A large number of adults are classified according to whether they were judged to need eyeglasses for reading and whether they actually used eyeglasses when reading. The proportions falling into the four categories are shown in the table. Used Eyeglasses for Reading Judged to Need Eyeglasses Yes No Yes 0.45 0.12 No 0.03 0.40 If a single adult is selected from this group, find the probability of each event. (a) The adult is judged to need eyeglasses. (b) The adult needs eyeglasses for reading but does not use them. (c) The adult uses eyeglasses for reading whether he or she needs them or not. (d) An adult used glasses when they didn't need them.
A large number of adults are classified according to whether they were judged to need eyeglasses for reading and whether they actually used eyeglasses when reading. The proportions falling into the four categories are shown in the table. Used Eyeglasses for Reading Judged to Need Eyeglasses Yes No Yes 0.45 0.12 No 0.03 0.40 If a single adult is selected from this group, find the probability of each event. (a) The adult is judged to need eyeglasses. (b) The adult needs eyeglasses for reading but does not use them. (c) The adult uses eyeglasses for reading whether he or she needs them or not. (d) An adult used glasses when they didn't need them.
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section11.8: Probabilities Of Disjoint And Overlapping Events
Problem 2C
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:A large number of adults are classified according to whether they were judged to need eyeglasses for reading and whether they actually used eyeglasses when reading. The proportions falling into the four categories are shown in the table.
Used Eyeglasses
for Reading
Judged to Need
Eyeglasses
Yes
No
Yes
0.45
0.12
No
0.03
0.40
If a single adult is selected from this group, find the probability of each event.
(a) The adult is judged to need eyeglasses.
(b) The adult needs eyeglasses for reading but does not use them.
(c) The adult uses eyeglasses for reading whether he or she needs them or not.
(d) An adult used glasses when they didn't need them.
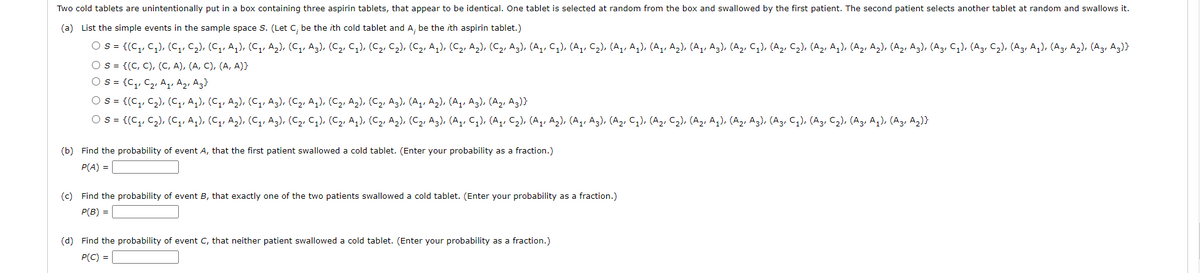
Transcribed Image Text:Two cold tablets are unintentionally put in a box containing three aspirin tablets, that appear to be identical. One tablet is selected at random from the box and swallowed by the first patient. The second patient selects another tablet at random and swallows it.
(a) List the simple events in the sample space S. (Let C, be the ith cold tablet and A, be the ith aspirin tablet.)
O s = {(C, C,), (C,, c2), (C, A,), (C, Ag), (C,, Az), (C2, C,), (C2, C2), (C, A,), (C2, A2), (C2, A3), (A,, C,), (A,, C2), (A,, Aq), (A,, A2), (Aq, A3), (A2, C,), (A2, C2), (A2, Aq), (A2, A2), (A2, A3), (A3, C,), (A3, C2), (A3, A,), (A3, A2), (A3, Az)}
O s = {(C, C), (C, A), (A, C), (A, A)}
O s = {C,, C2, Aq, Az, Ag}
O s= {(C,, C2), (C1, Aq), (C, A2), (C,, A3), (C2, A,), (C2, A,), (C2, A3), (A,, Az), (A,, Az), (A, Ag)}
O s = {(C,, C,), (C,, Aq), (C,, A,), (C, Ag), (C2, C,), (C2, A,), (C2, A,), (C2, A3), (A,, C,), (A,, C2), (Aq, Az), (A, A3), (A,, C,), (A2, C2), (A2, A,), (A2, A3), (A3, C,), (A3, C2), (A3, Aq), (A3, A2)}
(b) Find the probability of event A, that the first patient swallowed a cold tablet. (Enter your probability as a fraction.)
P(A) =
(c) Find the probability of event B, that exactly one of the two patients swallowed a cold tablet. (Enter your probability as a fraction.)
P(B) =
(d) Find the probability of event C, that neither patient swallowed a cold tablet. (Enter your probability as a fraction.)
P(C) =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL


Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
