A rod is bent into an L shape and attached at one point to a pivot. (Figure 1)The rod sits on a frictionless table and the diagram is a view from above. This means that gravity can be ignored for this problem. There are three forces that are applied to the rod at different points and Part A If F = 0 and F = 12 N, what does the magnitude of F2 have to be for there to be rotational equilibrium? Answer numerically in newtons to two significant figures. F, F2, and F3. Note that the dimensions of the angles: bent rod are in centimeters in the figure, although the answers are requested in SI units (kilograms, meters, seconds). • View Available Hint(s) ? F2 = Submit Figure 1 of 1 > Part B If the L-shaped rod has a moment of inertia I = 9 kg m?, F = 12 N, F, = 27 N, and again F = 0, how long a time t would it take for the object to move through 45° ( 7/4 radians)? F Assume that as the object starts to move, each force moves with the object so as to retain its initial angle relative to the object. Express the time in seconds to two significant figures. 3 ст • View Available Hint(s) 30° Pivot 8 cm ? t=
A rod is bent into an L shape and attached at one point to a pivot. (Figure 1)The rod sits on a frictionless table and the diagram is a view from above. This means that gravity can be ignored for this problem. There are three forces that are applied to the rod at different points and Part A If F = 0 and F = 12 N, what does the magnitude of F2 have to be for there to be rotational equilibrium? Answer numerically in newtons to two significant figures. F, F2, and F3. Note that the dimensions of the angles: bent rod are in centimeters in the figure, although the answers are requested in SI units (kilograms, meters, seconds). • View Available Hint(s) ? F2 = Submit Figure 1 of 1 > Part B If the L-shaped rod has a moment of inertia I = 9 kg m?, F = 12 N, F, = 27 N, and again F = 0, how long a time t would it take for the object to move through 45° ( 7/4 radians)? F Assume that as the object starts to move, each force moves with the object so as to retain its initial angle relative to the object. Express the time in seconds to two significant figures. 3 ст • View Available Hint(s) 30° Pivot 8 cm ? t=
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter10: Rotational Motion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 74P: A stepladder of negligible weight is constructed as shown in Figure P10.73, with AC = BC = ℓ. A...
Related questions
Question
100%
Part A, B, C
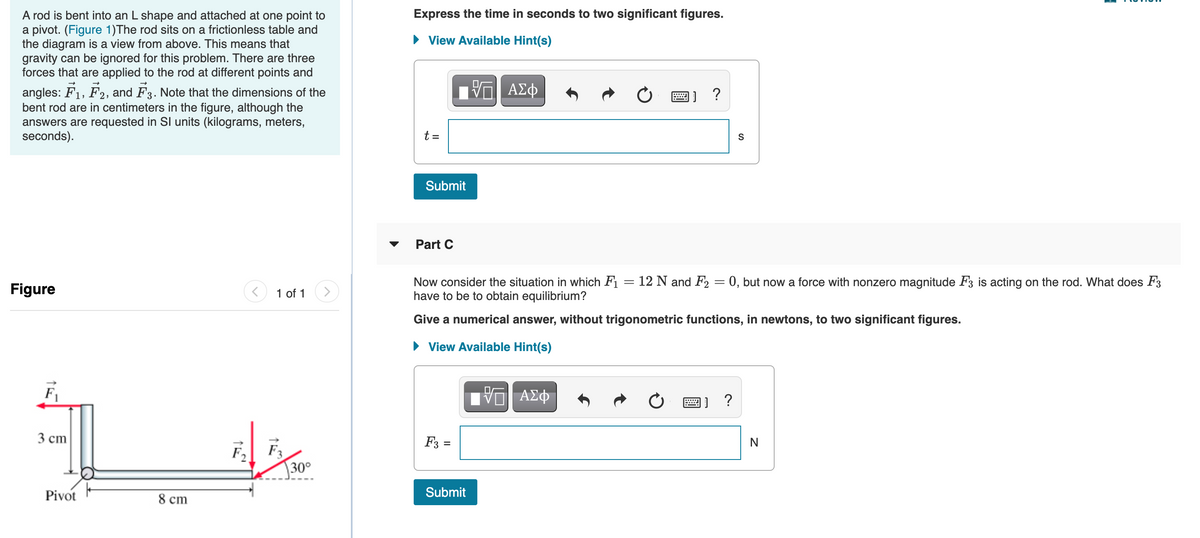
Transcribed Image Text:Express the time in seconds to two significant figures.
A rod is bent into an L shape and attached at one point to
a pivot. (Figure 1)The rod sits on a frictionless table and
the diagram is a view from above. This means that
gravity can be ignored for this problem. There are three
forces that are applied to the rod at different points and
• View Available Hint(s)
Πνα ΑΣφ
angles: F1, F2, and F3. Note that the dimensions of the
bent rod are in centimeters in the figure, although the
answers are requested in SI units (kilograms, meters,
seconds).
t =
S
Submit
Part C
Now consider the situation in which F1 = 12 N and F2 = 0, but now a force with nonzero magnitude F3 is acting on the rod. What does F3
have to be to obtain equilibrium?
%3D
Figure
1 of 1
Give a numerical answer, without trigonometric functions, in newtons, to two significant figures.
• View Available Hint(s)
F
ν ΑΣφ
3 сm
F3
F3
30°
F2
Pivot
8 сm
Submit
II
![A rod is bent into an L shape and attached at one point to
a pivot. (Figure 1)The rod sits on a frictionless table and
the diagram is a view from above. This means that
gravity can be ignored for this problem. There are three
forces that are applied to the rod at different points and
Part A
If F3
O and Fi = 12 N, what does the magnitude of F2 have to be for there to be rotational equilibrium?
Answer numerically in newtons to two significant figures.
angles: F1, F2, and F3. Note that the dimensions of the
bent rod are in centimeters in the figure, although the
answers are requested in SI units (kilograms, meters,
seconds).
• View Available Hint(s)
画] ?
F2 =
N
Submit
Figure
1 of 1
▼
Part B
If the L-shaped rod has a moment of inertia I = 9 kg m², F1 = 12 N, F2 = 27 N, and again F3 = 0, how long a time t would it take for the
object to move through 45° ( T/4 radians)?
||
F
Assume that as the object starts to move, each force moves with the object so as to retain its initial angle relative to the object.
Express the time in seconds to two significant figures.
3 сm
• View Available Hint(s)
F3
30°
F2
Pivot
8 cm
G AEO
ΑΣφ
t =
S
II](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F50fa29ee-fb07-4aea-bb82-7d613cb3c869%2F51af398a-5a72-497b-894c-45945d72c70a%2Fhfg8b6o_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:A rod is bent into an L shape and attached at one point to
a pivot. (Figure 1)The rod sits on a frictionless table and
the diagram is a view from above. This means that
gravity can be ignored for this problem. There are three
forces that are applied to the rod at different points and
Part A
If F3
O and Fi = 12 N, what does the magnitude of F2 have to be for there to be rotational equilibrium?
Answer numerically in newtons to two significant figures.
angles: F1, F2, and F3. Note that the dimensions of the
bent rod are in centimeters in the figure, although the
answers are requested in SI units (kilograms, meters,
seconds).
• View Available Hint(s)
画] ?
F2 =
N
Submit
Figure
1 of 1
▼
Part B
If the L-shaped rod has a moment of inertia I = 9 kg m², F1 = 12 N, F2 = 27 N, and again F3 = 0, how long a time t would it take for the
object to move through 45° ( T/4 radians)?
||
F
Assume that as the object starts to move, each force moves with the object so as to retain its initial angle relative to the object.
Express the time in seconds to two significant figures.
3 сm
• View Available Hint(s)
F3
30°
F2
Pivot
8 cm
G AEO
ΑΣφ
t =
S
II
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill