A Geiger-Mueller tube is a radiation detector that consists of a closed, hol- low, metal cylinder (the cathode) of inner radius r, and a coaxial cylindri- cal wire (the anode) of radius r, (Fig. P24.42a). The charge per unit length on the anode is A, and the charge per unit length on the cathode is -A. A gas fills the space between the electrodes. When the tube is in use (for example, in measuring radioactivity from fruit in Fig. P24.42b) and a high-energy elementary particle passes through this space, it can ionize an atom of the gas. The strong electric field makes the resulting ion and electron accelerate in opposite directions. They strike other mole- cules of the gas to ionize them, producing an avalanche of electrical discharge. The pulse of electric current between the wire and the cylinder is counted by an external circuit. (a) Show that the magnitude of the electric potential differ- ence between the wire and the cylinder is AV= 2k Aln (b) Show that the magnitude of the electric field in the space between cathode and anode is AV E = In (r. /r.) (7) where r is the distance from the axis of the anode to the point where the field is to be calculated. Cathode Anode a Figure P24.42 wellphoto/Shutterstock
A Geiger-Mueller tube is a radiation detector that consists of a closed, hol- low, metal cylinder (the cathode) of inner radius r, and a coaxial cylindri- cal wire (the anode) of radius r, (Fig. P24.42a). The charge per unit length on the anode is A, and the charge per unit length on the cathode is -A. A gas fills the space between the electrodes. When the tube is in use (for example, in measuring radioactivity from fruit in Fig. P24.42b) and a high-energy elementary particle passes through this space, it can ionize an atom of the gas. The strong electric field makes the resulting ion and electron accelerate in opposite directions. They strike other mole- cules of the gas to ionize them, producing an avalanche of electrical discharge. The pulse of electric current between the wire and the cylinder is counted by an external circuit. (a) Show that the magnitude of the electric potential differ- ence between the wire and the cylinder is AV= 2k Aln (b) Show that the magnitude of the electric field in the space between cathode and anode is AV E = In (r. /r.) (7) where r is the distance from the axis of the anode to the point where the field is to be calculated. Cathode Anode a Figure P24.42 wellphoto/Shutterstock
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter19: Electric Forces And Electric Fields
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 18P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:A Geiger-Mueller tube is a radiation
detector that consists of a closed, hol-
low, metal cylinder (the cathode) of
inner radius r, and a coaxial cylindri-
cal wire (the anode) of radius r, (Fig.
P24.42a). The charge per unit length
on the anode is A, and the charge per
unit length on the cathode is -A. A
gas fills the space between the electrodes. When the tube is
in use (for example, in measuring radioactivity from fruit in
Fig. P24.42b) and a high-energy elementary particle passes
through this space, it can ionize an atom of the gas. The
strong electric field makes the resulting ion and electron
accelerate in opposite directions. They strike other mole-
cules of the gas to ionize them, producing an avalanche of
electrical discharge. The pulse of electric current between
the wire and the cylinder is counted by an external circuit.
(a) Show that the magnitude of the electric potential differ-
ence between the wire and the cylinder is
AV= 2k Aln
(b) Show that the magnitude of the electric field in the
space between cathode and anode is
AV
E =
In (r. /r.) (7)
where r is the distance from the axis of the anode to the
point where the field is to be calculated.
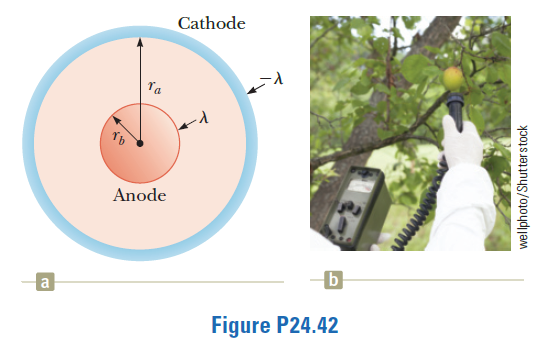
Transcribed Image Text:Cathode
Anode
a
Figure P24.42
wellphoto/Shutterstock
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning