won't leave you hanging. Plus, we're giving you back one question for the inconvenience.
Submit your question and receive a step-by-step explanation from our experts in as fast as 30 minutes.
You have no more questions left.
Message from our expert:
It looks like you may have submitted a graded question that, per our Honor Code, experts cannot answer. We've credited a question to your account.
Your Question:
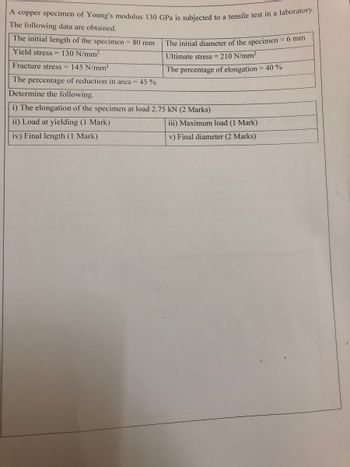
Transcribed Image Text:A copper specimen of Young's modulus 130 GPa is subjected to a tensile test in a laboratory.
The following data are obtained.
The initial length of the specimen = 80 mm
Yield stress = 130 N/mm²
Fracture stress = 145 N/mm²
The initial diameter of the specimen = 6 mm
Ultimate stress = 210 N/mm²
The percentage of elongation = 40 %
The percentage of reduction in area = 45%
Determine the following.
i) The elongation of the specimen at load 2.75 kN (2 Marks)
ii) Load at yielding (1 Mark)
iv) Final length (1 Mark)
iii) Maximum load (1 Mark)
v) Final diameter (2 Marks)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY
