A solid rectangular object having dimensions of I = 4.00 cm, w = 3.00 cm, and h = 1.00 cm is subjected to a compressive stress having a force of F = 2.00x105 N applied perpendicularly on the right and left faces of the rectangular object. This stress causes compression on the box by Al = 1.25% of its length as shown in Figure A. The Shear modulus of the rectangular object is just 35% of its Young's modulus. If this force was instead applied on the upper and lower faces on the rectangular object without changing the direction of the force (Figure B), by how much distance would the upper face be deformed with respect to the lower face of the rectangular object? * F F AL A B
A solid rectangular object having dimensions of I = 4.00 cm, w = 3.00 cm, and h = 1.00 cm is subjected to a compressive stress having a force of F = 2.00x105 N applied perpendicularly on the right and left faces of the rectangular object. This stress causes compression on the box by Al = 1.25% of its length as shown in Figure A. The Shear modulus of the rectangular object is just 35% of its Young's modulus. If this force was instead applied on the upper and lower faces on the rectangular object without changing the direction of the force (Figure B), by how much distance would the upper face be deformed with respect to the lower face of the rectangular object? * F F AL A B
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Chapter10: Stresses In A Soil Mass
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10.1CTP: EB and FG are two planes inside a soil element ABCD as shown in Figure 10.50. Stress conditions on...
Related questions
Question
A solid rectangular object having dimensions of l = 4.00 cm, w = 3.00 cm, and h = 1.00 cm is subjected to a compressive stress having a force of F = 2.00×10⁵ N applied perpendicularly on the right and left faces of the rectangular object. This stress causes compression on the box by Δl = 1.25% of its length as shown in Figure A. The Shear modulus of the rectangular object is just 35% of its Young's modulus. If this force was instead applied on the upper and lower faces on the rectangular object without changing the direction of the force (Figure B), by how much distance would the upper face be deformed with respect to the lower face of the rectangular object?
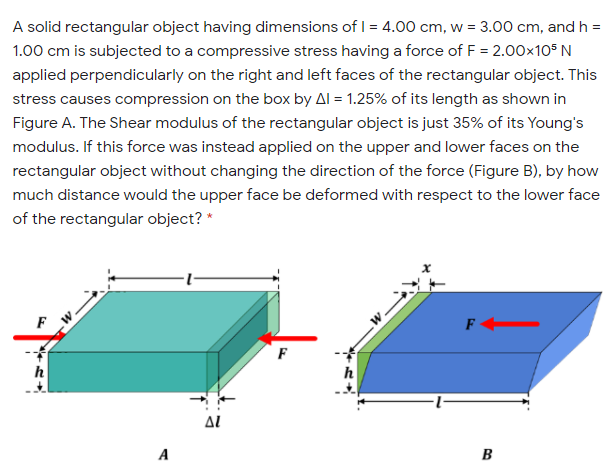
Transcribed Image Text:A solid rectangular object having dimensions of I = 4.00 cm, w = 3.00 cm, and h =
1.00 cm is subjected to a compressive stress having a force of F = 2.00x105 N
applied perpendicularly on the right and left faces of the rectangular object. This
stress causes compression on the box by Al = 1.25% of its length as shown in
Figure A. The Shear modulus of the rectangular object is just 35% of its Young's
modulus. If this force was instead applied on the upper and lower faces on the
rectangular object without changing the direction of the force (Figure B), by how
much distance would the upper face be deformed with respect to the lower face
of the rectangular object? *
F
F
AL
A
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305970939
Author:
Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305970939
Author:
Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning