A motorbike wheel with an 8 kg mass has a 0.4 m radius of gyration around the z-axis, as shown in Figure. The wheel's shaft is supported by bearings A and B and rotates at a constant rate of 150 rpm in a counter-clockwise direction from the z-axis, while the frame rotates at 12 rpm in a counter- clockwise direction from the y-axis. Determine the resultant reaction forces at each bearing A and B due to the mass and gyroscopic effects. With the result of forces, which bearing has a tendency to fail first, which bearing should be considered for design purposes and explain the effect on motor if the bearing fail. 0.55 0.4
A motorbike wheel with an 8 kg mass has a 0.4 m radius of gyration around the z-axis, as shown in Figure. The wheel's shaft is supported by bearings A and B and rotates at a constant rate of 150 rpm in a counter-clockwise direction from the z-axis, while the frame rotates at 12 rpm in a counter- clockwise direction from the y-axis. Determine the resultant reaction forces at each bearing A and B due to the mass and gyroscopic effects. With the result of forces, which bearing has a tendency to fail first, which bearing should be considered for design purposes and explain the effect on motor if the bearing fail. 0.55 0.4
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Chapter8: Centroids And Distributed Loads
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8.91P: What is the ratio L/R for which the uniform wire figure can be balanced in the position shown?
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
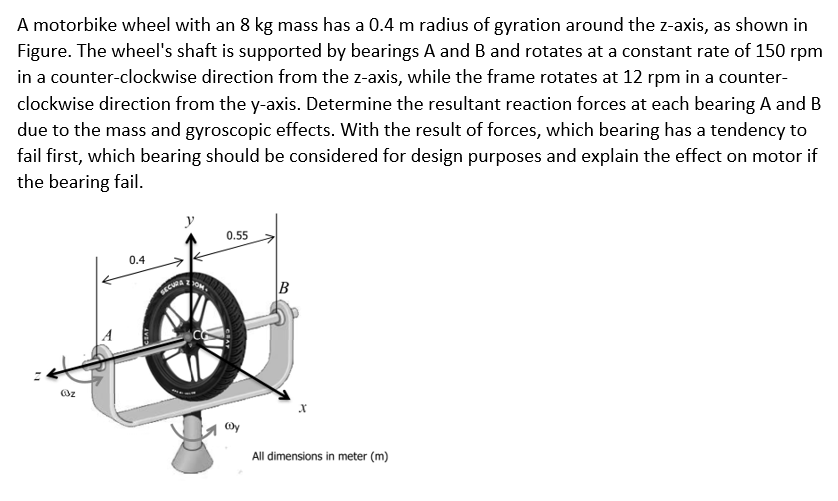
Transcribed Image Text:SECW OM
A motorbike wheel with an 8 kg mass has a 0.4 m radius of gyration around the z-axis, as shown in
Figure. The wheel's shaft is supported by bearings A and B and rotates at a constant rate of 150 rpm
in a counter-clockwise direction from the z-axis, while the frame rotates at 12 rpm in a counter-
clockwise direction from the y-axis. Determine the resultant reaction forces at each bearing A and B
due to the mass and gyroscopic effects. With the result of forces, which bearing has a tendency to
fail first, which bearing should be considered for design purposes and explain the effect on motor if
the bearing fail.
y
0.55
0.4
All dimensions in meter (m)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L