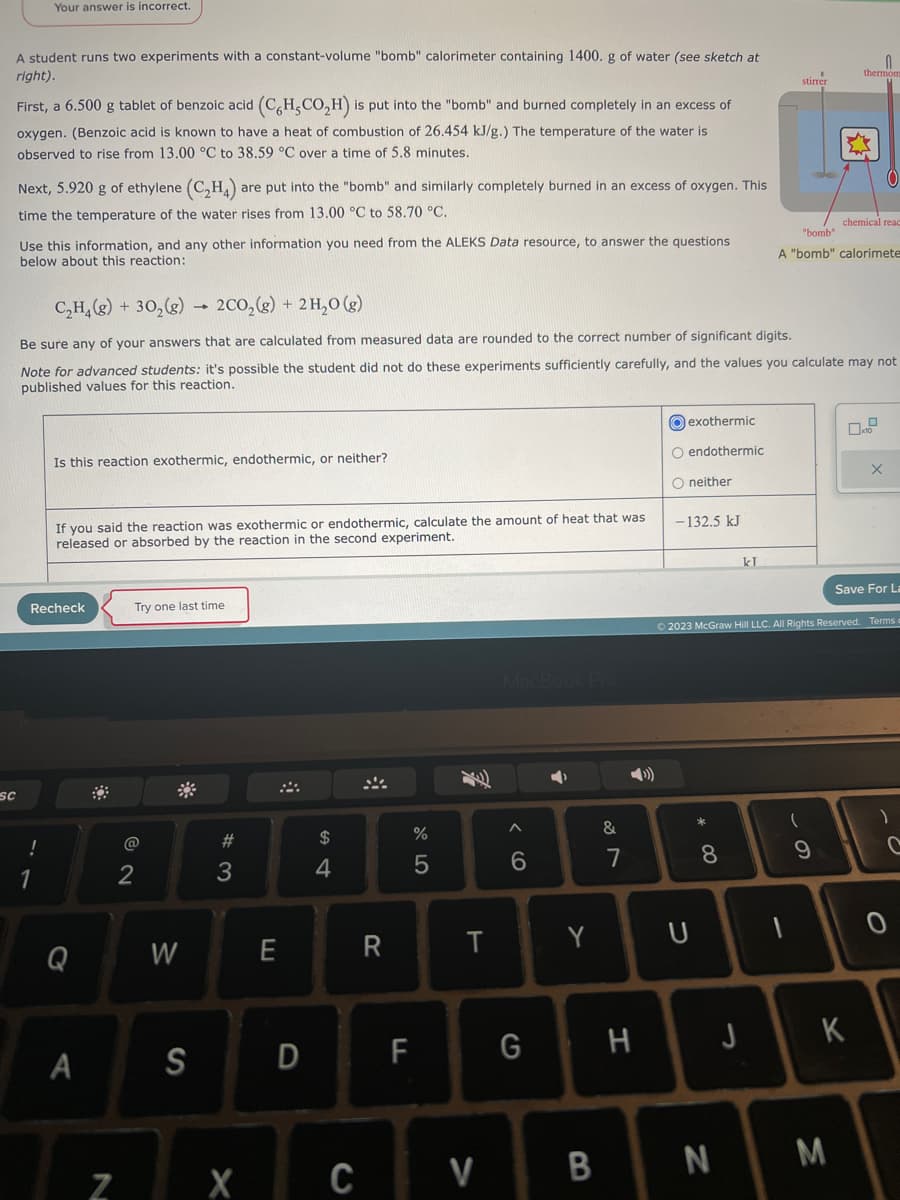
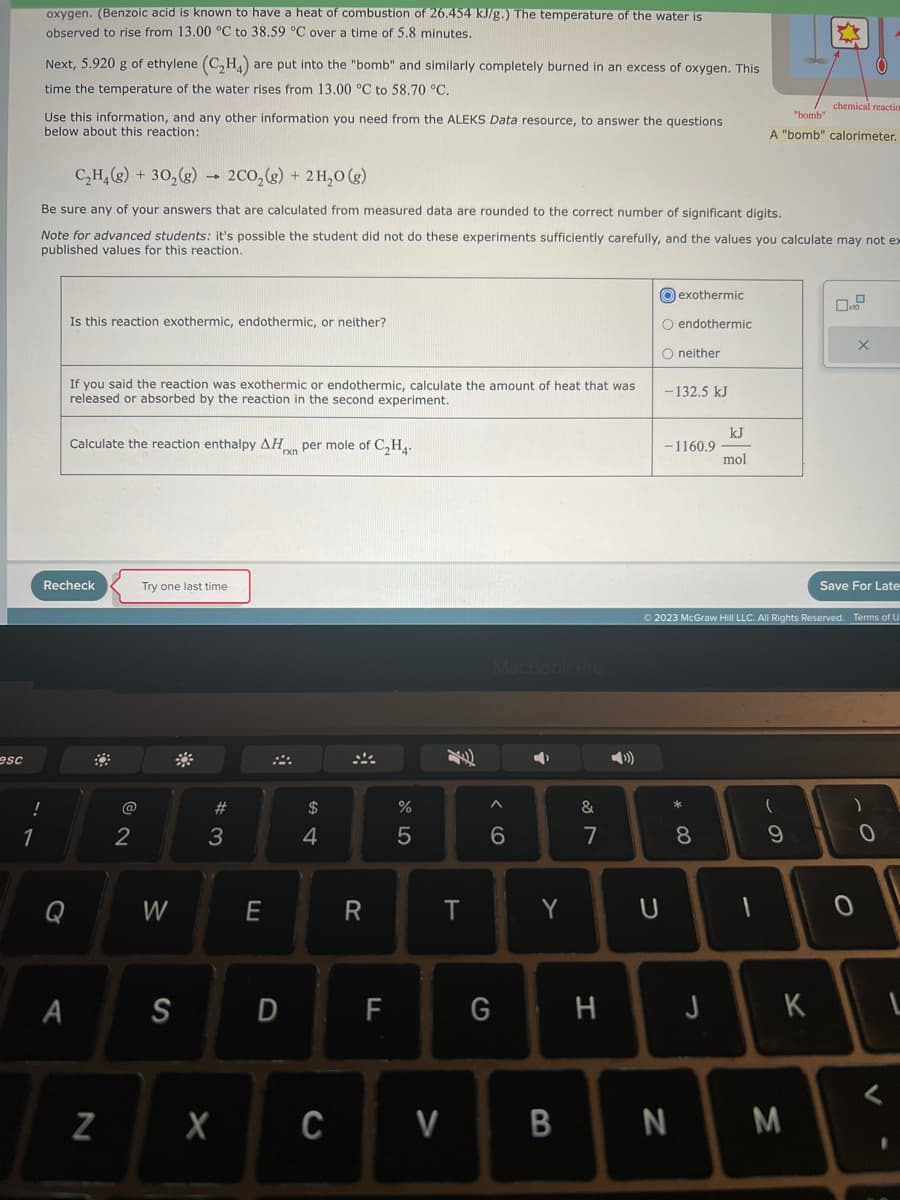
A student runs two experiments with a constant-volume "bomb" calorimeter containing 1400. g of water (see sketch at -ight). First, a 6.500 g tablet of benzoic acid (C6H,CO₂H) is put into the "bomb" and burned completely in an excess of oxygen. (Benzoic acid is known to have a heat of combustion of 26.454 kJ/g.) The temperature of the water is observed to rise from 13.00 °C to 38.59 °C over a time of 5.8 minutes. Next, 5.920 g of ethylene (C₂H4) are put into the "bomb" and similarly completely burned in an excess of oxygen. This time the temperature of the water rises from 13.00 °C to 58.70 °C. Use this information, and any other information you need from the ALEKS Data resource, to answer the questions below about this reaction: 4 exothermic stirrer endothermic thermom O C₂H₂(g) + 30₂(g) 2CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(g) Be sure any of your answers that are calculated from measured data are rounded to the correct number of significant digits. Note for advanced students: it's possible the student did not do these experiments sufficiently carefully, and the values you calculate may not published values for this reaction. chemical reac "bomb" A "bomb" calorimete
Thermochemistry
Thermochemistry can be considered as a branch of thermodynamics that deals with the connections between warmth, work, and various types of energy, formed because of different synthetic and actual cycles. Thermochemistry describes the energy changes that occur as a result of reactions or chemical changes in a substance.
Exergonic Reaction
The term exergonic is derived from the Greek word in which ‘ergon’ means work and exergonic means ‘work outside’. Exergonic reactions releases work energy. Exergonic reactions are different from exothermic reactions, the one that releases only heat energy during the course of the reaction. So, exothermic reaction is one type of exergonic reaction. Exergonic reaction releases work energy in different forms like heat, light or sound. For example, a glow stick releases light making that an exergonic reaction and not an exothermic reaction since no heat is released. Even endothermic reactions at very high temperature are exergonic.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 3 images









