A population consists of the following 6 values: {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60}. A sample of size 3 will be chosen from this population without replacement and the median of the sample will be computed: { (0.5 (£n/2 + £n/2+1) m = x(n+1)/2 n odd n even In other words, in a sample of size n = 3 ordered from smallest to largest the median is the 2nd number. The median of a discrete random variable, μ, is defined as the value of such that and P(X M) ≤ 0.5 Determine the median of the population. Think of the population as an equally likely sample space. Determine the sampling distribution of the sample median, m for this population by (1) identifying all possible samples (how many are there?), (2) calculating the median in each sample and (3) using that to determine the probability of each median. Calculate E (m) Determine the standard error or the sample median
A population consists of the following 6 values: {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60}. A sample of size 3 will be chosen from this population without replacement and the median of the sample will be computed: { (0.5 (£n/2 + £n/2+1) m = x(n+1)/2 n odd n even In other words, in a sample of size n = 3 ordered from smallest to largest the median is the 2nd number. The median of a discrete random variable, μ, is defined as the value of such that and P(X M) ≤ 0.5 Determine the median of the population. Think of the population as an equally likely sample space. Determine the sampling distribution of the sample median, m for this population by (1) identifying all possible samples (how many are there?), (2) calculating the median in each sample and (3) using that to determine the probability of each median. Calculate E (m) Determine the standard error or the sample median
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.8: Probability
Problem 32E
Related questions
Question
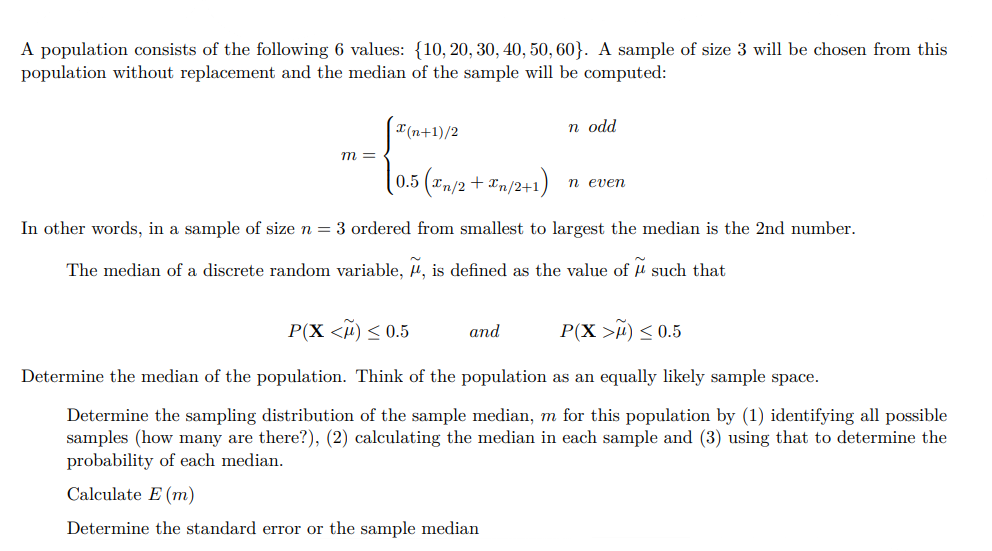
Transcribed Image Text:A population consists of the following 6 values: {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60}. A sample of size 3 will be chosen from this
population without replacement and the median of the sample will be computed:
{
(0.5 (£n/2 + £n/2+1)
m =
x(n+1)/2
n odd
n even
In other words, in a sample of size n = 3 ordered from smallest to largest the median is the 2nd number.
The median of a discrete random variable, μ, is defined as the value of such that
and
P(X <M) ≤ 0.5
P(X>M) ≤ 0.5
Determine the median of the population. Think of the population as an equally likely sample space.
Determine the sampling distribution of the sample median, m for this population by (1) identifying all possible
samples (how many are there?), (2) calculating the median in each sample and (3) using that to determine the
probability of each median.
Calculate E (m)
Determine the standard error or the sample median
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill