a) Set up but do not compute the integral for the volume of the solid below using cross-sectional method: The solid lies between planes perpendicular to the x-axis at x = 0 and x = 6. The cross-sections between these planes are squares whose bases run from the x-axis up to the curve x¹/2 + y¹/2 = √6.
a) Set up but do not compute the integral for the volume of the solid below using cross-sectional method: The solid lies between planes perpendicular to the x-axis at x = 0 and x = 6. The cross-sections between these planes are squares whose bases run from the x-axis up to the curve x¹/2 + y¹/2 = √6.
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Chapter10: Analytic Geometry
Section10.1: The Rectangular Coordinate System
Problem 40E: Find the exact volume of the solid that results when the region bounded in quadrant I by the axes...
Related questions
Question
Please do not skip steps.
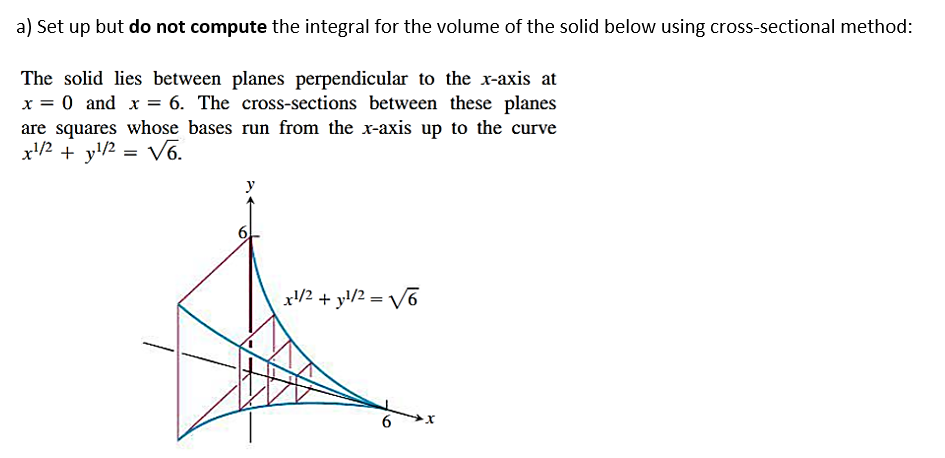
Transcribed Image Text:a) Set up but do not compute the integral for the volume of the solid below using cross-sectional method:
The solid lies between planes perpendicular to the x-axis at
x = 0 and x = 6. The cross-sections between these planes
are squares whose bases run from the x-axis up to the curve
x/2 + y/2 = V6.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,