A solution of (S)-valine (molar mass = 117.15) is observed to have a rotation of +16.2 degrees in a 10 cm pathlength cell. Assuming the valine is pure, if the molar specific rotation of (S)-valine is 72.6 degrees, what is the concentration of (S) valine in grams per liter?
A solution of (S)-valine (molar mass = 117.15) is observed to have a rotation of +16.2 degrees in a 10 cm pathlength cell. Assuming the valine is pure, if the molar specific rotation of (S)-valine is 72.6 degrees, what is the concentration of (S) valine in grams per liter?
Chapter26: Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, And Proteins
Section26.1: Structures Of Amino Acids
Problem 3P
Related questions
Question
100%
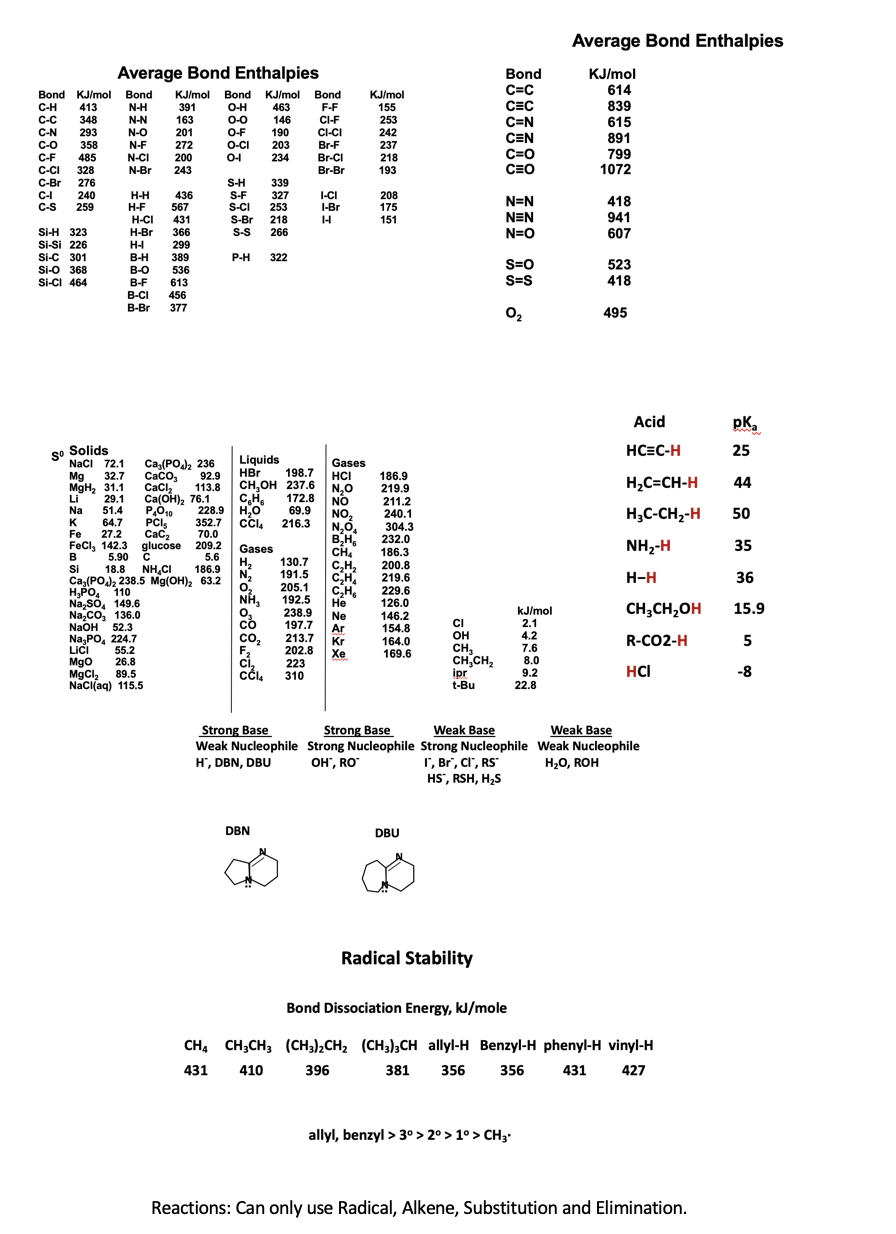
Transcribed Image Text:Average Bond Enthalpies
Average Bond Enthalpies
Bond
C=C
CEC
C=N
KJ/mol
614
839
Bond KJ/mol Bond
KJ/mol Bond KJ/mol Bond
KJ/mol
С-Н
413
N-H
391
O-H
463
F-F
155
146
190
C-C
348
N-N
163
201
0-0
O-F
CI-F
253
242
615
891
799
1072
C-N
293
N-O
CI-CI
CEN
C-O
C-F
C-CI
C-Br
358
N-F
N-CI
272
O-CI
203
Br-F
Br-CI
Br-Br
237
485
200
234
218
C=0
328
N-Br
243
193
CEO
276
240
259
S-H
S-F
S-CI
S-Br
339
327
253
218
C-I
C-S
H-H
H-F
H-CI
H-Br
436
567
431
I-CI
I-Br
208
175
151
N=N
418
NEN
941
Si-H 323
Si-Si 226
366
S-S
266
N=O
607
299
Si-C 301
B-H
389
P-H
322
S=0
S=S
523
418
Si-O 368
B-O
B-F
536
Si-CI 464
613
B-CI
456
B-Br
377
O2
495
Acid
pK,
so Solids
Naci 72.1
HC=C-H
25
Liquids
HBr
сH,он 237.6
CH,
228.9 H,0
Ca,(PO 236
Gases
HCI
| N.O
Mg
CaCo,
198.7
32.7
MgH, 31.1
29.1
51.4
64.7
27.2
92.9
186.9
219.9
211.2
240.1
304.3
232.0
Cacl,
H,C=CH-H
44
N,0
NO
113.8
Li
Cа(он), 76.1
Na
K
Fe
172.8
69.9
216.3
NO,
H;C-CH2-H
50
PCI,
Cac,
glucose
352.7
70.0
209.2
5.6
186.9
B,H,
CH
NH2-H
FeCl, 142.3
35
Gases
H,
N,
186.3
в
B
5.90
130.7
C,H,
C,H.
C,H,
200.8
219.6
229.6
126.0
146.2
Si
I
18.8 NH,CI
Ca,(PO, 238.5 Mg(OH), 63.2
191.5
H-H
36
205.1
192.5
238.9
197.7
H,PO, "110
Na,so, 149.6
Na,co, 136.0
NaOH 52.3
Na, PO, 224.7
LICI
Mgo
MgCl,
Naci(aq) 115.5
Не
CH,CH,OH
15.9
kJ/mol
2.1
4.2
Ne
CI
OH
Ar
154.8
co,
F2
ci,
213.7
202.8
223
310
Kr
R-CO2-H
5
164.0
169.6
CH,
55.2
26.8
89.5
7.6
8.0
9.2
22.8
Xe
CH,CH,
HCI
-8
ipr
t-Bu
Strong Base
Weak Base
Weak Base
Strong Base
Weak Nucleophile Strong Nucleophile Strong Nucleophile Weak Nucleophile
H', DBN, DBU
OH", RO
I, Br", CI', RS"
HS', RSH, H,S
H20, ROH
DBN
DBU
Radical Stability
Bond Dissociation Energy, kJ/mole
CH, CH;CH; (CH3)2CH2 (CH3);CH allyl-H Benzyl-H phenyl-H vinyl-H
431
410
396
381
356
356
431
427
allyl, benzyl > 3° > 2° > 1° > CH3
Reactions: Can only use Radical, Alkene, Substitution and Elimination.

Transcribed Image Text:117.15) is observed to have a rotation of +16.2 degrees in a
A solution of (S)-valine (molar mass =
10 cm pathlength cell. Assuming the valine is pure, if the molar specific rotation of (S)-valine is
72.6 degrees, what is the concentration of (S) valine in grams per liter?
T T T
* 3 (12pt)
ABC
Arial
Path: p
Words:0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577190
Author:
Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:
Brooks Cole


Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577190
Author:
Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:
Brooks Cole