A) He might be more likely heterozygous black B He might be more likely homozygous brown C) He must be heterozygous brown. D) He must be homozygous black E He must be homozygous brown 2-11 "Dumpy" is a commonly used mutant phenotype in the nematode wom C. elegans. Two "Dumpy individuals are crossed to each other and this cross produces 210 "Dumpy" and 68 wild-type individuals. If one of the "Dumpy" individuals used in this cros5 was mated with a wild-type, what ratio of "Dumpy" wild-type would we observe in the offspring? A) 0:1 B) 1:0 C) 1:1 D) 1:3 E) 3:1 2-12 If genes assort independently, a testcrossed dihybrid characteristically produces progeny phenotypes in the ratio: A) 1:1 B) 1:1:1:1 c) 1:2:1 D) 3:1 E) 9:3:3:1 2-13 A fish of genotype a/a; B/b is crossed to a fish whose genotype is 4/a; B/b. What proportion of the progeny will be heterozygous for at least one of the genes? (Assume independent assortment.) A) 1/8 B) 1/4 C) 1/2 D) 5/8 E) 3/4 2-14 In hogs, a dominant allele B results in a white belt around the body. At a separate locus the dominant allele S causes fusion of the two parts of the normallly cloven hoof resulting in a condition known as syndactyly. A belted syndactylous sow was crossed to an unbelted cloven-hoofed boar, and in the litter there were: 25% belted syndactylous 25% belted cloven 25% unbelted syndactylous 25% unbelted cloven The genotypes of the parents can best be represented as: A) B/B;S/SX bbs/s B) B/b;S/s X bb;S/S C) B/b:S/s X B/B;s/s D) b/b;S/s X B/bs/s E) B/b;S/s X b/b;s/s 2-15 In the cross between a female A/a B/b;c/cD/dele and male A/a,b/b;C/c D/d;e/e, what proportion of the progeny will be phenotypically identical to the female parent? (Assume independent assortment of all genes and complete dominance.) A) 1/16 B) 9/64 C) 3/16 D) 9/16 E) 3/8 2-16 Huntington's disease is an autosomal dominant trait. Given the pedigree below, use H to represent dominant, h to represent recessive, answer the following questions d. 1956 1960 O D d. 1988 d. 1990 14 15 13, 16 19 II d. 1972 10 11 12 (1) What is IV2's genotype? (2) What is the probability of Il being homozygous, assuming no mutation? (3) What is III15's genotype? (4) What is the probability of II15 and II16 have the same genotype? (5) What is IV9's genotype? (6) Knowing IV9 has Huntington's disease, what is the probability of IV9 being homozygous? (7) IfIV3 and IV9 have children what is the probability of havinga child without Huntington's disease?
A) He might be more likely heterozygous black B He might be more likely homozygous brown C) He must be heterozygous brown. D) He must be homozygous black E He must be homozygous brown 2-11 "Dumpy" is a commonly used mutant phenotype in the nematode wom C. elegans. Two "Dumpy individuals are crossed to each other and this cross produces 210 "Dumpy" and 68 wild-type individuals. If one of the "Dumpy" individuals used in this cros5 was mated with a wild-type, what ratio of "Dumpy" wild-type would we observe in the offspring? A) 0:1 B) 1:0 C) 1:1 D) 1:3 E) 3:1 2-12 If genes assort independently, a testcrossed dihybrid characteristically produces progeny phenotypes in the ratio: A) 1:1 B) 1:1:1:1 c) 1:2:1 D) 3:1 E) 9:3:3:1 2-13 A fish of genotype a/a; B/b is crossed to a fish whose genotype is 4/a; B/b. What proportion of the progeny will be heterozygous for at least one of the genes? (Assume independent assortment.) A) 1/8 B) 1/4 C) 1/2 D) 5/8 E) 3/4 2-14 In hogs, a dominant allele B results in a white belt around the body. At a separate locus the dominant allele S causes fusion of the two parts of the normallly cloven hoof resulting in a condition known as syndactyly. A belted syndactylous sow was crossed to an unbelted cloven-hoofed boar, and in the litter there were: 25% belted syndactylous 25% belted cloven 25% unbelted syndactylous 25% unbelted cloven The genotypes of the parents can best be represented as: A) B/B;S/SX bbs/s B) B/b;S/s X bb;S/S C) B/b:S/s X B/B;s/s D) b/b;S/s X B/bs/s E) B/b;S/s X b/b;s/s 2-15 In the cross between a female A/a B/b;c/cD/dele and male A/a,b/b;C/c D/d;e/e, what proportion of the progeny will be phenotypically identical to the female parent? (Assume independent assortment of all genes and complete dominance.) A) 1/16 B) 9/64 C) 3/16 D) 9/16 E) 3/8 2-16 Huntington's disease is an autosomal dominant trait. Given the pedigree below, use H to represent dominant, h to represent recessive, answer the following questions d. 1956 1960 O D d. 1988 d. 1990 14 15 13, 16 19 II d. 1972 10 11 12 (1) What is IV2's genotype? (2) What is the probability of Il being homozygous, assuming no mutation? (3) What is III15's genotype? (4) What is the probability of II15 and II16 have the same genotype? (5) What is IV9's genotype? (6) Knowing IV9 has Huntington's disease, what is the probability of IV9 being homozygous? (7) IfIV3 and IV9 have children what is the probability of havinga child without Huntington's disease?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Chapter1: The Human Body: An Orientation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:A) He might be more likely heterozygous black
B He might be more likely homozygous brown
C) He must be heterozygous brown.
D) He must be homozygous black
E He must be homozygous brown
2-11 "Dumpy" is a commonly used mutant phenotype in the nematode wom C. elegans. Two "Dumpy
individuals are crossed to each other and this cross produces 210 "Dumpy" and 68 wild-type individuals. If
one of the "Dumpy" individuals used in this cros5 was mated with a wild-type, what ratio of "Dumpy"
wild-type would we observe in the offspring?
A) 0:1 B) 1:0 C) 1:1 D) 1:3 E) 3:1
2-12 If genes assort independently, a testcrossed dihybrid characteristically produces progeny
phenotypes in the ratio:
A) 1:1 B) 1:1:1:1 c) 1:2:1 D) 3:1 E) 9:3:3:1
2-13 A fish of genotype a/a; B/b is crossed to a fish whose genotype is 4/a; B/b. What proportion of the
progeny will be heterozygous for at least one of the genes? (Assume independent assortment.)
A) 1/8 B) 1/4 C) 1/2 D) 5/8 E) 3/4
2-14 In hogs, a dominant allele B results in a white belt around the body. At a separate locus the dominant
allele S causes fusion of the two parts of the normallly cloven hoof resulting in a condition known as
syndactyly. A belted syndactylous sow was crossed to an unbelted cloven-hoofed boar, and in the litter
there were:
25% belted syndactylous
25% belted cloven
25% unbelted syndactylous
25% unbelted cloven
The genotypes of the parents can best be represented as:
A) B/B;S/SX bbs/s B) B/b;S/s X bb;S/S C) B/b:S/s X B/B;s/s D) b/b;S/s X B/bs/s
E) B/b;S/s X b/b;s/s
2-15 In the cross between a female A/a B/b;c/cD/dele and male A/a,b/b;C/c D/d;e/e, what proportion of
the progeny will be phenotypically identical to the female parent? (Assume independent assortment of all
genes and complete dominance.)
Transcribed Image Text:A) 1/16 B) 9/64 C) 3/16 D) 9/16 E) 3/8
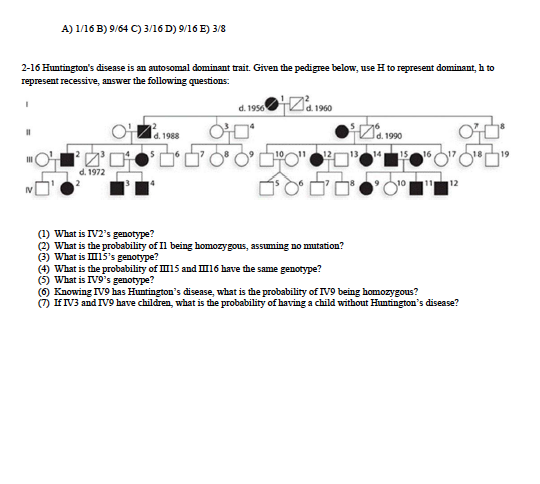
2-16 Huntington's disease is an autosomal dominant trait. Given the pedigree below, use H to represent dominant, h to
represent recessive, answer the following questions
d. 1956
1960
O D
d. 1988
d. 1990
14 15
13,
16
19
II
d. 1972
10 11
12
(1) What is IV2's genotype?
(2) What is the probability of Il being homozygous, assuming no mutation?
(3) What is III15's genotype?
(4) What is the probability of II15 and II16 have the same genotype?
(5) What is IV9's genotype?
(6) Knowing IV9 has Huntington's disease, what is the probability of IV9 being homozygous?
(7) IfIV3 and IV9 have children what is the probability of havinga child without Huntington's disease?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780815344322
Author:
Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:
W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781260159363
Author:
Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9781260231700
Author:
Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:
McGraw Hill Education