Exercise 4 - Floating-point Number Comparison Add a new class to the Lab2 project called FloatEqu. This should implement a program that performs the following: a) Declare a double variable and initialize it to (1.0/10) * (1.0/10) Declare another double variable and initialize it to (1.0/100) Insert an if . else statement and print out "EQUAL" if both variables are equal (use ==) and "NOT EQUAL" otherwise. Run the program and check the output. Is it what you would expect? b) Modify the program by adding an if . else statement to determine if the variables are approximately equal, using the approach discussed in the lecture. That is, take the absolute value of the difference between the two numbers, and check if it is lower than the TOLARANCE value (some very small number). The TOLARANCE should be a constant set at the beginning of the program, like this: final double TOLARANCE = 0.000001; The keywordfinal makes it a constant, which means Java will make sure we don't accidentally change the value. Note: to take the absolute value of a number, use Math.abs ()
Exercise 4 - Floating-point Number Comparison Add a new class to the Lab2 project called FloatEqu. This should implement a program that performs the following: a) Declare a double variable and initialize it to (1.0/10) * (1.0/10) Declare another double variable and initialize it to (1.0/100) Insert an if . else statement and print out "EQUAL" if both variables are equal (use ==) and "NOT EQUAL" otherwise. Run the program and check the output. Is it what you would expect? b) Modify the program by adding an if . else statement to determine if the variables are approximately equal, using the approach discussed in the lecture. That is, take the absolute value of the difference between the two numbers, and check if it is lower than the TOLARANCE value (some very small number). The TOLARANCE should be a constant set at the beginning of the program, like this: final double TOLARANCE = 0.000001; The keywordfinal makes it a constant, which means Java will make sure we don't accidentally change the value. Note: to take the absolute value of a number, use Math.abs ()
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Chapter1: Computer Networks And The Internet
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem R1RQ: What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end...
Related questions
Question
Use java.
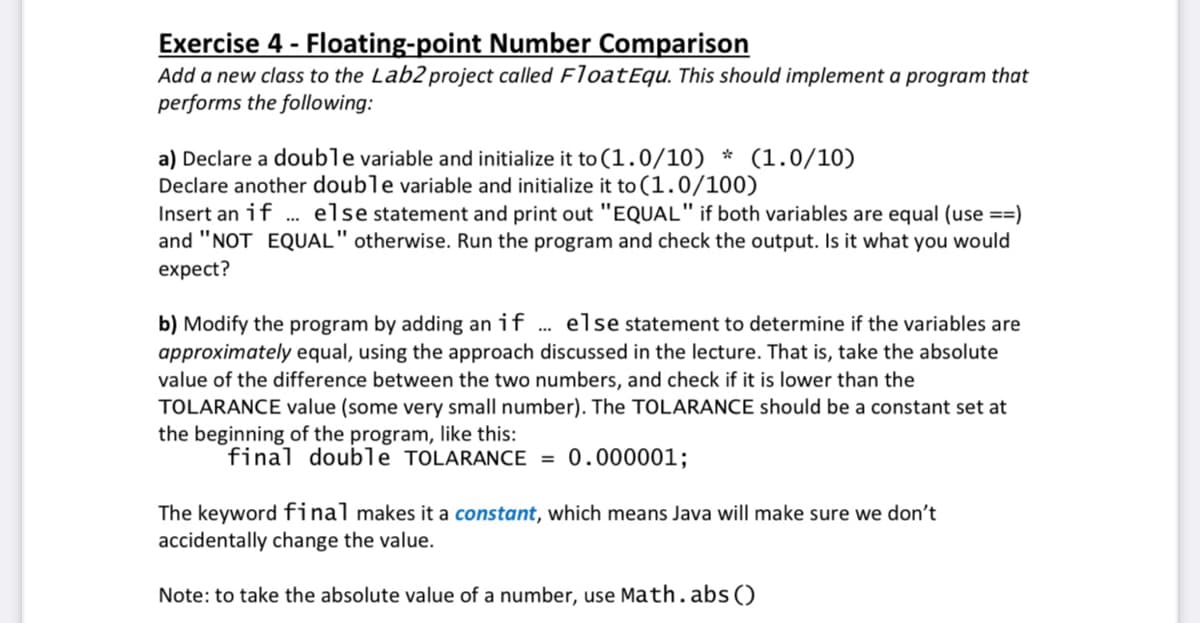
Transcribed Image Text:Exercise 4 - Floating-point Number Comparison
Add a new class to the Lab2 project called FloatEqu. This should implement a program that
performs the following:
a) Declare a double variable and initialize it to (1.0/10) * (1.0/10)
Declare another double variable and initialize it to (1.0/100)
Insert an if . else statement and print out "EQUAL" if both variables are equal (use ==)
and "NOT EQUAL" otherwise. Run the program and check the output. Is it what you would
expect?
b) Modify the program by adding an if
approximately equal, using the approach discussed in the lecture. That is, take the absolute
value of the difference between the two numbers, and check if it is lower than the
TOLARANCE value (some very small number). The TOLARANCE should be a constant set at
the beginning of the program, like this:
else statement to determine if the variables are
..
final double TOLARANCE = 0.000001;
The keyword final makes it a constant, which means Java will make sure we don't
accidentally change the value.
Note: to take the absolute value of a number, use Math.abs ()
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093422
Author:
Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133750423
Author:
VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:
Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781119368830
Author:
FITZGERALD
Publisher:
WILEY