(a) What is the volumetric rate à of heat generation in the wall? (b) Determine the surface heat fluxes, q (L)and q (+ L).
(a) What is the volumetric rate à of heat generation in the wall? (b) Determine the surface heat fluxes, q (L)and q (+ L).
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter2: Steady Heat Conduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2.29P: 2.29 In a cylindrical fuel rod of a nuclear reactor, heat is generated internally according to the...
Related questions
Question
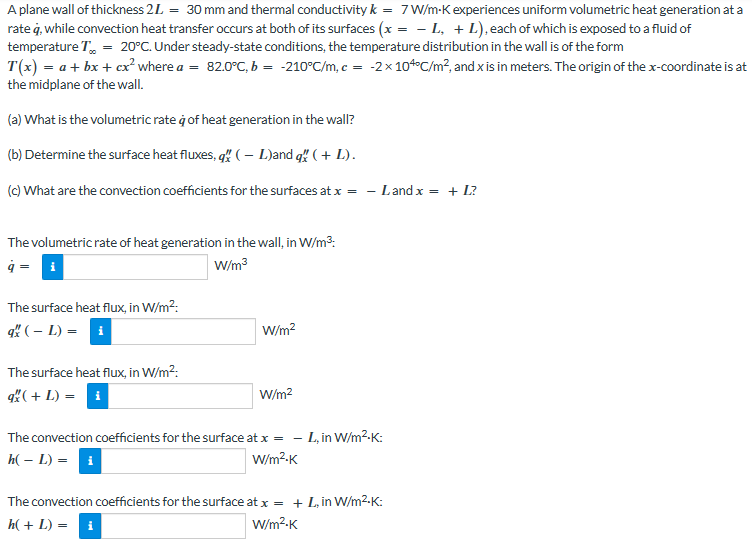
Transcribed Image Text:A plane wall of thickness 2L = 30 mm and thermal conductivity k = 7 W/m-K experiences uniform volumetric heat generation at a
rate q, while convection heat transfer occurs at both of its surfaces (x = − L, + L), each of which is exposed to a fluid of
temperature T = 20°C. Under steady-state conditions, the temperature distribution in the wall is of the form
T(x) = a + bx + cx² where a = 82.0°C, b = -210°C/m, c = -2x 10°C/m², and x is in meters. The origin of the x-coordinate is at
the midplane of the wall.
(a) What is the volumetric rate à of heat generation in the wall?
(b) Determine the surface heat fluxes, q" (L)and q ( + L).
(c) What are the convection coefficients for the surfaces at x = - Land x = + L?
The volumetric rate of heat generation in the wall, in W/m³:
q = i
W/m³
The surface heat flux, in W/m²:
qx ( - L) = i
The surface heat flux, in W/m²:
q (+ L) = i
W/m²
W/m²
The convection coefficients for the surface at x = - L, in W/m²-K:
h(- L) = i
W/m².K
The convection coefficients for the surface at x = + L, in W/m².K:
h(+ L) = i
W/m².K
Expert Solution
Step 1
Given:
The thickness of the wall is,
The thermal conductivity of wall is,
Part (a)
The 1-0 heat conduction with heat generation can be represented as,
.....................(1)
We have steady state condition
Differentiate the above equation we have
Again differentiate above equation,
Substitute above value in equation (1)
Substitute for c and for k in the above equation,
Thus the heat generation is, .
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning