A simple circuit of the form shown in the figure below is constructed using a battery and three lightbulbs. The bulbs may have different resistances as given in the six circumstances below. For each situation, however, the battery in the circuit is always the same, as are the wire connections. Rank these circuits from greatest to smallest, according to the voltage across the bulb shown in purple in the list. If two circuits have the same voltage associated with the selected bulb, give them the same ranking. (Use only ">" or "=" symbols. Do not include any parentheses around the letters or symbols.) a. Bulb 1: 10 Q; bulb 2: 20 Q; bulb 3: 30 0 b. Bulb 1: 1o n; bulb 2: 10 0; bulb 3: 20 0 c. Bulb 1: 1o N; bulb 2: 20 Q; bulb 3: 10 Q d. Bulb 1: 10 Q; bulb 2: 2o Q; bulb 3: 30n e. Bulb 1: 1o Q; bulb 2: 10o n; bulb 3: 20n f. Bulb 1: 10 Q: bulb 2: 20 Q; bulb 3: 10 Q Justify your rankings using your knowledge of the physics of such circuits. (Select all that apply.) O The voltage drop across any bulb is the current passing through the bulb multiplied by the resistance of that bulb. O The current that passes through all bulbs is the battery voltage divided by the sum of the bulbs' resistances. O The voltage drop across any bulb is the current passing through the bulb divided by the resistance of that bulb. O The current that passes through all bulbs is the battery voltage multiplied by the sum of the bulbs' resistances.
A simple circuit of the form shown in the figure below is constructed using a battery and three lightbulbs. The bulbs may have different resistances as given in the six circumstances below. For each situation, however, the battery in the circuit is always the same, as are the wire connections. Rank these circuits from greatest to smallest, according to the voltage across the bulb shown in purple in the list. If two circuits have the same voltage associated with the selected bulb, give them the same ranking. (Use only ">" or "=" symbols. Do not include any parentheses around the letters or symbols.) a. Bulb 1: 10 Q; bulb 2: 20 Q; bulb 3: 30 0 b. Bulb 1: 1o n; bulb 2: 10 0; bulb 3: 20 0 c. Bulb 1: 1o N; bulb 2: 20 Q; bulb 3: 10 Q d. Bulb 1: 10 Q; bulb 2: 2o Q; bulb 3: 30n e. Bulb 1: 1o Q; bulb 2: 10o n; bulb 3: 20n f. Bulb 1: 10 Q: bulb 2: 20 Q; bulb 3: 10 Q Justify your rankings using your knowledge of the physics of such circuits. (Select all that apply.) O The voltage drop across any bulb is the current passing through the bulb multiplied by the resistance of that bulb. O The current that passes through all bulbs is the battery voltage divided by the sum of the bulbs' resistances. O The voltage drop across any bulb is the current passing through the bulb divided by the resistance of that bulb. O The current that passes through all bulbs is the battery voltage multiplied by the sum of the bulbs' resistances.
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter29: Direct Current (dc) Circuits
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 51PQ
Related questions
Question
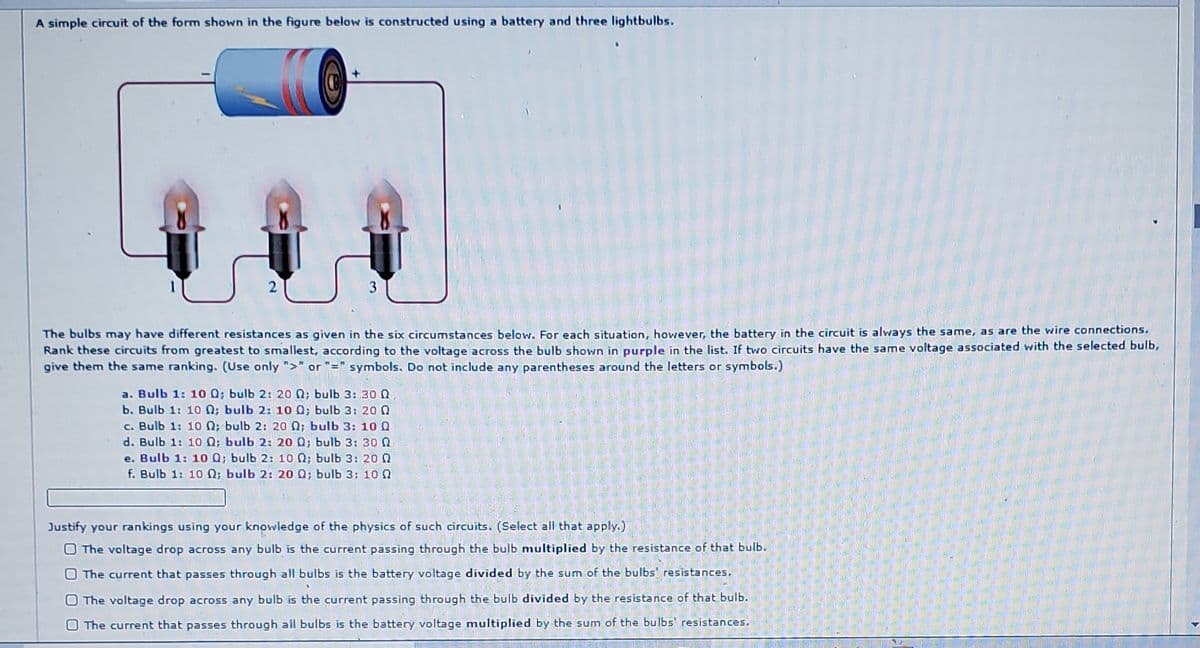
Transcribed Image Text:A simple circuit of the form shown in the figure below is constructed using a battery and three lightbulbs.
3
The bulbs may have different resistances as given in the six circumstances below, For each situation, however, the battery in the circuit is always the same, as are the wire connections.
Rank these circuits from greatest to smallest, according to the voltage across the bulb shown in purple in the list. If two circuits have the same voltage associated with the selected bulb,
give them the same ranking. (Use only ">" or "=" symbols. Do not include any parentheses around the letters or symbols.)
a. Bulb 1: 10 Q; bulb 2: 20 Q; bulb 3: 30 Q
b. Bulb 1: 1o N; bulb 2: 10 Q; bulb 3: 20 Q
c. Bulb 1: 1o Q; bulb 2: 20 Q; bulb 3: 10 Q
d. Bulb 1: 10 Q; bulb 2: 20 Q; bulb 3: 30 Q
e. Bulb 1: 10 Q; bulb 2: 10 Q; bulb 3: 20 0
f. Bulb 1: 10 n; bulb 2: 20 Q; bulb 3: 1o n
Justify your rankings using your knowledge of the physics of such circuits. (Select all that apply.)
OThe voltage drop across any bulb is the current passing through the bulb multiplied by the resistance of that bulb.
OThe current that passes through all bulbs is the battery voltage divided by the sum of the bulbs' resistances.
O The voltage drop across any bulb is the current passing through the bulb divided by the resistance of that bulb.
O The current that passes through all bulbs is the battery voltage multiplied by the sum of the bulbs resistances.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill