A large diffuse surface has spectral absorptivity of a = 0.9 for <1 μm and a = 0.2 for 2 1 um. The surface is insulated in the bottom, and exposed to two different conditions on the top: sun Tp T. TE T₂ Insulated Insulated Case (1) Case (2) 6-1) Case 1): What is the value of the total hemispherical absorptivity of the large diffuse surface? Note that the sun emits approximately as a blackbody at 5800 K. Blackbody Radiation Functions AT AT (pm-K) (pm-K) 200 0.000000 4,000 0.480877 400 0.000000 4,200 0.516014 600 0.000000 4,400 0.548796 800 0.000016 4,600 0.579280 1,000 0.000321 4,800 0.607559 1.200 0.002134 5,000 0.633747 1,400 0.007790 5.200 0.658970 1,600 0.019718 5,400 0.680360 1,800 0.039341 5,600 0.701046 2,000 0.066728 5,800 0.720158 2.200 0.100888 6,000 0.737818 2,400 0.140256 6,200 0.754140 2,600 0.183120 6,400 0.769234 2,800 0.227897 6,600 0.783199 2,898 0.250108 6,800 0.796129 3,000 0.273232 7,000 0.808109 3,200 0.318102 7,200 0.819217 3,400 0.361735 7,400 0.829527 3,600 0.403607 7,600 0.839102 3,800 0.443382 7,800 0.848005 6-2) Case 1): The surface is exposed to the sun and G₁ = 1200 W/m². Flowing air temperature
A large diffuse surface has spectral absorptivity of a = 0.9 for <1 μm and a = 0.2 for 2 1 um. The surface is insulated in the bottom, and exposed to two different conditions on the top: sun Tp T. TE T₂ Insulated Insulated Case (1) Case (2) 6-1) Case 1): What is the value of the total hemispherical absorptivity of the large diffuse surface? Note that the sun emits approximately as a blackbody at 5800 K. Blackbody Radiation Functions AT AT (pm-K) (pm-K) 200 0.000000 4,000 0.480877 400 0.000000 4,200 0.516014 600 0.000000 4,400 0.548796 800 0.000016 4,600 0.579280 1,000 0.000321 4,800 0.607559 1.200 0.002134 5,000 0.633747 1,400 0.007790 5.200 0.658970 1,600 0.019718 5,400 0.680360 1,800 0.039341 5,600 0.701046 2,000 0.066728 5,800 0.720158 2.200 0.100888 6,000 0.737818 2,400 0.140256 6,200 0.754140 2,600 0.183120 6,400 0.769234 2,800 0.227897 6,600 0.783199 2,898 0.250108 6,800 0.796129 3,000 0.273232 7,000 0.808109 3,200 0.318102 7,200 0.819217 3,400 0.361735 7,400 0.829527 3,600 0.403607 7,600 0.839102 3,800 0.443382 7,800 0.848005 6-2) Case 1): The surface is exposed to the sun and G₁ = 1200 W/m². Flowing air temperature
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter11: Heat Transfer By Radiation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11.68P: 11.68 Two infinitely large, black, plane surfaces are 0.3 m apart, and the space between them is...
Related questions
Question
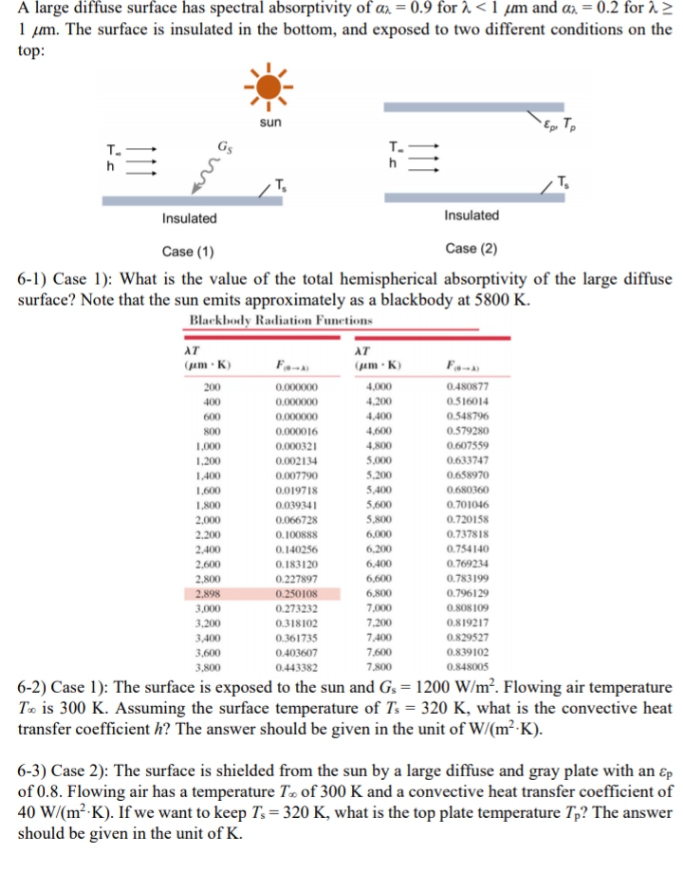
Transcribed Image Text:A large diffuse surface has spectral absorptivity of ax = 0.9 for 2 <1 μm and ax = 0.2 for >>
1 m. The surface is insulated in the bottom, and exposed to two different conditions on the
top:
sun
TE
Insulated
Insulated
Case (1)
Case (2)
6-1) Case 1): What is the value of the total hemispherical absorptivity of the large diffuse
surface? Note that the sun emits approximately as a blackbody at 5800 K.
Blackbody Radiation Functions
AT
AT
(pm-K)
(pm-K)
200
0.000000
4,000
0.480877
400
0.000000
4,200
0.516014
600
0.000000
4,400
0.548796
800
0.000016
0.579280
1,000
0.000321
4,800
0.607559
1.200
0.002134
5,000
0.633747
1,400
0.007790
5,200
0.658970
1,600
0.019718
5,400
0.680360
1,800
0.039341
5,600
0.701046
2,000
0.066728
5,800
0.720158
2.200
0.100888
6,000
0.737818
2,400
0.140256
6,200
0.754140
2,600
0.183120
6,400
0.769234
2,800
0.227897
6,600
0.783199
2,898
0.250108
6,800
0.796129
3,000
0.273232
7,000
0.808109
3,200
0.318102
7,200
0.819217
3,400
0.361735
7,400
0.829527
3,600
0.403607
7,600
0.839102
3,800
0.443382
7,800
0.848005
6-2) Case 1): The surface is exposed to the sun and Gs = 1200 W/m². Flowing air temperature
To is 300 K. Assuming the surface temperature of Ts= 320 K, what is the convective heat
transfer coefficient h? The answer should be given in the unit of W/(m²K).
6-3) Case 2): The surface is shielded from the sun by a large diffuse and gray plate with an Ep
of 0.8. Flowing air has a temperature T.. of 300 K and a convective heat transfer coefficient of
40 W/(m²-K). If we want to keep Ts=320 K, what is the top plate temperature Tp? The answer
should be given in the unit of K.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning