A laser beam is used to levitate a metal disk against the force of Earth's gravity. (a) Derive an equation giving the required intensity of light, I, in terms of the mass m of the disk, the gravitational acceleration g, the speed of light c, and the cross-sectional area of the disk A. Assume the disk is perfectly reflecting and the beam is directed perpendicular to the disk. (Do not substitute numerical values; use variables only.) mgc 24 (b) If the disk has mass 6.27 g and radius 4.20 cm, find the necessary light intensity. 1.22e6 Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. W/m2
A laser beam is used to levitate a metal disk against the force of Earth's gravity. (a) Derive an equation giving the required intensity of light, I, in terms of the mass m of the disk, the gravitational acceleration g, the speed of light c, and the cross-sectional area of the disk A. Assume the disk is perfectly reflecting and the beam is directed perpendicular to the disk. (Do not substitute numerical values; use variables only.) mgc 24 (b) If the disk has mass 6.27 g and radius 4.20 cm, find the necessary light intensity. 1.22e6 Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. W/m2
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter24: Electromagnetic Waves
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 28P
Related questions
Question
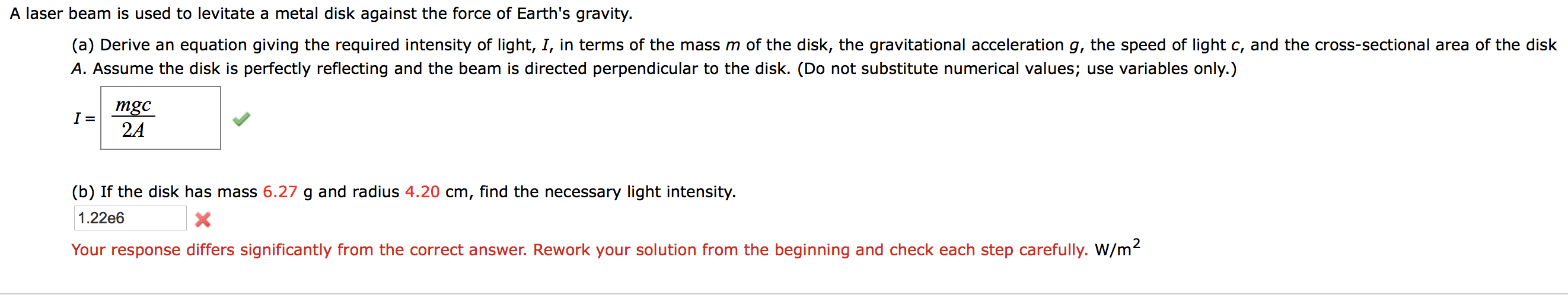
Transcribed Image Text:A laser beam is used to levitate a metal disk against the force of Earth's gravity.
(a) Derive an equation giving the required intensity of light, I, in terms of the mass m of the disk, the gravitational acceleration g, the speed of light c, and the cross-sectional area of the disk
A. Assume the disk is perfectly reflecting and the beam is directed perpendicular to the disk. (Do not substitute numerical values; use variables only.)
mgc
24
(b) If the disk has mass 6.27 g and radius 4.20 cm, find the necessary light intensity.
1.22e6
Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. W/m2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
