A mass-less spring having a spring constant k = 185 N/m, is inside a horizontal barrel. Its left end is rigidly fixed at position x = 0.0 cm, and its right end is at X = L, where L = 19.7 cm. The spring is then squeezed so that the right end of the spring is at X = S, where S = 13 cm. A ball of mass 50 g is put in front of the spring, and the spring is released. Calculate the speed of the ball (in m/s) as it comes out of the barrel. Ignore friction inside the barrel. X = 0.0 cm X = Lcm Equilibrium Position Squeezed Position X 0.0 cm X =S cm
A mass-less spring having a spring constant k = 185 N/m, is inside a horizontal barrel. Its left end is rigidly fixed at position x = 0.0 cm, and its right end is at X = L, where L = 19.7 cm. The spring is then squeezed so that the right end of the spring is at X = S, where S = 13 cm. A ball of mass 50 g is put in front of the spring, and the spring is released. Calculate the speed of the ball (in m/s) as it comes out of the barrel. Ignore friction inside the barrel. X = 0.0 cm X = Lcm Equilibrium Position Squeezed Position X 0.0 cm X =S cm
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter2: Steady Heat Conduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2.34P: 2.34 Show that the temperature distribution in a sphere of radius . made of a homogeneous material...
Related questions
Question
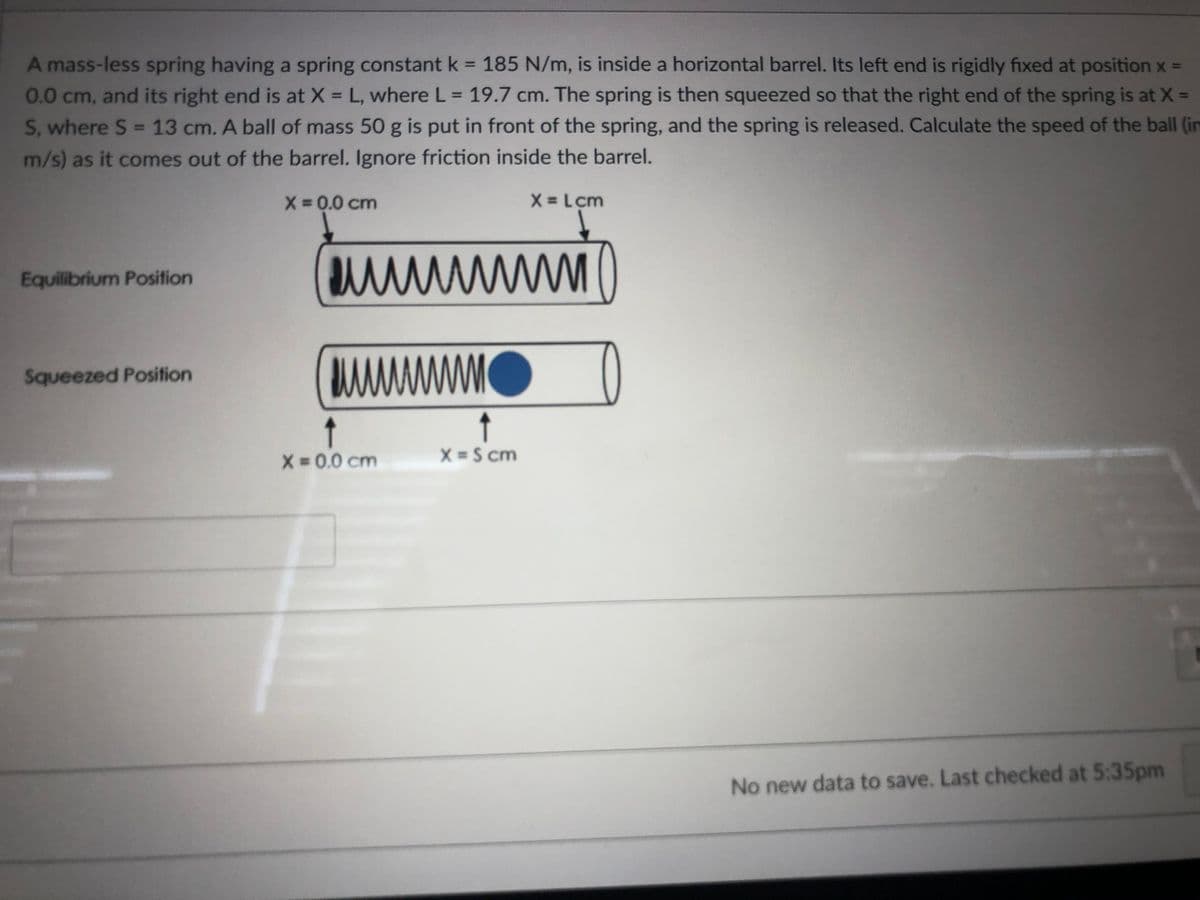
Transcribed Image Text:A mass-less spring having a spring constant k = 185 N/m, is inside a horizontal barrel. Its left end is rigidly fixed at position x =
0.0 cm, and its right end is at X L, where L = 19.7 cm. The spring is then squeezed so that the right end of the spring is at X =
S, where S = 13 cm. A ball of mass 50 g is put in front of the spring, and the spring is released. Calculate the speed of the ball (in
%3D
%3D
%3D
m/s) as it comes out of the barrel. Ignore friction inside the barrel.
X 0.0 cm
X = Lcm
Equilibrium Position
Squeezed Position
↑
X 0.0 cm
X = S cm
No new data to save. Last checked at 5:35pm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning