A Queue that has been implemented with a singly-linked list has the following structure: z -> e -> m -> |->j Where z is the 'front' of the queue, j is the 'back, and the 'count' is 5. What would the psuedocode for enqueueing a new element, h, look like? 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp 2. Set temp's element pointer to h 3. Set the back node's next pointer to temp 4. Set the back pointer to temp 5. Increment count O 1. Create a new Character called temp 2. Set temp to be h 3. Set the back node's element pointer to temp 4. Increment count 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp 2. Set temp's element pointer to h 3. Set temp's next pointer to front 4. Set the front pointer to temp 5. Increment count O 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp 2. Set temp's element pointer to h 3. Set the back pointer to temp 4. Increment count O 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp 2. Set temp's element pointer to h 3. Set the back node's next pointer to temp 4. Set the front pointer to temp 5. Increment count
A Queue that has been implemented with a singly-linked list has the following structure: z -> e -> m -> |->j Where z is the 'front' of the queue, j is the 'back, and the 'count' is 5. What would the psuedocode for enqueueing a new element, h, look like? 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp 2. Set temp's element pointer to h 3. Set the back node's next pointer to temp 4. Set the back pointer to temp 5. Increment count O 1. Create a new Character called temp 2. Set temp to be h 3. Set the back node's element pointer to temp 4. Increment count 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp 2. Set temp's element pointer to h 3. Set temp's next pointer to front 4. Set the front pointer to temp 5. Increment count O 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp 2. Set temp's element pointer to h 3. Set the back pointer to temp 4. Increment count O 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp 2. Set temp's element pointer to h 3. Set the back node's next pointer to temp 4. Set the front pointer to temp 5. Increment count
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design
8th Edition
ISBN:9781337102087
Author:D. S. Malik
Publisher:D. S. Malik
Chapter18: Stacks And Queues
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 21SA
Related questions
Question
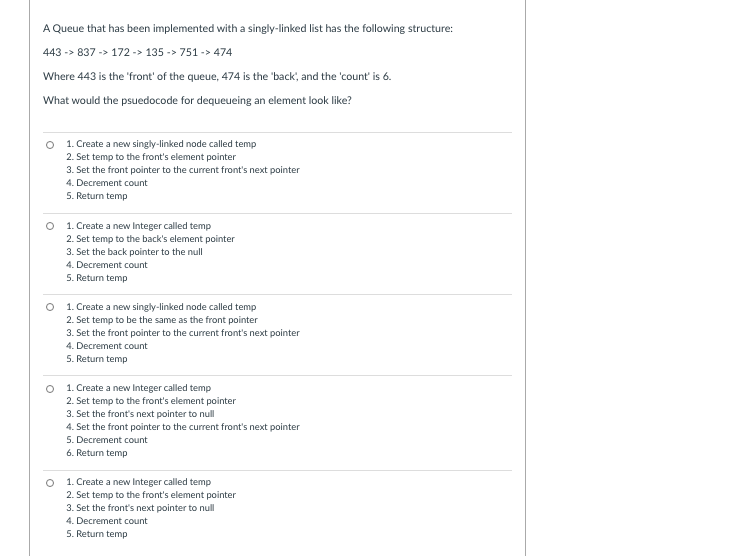
Transcribed Image Text:A Queue that has been implemented with a singly-linked list has the following structure:
443 -> 837 -> 172 -> 135 -> 751 -> 474
Where 443 is the 'front' of the queue, 474 is the 'back, and the 'count' is 6.
What would the psuedocode for dequeueing an element look like?
1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp
2. Set temp to the front's element pointer
3. Set the front pointer to the current front's next pointer
4. Decrement count
5. Return temp
1. Create a new Integer called temp
2. Set temp to the back's element pointer
3. Set the back pointer to the null
4. Decrement count
5. Return temp
O 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp
2. Set temp to be the same as the front pointer
3. Set the front pointer to the current front's next pointer
4. Decrement count
5. Return temp
O 1. Create a new Integer called temp
2. Set temp to the front's element pointer
3. Set the front's next pointer to null
4. Set the front pointer to the current front's next pointer
5. Decrement count
6. Return temp
1. Create a new Integer called temp
2. Set temp to the front's element pointer
3. Set the front's next pointer to null
4. Decrement count
5. Return temp
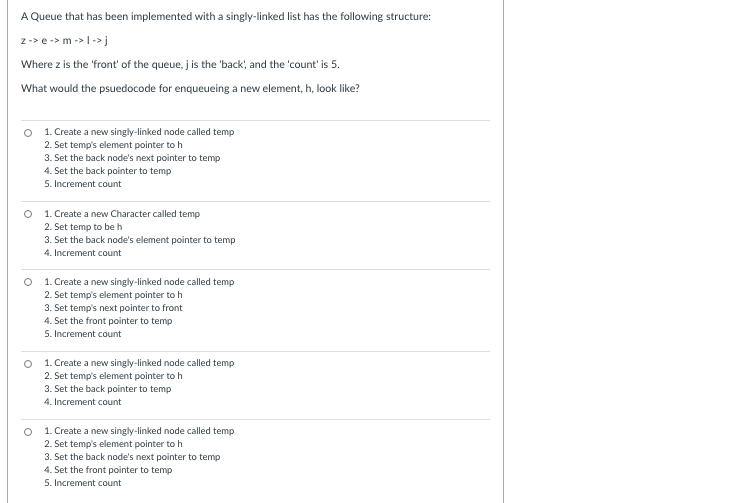
Transcribed Image Text:A Queue that has been implemented with a singly-linked list has the following structure:
z-> e-> m ->|->j
Where z is the 'front' of the queue, j is the 'back, and the 'count' is 5.
What would the psuedocode for enqueueing a new element, h, look like?
1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp
2. Set temp's element pointer to h
3. Set the back node's next pointer to temp
4. Set the back pointer to temp
5. Increment count
1. Create a new Character called temp
2. Set temp to beh
3. Set the back node's element pointer to temp
4. Increment count
1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp
2. Set temp's element pointer to h
3. Set temp's next pointer to front
4. Set the front pointer to temp
5. Increment count
1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp
2. Set temp's element pointer to h
3. Set the back pointer to temp
4. Increment count
O 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp
2. Set temp's element pointer to h
3. Set the back node's next pointer to temp
4. Set the front pointer to temp
5. Increment count
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337102087
Author:
D. S. Malik
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337102087
Author:
D. S. Malik
Publisher:
Cengage Learning