a. P(E) < P(E N F). b. P(E) > P(E U F). c. P(E U F) < P(E) + P(F). С. d. P(E N FC) = 1 - P(E U F). e. P(E*|F) = 1 - P(E|F).
a. P(E) < P(E N F). b. P(E) > P(E U F). c. P(E U F) < P(E) + P(F). С. d. P(E N FC) = 1 - P(E U F). e. P(E*|F) = 1 - P(E|F).
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.8: Probability
Problem 31E
Related questions
Question
E and F are two events of a
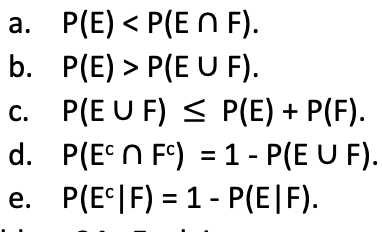
Transcribed Image Text:a. P(E) < P(E N F).
b. P(E) > P(E U F).
c. P(E U F) < P(E) + P(F).
С.
d. P(E N FC) = 1 - P(E U F).
e. P(E*|F) = 1 - P(E|F).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage