A flexible cable suspended between two vertical supports is hanging under its own weight. The weight of a horizontal roadbed is distributed evenly along the x-axis with the density p = 0.1 lb/ft. The coordinate system is chosen so that the y-axis passes through the lowest point P₁ and the x-axis is a = 2 ft below P₁. If the absolute value of tension force in the cable at point P₁ is T = 3.5, then the initial value problem that governs the shape of the cable is (Use the notation dy/dx for the first derivative) d'y dx² y(0) = (0) = The solution of this problem is y = y(x), where y(x) =
A flexible cable suspended between two vertical supports is hanging under its own weight. The weight of a horizontal roadbed is distributed evenly along the x-axis with the density p = 0.1 lb/ft. The coordinate system is chosen so that the y-axis passes through the lowest point P₁ and the x-axis is a = 2 ft below P₁. If the absolute value of tension force in the cable at point P₁ is T = 3.5, then the initial value problem that governs the shape of the cable is (Use the notation dy/dx for the first derivative) d'y dx² y(0) = (0) = The solution of this problem is y = y(x), where y(x) =
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
ChapterA: Appendix
SectionA.2: Geometric Constructions
Problem 9P: A soda can is made from 40 square inches of aluminum. Let x denote the radius of the top of the can,...
Related questions
Question
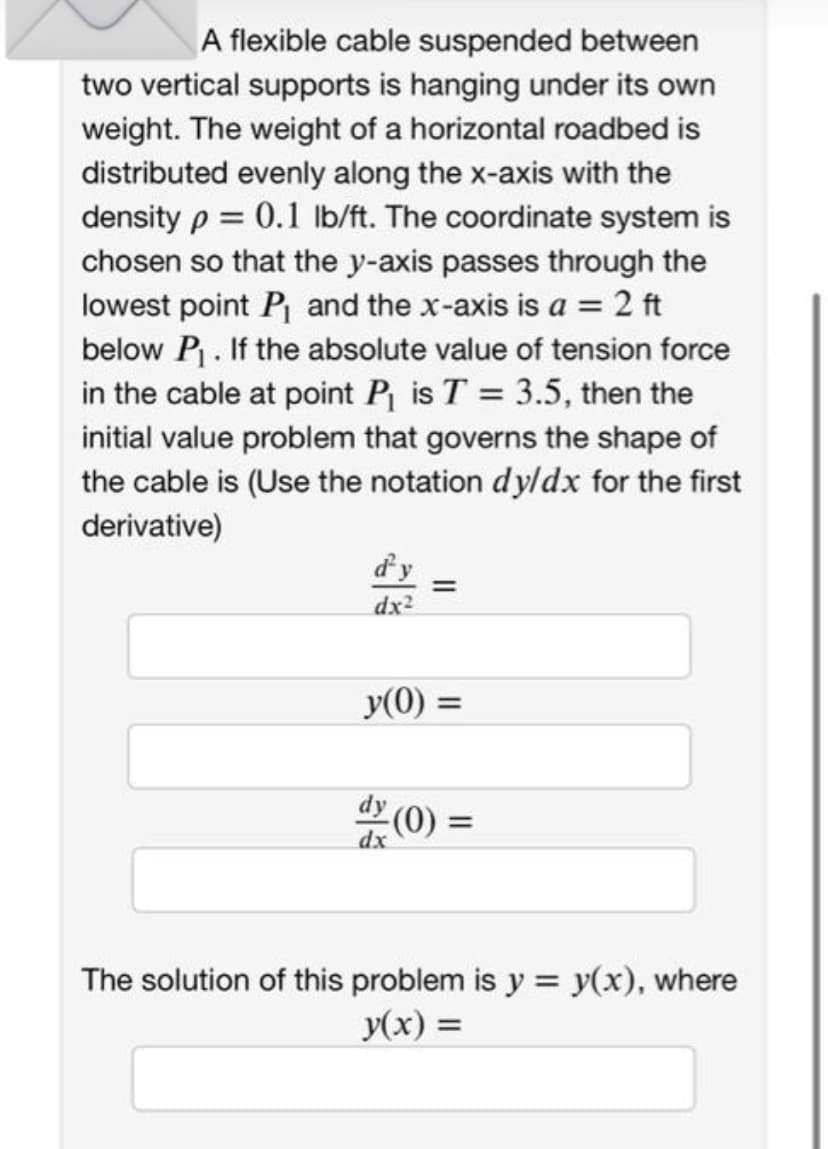
Transcribed Image Text:A flexible cable suspended between
two vertical supports is hanging under its own
weight. The weight of a horizontal roadbed is
distributed evenly along the x-axis with the
density p = 0.1 lb/ft. The coordinate system is
chosen so that the y-axis passes through the
lowest point P₁ and the x-axis is a = 2 ft
below P₁. If the absolute value of tension force
in the cable at point P₁ is T = 3.5, then the
initial value problem that governs the shape of
the cable is (Use the notation dy/dx for the first
derivative)
d'y =
dx²
y(0) =
(0) =
The solution of this problem is y = y(x), where
y(x) =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning